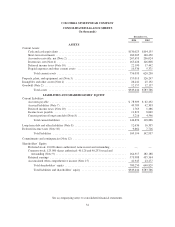
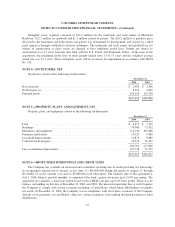
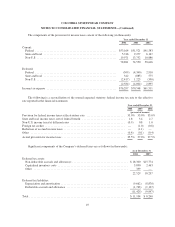
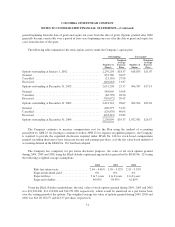
Columbia Sportswear 2004 Annual Report Download - page 46
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 46 of the 2004 Columbia Sportswear annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.COLUMBIA SPORTSWEAR COMPANY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
between the amount of assets and liabilities for financial and tax reporting purposes. Deferred tax assets are
reduced by a valuation allowance when it is estimated to be more likely than not that some portion of the
deferred tax assets will not be realized.
Revenue Recognition:
The Company records wholesale and licensed product revenues when title passes and the risks and rewards
of ownership have passed to the customer, based on the terms of sale. Title generally passes upon shipment or
upon receipt by the customer depending on the country of the sale and the agreement with the customer. Retail
store revenues are recorded at the time of sale.
In some countries outside of the U.S., predominantly where the Company sells direct in Western Europe,
precise information regarding the date of receipt by the customer is not readily available. In these cases, the
Company estimates the date of receipt by the customer based on historical and expected delivery times by
geographic location. Delivery times vary by geographic location, generally from one to four days.
Upon shipment, the Company also provides for estimated sales returns and miscellaneous claims from
customers as reductions to revenues. The estimates are based on historical rates of product returns and claims that
have ranged from approximately one to two percent of sales. However, actual returns and claims in any future
period are inherently uncertain and thus may differ from the estimates. If actual or expected future returns and
claim were significantly greater or lower than the reserves that had been established, the Company would record
a reduction or increase to net revenues in the period in which it made such determination.
Cost of sales:
The expenses that are included in cost of sales include all direct product and conversion-related costs, and
costs related to shipping, duties and importation. Product warranty costs and specific provisions for excess, close-
out or slow moving inventory are also included in cost of sales.
Selling, general and administrative expense:
Selling, general and administrative expense consists of commissions, advertising, other selling costs,
personnel related costs, planning, receiving finished goods, warehousing, depreciation and other general
operating expenses.
Shipping and handling costs:
Shipping and handling fees billed to customers are recorded as revenue. The direct costs associated with
shipping goods to customers are recorded as cost of sales. Inventory planning, receiving and handling costs are
recorded as a component of selling, general, and administrative expenses and were $43,110,000, $39,335,000 and
$29,411,000 for the years ended 2004, 2003 and 2002, respectively.
Foreign currency translation:
The assets and liabilities of the Company’s foreign subsidiaries have been translated into U.S. dollars using
the exchange rates in effect at period end, and the net sales and expenses have been translated into U.S. dollars
using average exchange rates in effect during the period. The foreign currency translation adjustments are
included as a separate component of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) in shareholders’ equity and
are not currently adjusted for income taxes as they relate to indefinite net investments in non-U.S. operations.
41