Honda 2014 Annual Report Download - page 40
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 40 of the 2014 Honda annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Credit losses are an expected cost of extending credit. The majority of the
credit risk is with consumer financing and to a lesser extent with dealer financing.
Credit risk on consumer finance receivables can be affected by general economic
conditions. Adverse changes such as a rise in unemployment rates can increase
the likelihood of defaults. Declines in used vehicle prices can reduce the amount
of recoveries on repossessed collateral. Exposure to credit risk on consumer
finance receivables is managed by monitoring and adjusting underwriting stan-
dards, which affect the level of credit risk that is assumed, pricing contracts for
expected losses, and focusing collection efforts to minimize losses.
Our finance subsidiaries are also exposed to credit risk on operating lease
assets. A portion of our finance subsidiaries’ operating leases are expected to termi-
nate prior to their scheduled maturities when lessees default on their contractual
obligations. Losses are generally realized upon the disposition of the repossessed
operating lease vehicles. The factors affecting credit risk on operating leases and
management of the risk are similar to that of consumer finance receivables.
Credit risk on dealer loans is affected primarily by the financial strength of the
dealers within the portfolio, the value of collateral securing the financings, and
economic factors that could affect the creditworthiness of dealers. Exposure to
credit risk in dealer financing is managed by performing comprehensive reviews
of dealers prior to establishing financing arrangements and continuously monitor-
ing the payment performance and creditworthiness of dealers with existing
financing arrangements.
The allowance for credit losses is management’s estimate of probable losses
incurred on finance receivables. Estimated losses on past due operating lease
rental payments are also recognized with an allowance for credit losses. Our
finance subsidiaries evaluate these estimates, at minimum, on a quarterly basis.
Consumer finance receivables are collectively evaluated for impairment.
Delinquencies and losses are continuously monitored and this historical experi-
ence provides the primary basis for estimating the allowance. Various methodolo-
gies are utilized when estimating the allowance for credit losses including models
that incorporate vintage loss and delinquency migration analysis. The models take
into consideration attributes of the portfolio including loan-to-value ratios, internal
and external credit scores, and collateral types. Economic factors such as used
vehicle prices, unemployment rates, and consumer debt service burdens are also
incorporated when estimating losses. Estimated losses on operating leases
expected to terminate early due to lessee defaults are also determined collectively,
consistent with the methodologies used for consumer finance receivables.
Wholesales receivables are individually evaluated for impairment when specifi-
cally identified as impaired. Wholesales receivables are considered to be impaired
when it is probable that our finance subsidiaries will be unable to collect all
amounts due according to the original terms of the loan. The determination of
whether dealer loans are impaired is based on evaluations of dealerships’ payment
history, financial condition and cash flows, and their ability to perform under the
terms of the loans. Dealer loans that have not been specifically identified as
impaired are collectively evaluated for impairment.
We believe our allowance for credit losses and impairment losses on operating
leases is a “critical accounting estimate” because it requires significant judgment
about inherently uncertain items. We regularly review the adequacy of the allow-
ance for credit losses and impairment losses on operating leases. The estimates
are based on information available as of each reporting date. However actual
losses may differ from the original estimates as a result of actual results varying
from those assumed in our estimates.
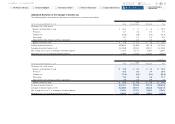
As an example of the sensitivity of the allowance calculation, the following
scenario demonstrates the impact that a deviation in one of the primary factors
estimated as a part of our allowance calculation would have on the provision and
allowance for credit losses. If we had experienced a 10% increase in net credit
losses during fiscal 2014, the provision for fiscal 2014 and the allowance balance
at the end of fiscal 2014 would have increased by approximately ¥4.1 billion and
¥2.4 billion, respectively. Note that this sensitivity analysis may be asymmetric,
and are specific to the base conditions in fiscal 2014.
Honda Motor Co., Ltd. Annual Report 2014 39
6 Financial Section
1 The Power of Dreams
2 Financial Highlights
3 To Our Shareholders
4 Review of Operations
5 Corporate Governance
7
Investor Relations
Information
Return to last
page opened
Go to
contents page