Cigna 2010 Annual Report Download - page 89
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 89 of the 2010 Cigna annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
CIGNA CORPORATION 2010 Form 10K 69
PART II
ITEM 7 Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Market Risk
Financial Instruments
e Company’s assets and liabilities include fi nancial instruments
subject to the risk of potential losses from adverse changes in market
rates and prices. e Company’s primary market risk exposures are:
•Interest-rate risk on fi xed-rate, domestic, medium-term
instruments. Changes in market interest rates aff ect the value of
instruments that promise a fi xed return and impact the value of
liabilities for reinsured GMDB and GMIB contracts.
•Foreign currency exchange rate risk of the U.S. dollar primarily
to the South Korean won, euro, Taiwan dollar, British pound, New
Zealand dollar, and Hong Kong dollar. An unfavorable change in
exchange rates reduces the carrying value of net assets denominated
in foreign currencies.
•Equity price risk for domestic equity securities and for the value of
reinsured GMDB and GMIB contracts resulting from unfavorable
changes in variable annuity account values based on underlying
mutual fund investments.
For further discussion of reinsured contracts, see Note 7 for GMDB
contracts and Note 11 for GMIB contracts in the Consolidated
Financial Statements.
e Company’s Management of Market Risks
e Company predominantly relies on three techniques to manage
its exposure to market risk:
•Investment/liability matching. e Company generally selects
investment assets with characteristics (such as duration, yield,
currency and liquidity) that correspond to the underlying
characteristics of its related insurance and contractholder liabilities
so that the Company can match the investments to its obligations.
Shorter-term investments support generally shorter-term life and
health liabilities. Medium-term, fi xed-rate investments support
interest-sensitive and health liabilities. Longer-term investments
generally support products with longer pay out periods such as
annuities and long-term disability liabilities.
•Use of local currencies for foreign operations. e Company
generally conducts its international business through foreign
operating entities that maintain assets and liabilities in local
currencies. While this technique does not reduce the Company’s
foreign currency exposure of its net assets, it substantially limits
exchange rate risk to those net assets.
•Use of derivatives. e Company generally uses derivative fi nancial
instruments to minimize certain market risks.
See Notes 2(C) and 13 to the Consolidated Financial Statements
for additional information about fi nancial instruments, including
derivative fi nancial instruments.
Eff ect of Market Fluctuations on the Company
e examples that follow illustrate the eff ect of hypothetical changes
in market rates or prices on the fair value of certain fi nancial
instruments including:
•hypothetical changes in market interest rates, primarily for fi xed
maturities and commercial mortgage loans, partially off set by
liabilities for long-term debt and GMIB contracts;
•hypothetical changes in market rates for foreign currencies,
primarily for the net assets of foreign subsidiaries denominated in a
foreign currency; and
•hypothetical changes in market prices for equity exposures,
primarily for equity securities and GMIB contracts.
In addition, hypothetical eff ects of changes in equity indices and
foreign exchange rates are presented separately for futures contracts
used in the GMDB equity hedge program.
Management believes that actual results could diff er materially from
these examples because:
•these examples were developed using estimates and assumptions;
•changes in the fair values of all insurance-related assets and liabilities
have been excluded because their primary risks are insurance rather
than market risk;
•changes in the fair values of investments recorded using the
equity method of accounting and liabilities for pension and other
postretirement and postemployment benefi t plans (and related
assets) have been excluded, consistent with the disclosure guidance;
and
•changes in the fair values of other signifi cant assets and liabilities
such as goodwill, deferred policy acquisition costs, taxes, and
various accrued liabilities have been excluded; because they are not
fi nancial instruments, their primary risks are other than market risk.
e eff ects of hypothetical changes in market rates or prices on the
fair values of certain of the Company’s fi nancial instruments, subject
to the exclusions noted above (particularly insurance liabilities),
would have been as follows as of December 31:
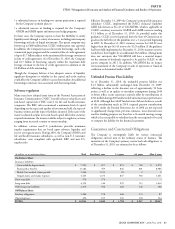
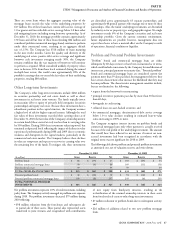
Market scenario for certain non-insurance nancial instruments (in millions)
Loss in fair value
2010 2009
100 basis point increase in interest rates $ 700 $ 700
10% strengthening in U.S. dollar to foreign currencies $ 190 $ 160
10% decrease in market prices for equity exposures $ 50 $ 50
e Company’s foreign operations hold investment assets, such
as fi xed maturities, that are generally invested in the currency of
the related liabilities. Due to the increase in the fair value of these
investments in 2010, which are primarily denominated in the South
Korean won, the eff ect of a hypothetical 10% strengthening in U.S.
dollar to foreign currencies at December 31, 2010 was greater than
that eff ect at December 31, 2009.