Cigna 2010 Annual Report Download - page 83
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 83 of the 2010 Cigna annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.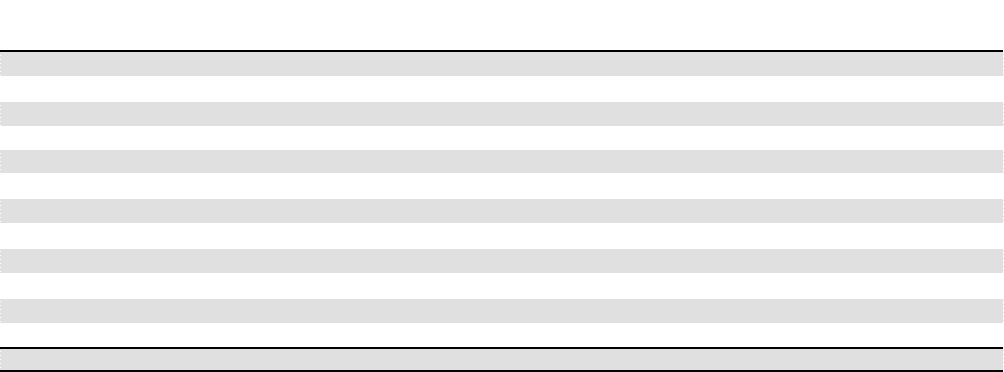
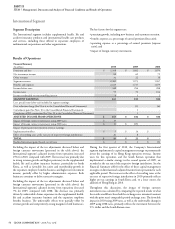
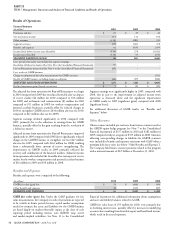
CIGNA CORPORATION 2010 Form 10K 63
PART II
ITEM 7 Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
•a substantial increase in funding over current projections is required
for the Company’s pension plan; or
•a substantial increase in funding is required for the Company’s
GMDB and GMIB equity and interest rate hedge programs.
In those cases, the Company expects to have the fl exibility to satisfy
liquidity needs through a variety of measures, including intercompany
borrowings and sales of liquid investments. e parent company may
borrow up to $600 million from CGLIC without prior state approval.
In addition, the Company may use short-term borrowings, such as the
commercial paper program and the committed line of credit agreement
of up to $1.7 billion subject to the maximum debt leverage covenant in
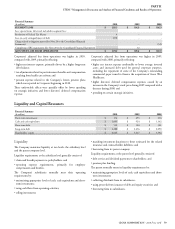
its line of credit agreement. As of December 31, 2010, the Company
had $1.7 billion of borrowing capacity within the maximum debt
leverage covenant in the line of credit agreement in addition to the
$2.8 billion of debt outstanding.
ough the Company believes it has adequate sources of liquidity,
signifi cant disruption or volatility in the capital and credit markets
could aff ect the Company’s ability to access those markets for additional
borrowings or increase costs associated with borrowing funds.
Solvency regulation
Many states have adopted some form of the National Association of
Insurance Commissioners (“NAIC”) model solvency-related laws and
risk-based capital rules (“RBC rules”) for life and health insurance
companies. e RBC rules recommend a minimum level of capital
depending on the types and quality of investments held, the types of
business written and the types of liabilities incurred. If the ratio of the
insurer’s adjusted surplus to its risk-based capital falls below statutory
required minimums, the insurer could be subject to regulatory actions
ranging from increased scrutiny to conservatorship.
In addition, various non-U.S. jurisdictions prescribe minimum
surplus requirements that are based upon solvency, liquidity and
reserve coverage measures. During 2010, the Company’s HMOs and
life and health insurance subsidiaries, as well as non-U.S. insurance
subsidiaries, were compliant with applicable RBC and non-U.S.
surplus rules.
Eff ective December 31, 2009 the Company’s principal life insurance
subsidiary, CGLIC, implemented the NAIC’s Actuarial Guideline
XLIII (also known as AG 43 or VACARVM), which is applicable to
CGLIC’s statutory reserves for GMDB and GMIB contracts totaling
$1.5 billion as of December 31, 2010. As provided under this
guidance, CGLIC received approval from the State of Connecticut to
grade-in the full eff ect of the guideline over a 3-year period beginning
in 2009. At December 31, 2010, statutory reserves for CGLIC were
higher than the pre-AG 43 reserves by $123 million. If the guidance
had been fully implemented at December 31, 2010, statutory reserves
would have been higher by an additional $62 million. Management
does not anticipate that VACARVM will have a material impact
on the amount of dividends expected to be paid by CGLIC to the
parent company in 2011. In addition, VACARVM has no impact
on measurement of the Company’s results of operations or fi nancial
condition as determined under GAAP.
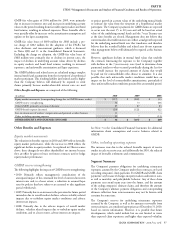
Unfunded Pension Plan Liability
As of December 31, 2010, the unfunded pension liability was
$1.5 billion, substantially unchanged from December 31, 2009,
refl ecting a decline in the discount rate of approximately 50 basis
points as well as an update to mortality assumptions during 2010
to better refl ect recent experience, entirely off set by contributions of
$212 million during 2010 and favorable investment asset performance
in 2010. Although the GAAP funded status did not decline as a result
of the contributions made in 2010, required pension contributions
in 2011 under the Pension Protection Act of 2006 are not expected
to signifi cantly change from previous estimates, since discount rates
used for funding purposes are based on a 24-month moving average
which is less susceptible to volatility than the rate required to be used
to compute the liability for the fi nancial statements.
Guarantees and Contractual Obligations
e Company is contingently liable for various contractual
obligations entered into in the ordinary course of business. e
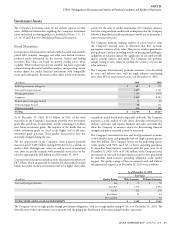
maturities of the Company’s primary contractual cash obligations, as
of December 31, 2010, are estimated to be as follows:
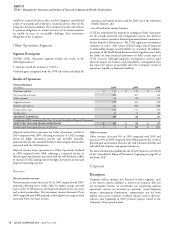
(In millions, on an undiscounted basis)
Total Less than 1year 1-3years 4-5years After 5years
On-Balance Sheet:
Insurance liabilities:
Contractholder deposit funds $ 7,293 $ 677 $ 875 $ 769 $ 4,972
Future policy benefi ts 11,182 459 846 891 8,986
Health Care medical claims payable 1,246 1,213 22 2 9
Unpaid claims and claims expenses 4,445 1,374 847 583 1,641
Short-term debt 574 574---
Long-term debt 4,390 146 299 313 3,632
Other long-term liabilities 1,274 556 220 132 366
O -Balance Sheet:
Purchase obligations 1,284 578 446 173 87
Operating leases 496 105 163 104 124
TOTAL $ 32,184 $ 5,682 $ 3,718 $ 2,967 $ 19,817