Columbia Sportswear 2013 Annual Report Download - page 72
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 72 of the 2013 Columbia Sportswear annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
COLUMBIA SPORTSWEAR COMPANY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
68
instrument’s cumulative change in fair value to offset the cumulative change in the present value of expected cash flows
on the underlying exposures. For forward contracts, the change in fair value attributable to changes in forward points are
excluded from the determination of hedge effectiveness and included in current cost of sales. Hedge ineffectiveness was
not material during the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011.
The Company also uses currency forward contracts not formally designated as hedges to manage the consolidated
currency exchange rate risk associated with the remeasurement of non-functional currency denominated monetary assets
and liabilities by subsidiaries that use European euros, Canadian dollars, Japanese yen, Korean won or Chinese renminbi
as their functional currency. Non-functional currency denominated monetary assets and liabilities consist primarily of cash
and cash equivalents, short-term investments, payables and intercompany loans. The gains and losses generated on these
currency forward contracts not formally designated as hedges are expected to be largely offset in other non-operating income
(expense), net by the gains and losses generated from the remeasurement of the non-functional currency denominated
monetary assets and liabilities.
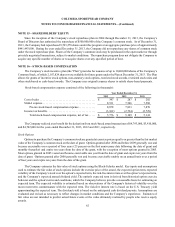
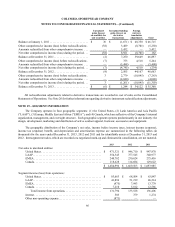
The following table presents the gross notional amount of outstanding derivative instruments (in thousands):
December 31,
2013 2012
Derivative instruments designated as cash flow hedges:
Currency forward contracts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . $ 99,000 $ 70,000
Derivative instruments not designated as hedges:
Currency forward contracts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109,000 121,934
At December 31, 2013, approximately $2,032,000 of deferred net gains on both outstanding and matured derivatives
accumulated in other comprehensive income are expected to be reclassified to net income during the next twelve months
as a result of underlying hedged transactions also being recorded in net income. Actual amounts ultimately reclassified to
net income are dependent on U.S. dollar exchange rates in effect against the European euro, Canadian dollar and Japanese
yen when outstanding derivative contracts mature.
At December 31, 2013, the Company’s derivative contracts had remaining maturities of approximately two years or
less. The maximum net exposure to any single counterparty, which is generally limited to the aggregate unrealized gain of
all contracts with that counterparty, was less than $2,000,000 at December 31, 2013. All of the Company’s derivative
counterparties have investment grade credit ratings and, as a result, the Company does not require collateral to facilitate
transactions. The Company does not hold derivatives featuring credit-related contingent terms. In addition, the Company
is not a party to any derivative master agreement featuring credit-related contingent terms. Finally, the Company has not
pledged assets or posted collateral as a requirement for entering into or maintaining derivative positions.
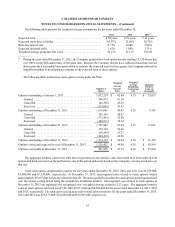
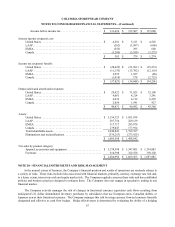
The following table presents the balance sheet classification and fair value of derivative instruments (in thousands):