JVC 2003 Annual Report Download - page 51
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 51 of the 2003 JVC annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
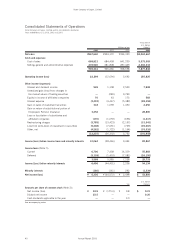
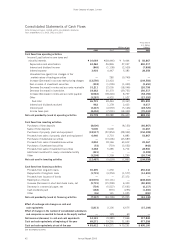
Victor Company of Japan, Limited
Annual Report 2003 49
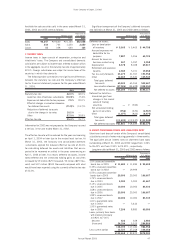
Not included in the above table is special retirement pay-
ments amounting to ¥4,260 million ($35,500 thousand),
¥1,199 million and ¥3,595 million which were expensed in
2003, 2002 and 2001.
The discount rate and the rate of expected return on plan
assets used by the Company are 3.0% and 3.0% in 2003, and
3.5% and 3.0% in 2002, and 4.0% and 3.0% in 2001,
respectively.
The estimated amount of all retirement benefits to be paid at
the future retirement date is allocated equally to each service
year using the estimated number of total service years. Prior
service costs are recognized in income or expense using the
straight-line method over 10 years, and actuarial gains and losses
are recognized in income or expense using the straight-line
method over 10 years commencing with the following period.
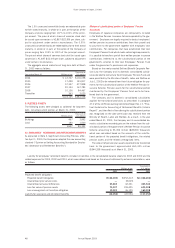
11. CONTINGENT LIABILITIES
The contingent liabilities of the Company and its consolidated
subsidiaries at March 31, 2003 were as follows:
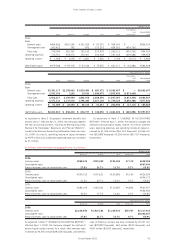
Thousands of
Millions of yen U.S. dollars
As endorser of export bills discounted
with banks ¥4,794 $39,950
As guarantor for loans to employees 2,422 20,183
As guarantor for lease obligations of
affiliated company and others 1,126 9,384
¥8,342 $69,517
12. STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
Under the Commercial Code of Japan (the “Code”), at least 50%
of the issue price of new shares is required to be designated as
stated capital. The portion which is to be designated as stated
capital is determined by resolution of the Board of Directors.
Proceeds in excess of the amounts designated as stated capital
are credited to additional paid-in capital, which is included in
capital surplus.
Effective October 1, 2001, the Code provides that an amount
equal to at least 10% of cash dividends and other cash appro-
priations shall be appropriated and set aside as a legal earnings
reserve until the total amount of legal earnings reserve and ad-
ditional paid-in capital equals 25% of common stock.
The legal earnings reserve and additional paid-in capital may
be used to eliminate or reduce a deficit by resolution of the
stockholders’ meeting or may be capitalized by resolution of the
Board of Directors.
On condition that the total amount of legal earnings reserve
and additional paid-in capital remains being equal to or exceed-
ing 25% of common stock, they are available for distributions
or certain other purposes by the resolution of stockholders’ meet-
ing. Legal earnings reserve is included in retained earnings in
the accompanying financial statements.
The maximum amount that the Company can distribute as
dividends is calculated based on the non-consolidated finan-
cial statements of the Company and in accordance with the Code.
13. DERIVATIVE FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
The Company and its consolidated subsidiaries uses derivative
financial instruments in the normal course of their business to
manage the exposure to fluctuations in foreign exchange rates
and interest rates. The primary classes of derivatives used by the
Company and its consolidated subsidiaries are forward exchange
contracts, option contracts and interest rate swap contracts.
These derivative financial transactions are executed and man-
aged by the Company’s accounting department and are autho-
rized by the Director responsible for accounting matters under
the supervision by the Board of Directors.
The following summarizes hedging derivative financial instru-
ments used by the Companies and items hedged:
Hedging instruments: Hedged items:
Forward exchange contracts Foreign currency
and option contracts trade receivables
and trade payables,
future transaction
denominated in a
foreign currency
Interest rate swap contracts Interest on bonds
The Companies evaluate hedge effectiveness by comparing
the cumulative changes in cash flows from or the changes in
fair value of hedged items and the corresponding changes in
the hedging derivative instruments.
The following tables summarize market value information as
of March 31, 2003 and 2002 of derivative transactions for which
hedge accounting has not been applied:
Millions of yen
Contract Market Recognized
March 31, 2003 amount value gain (loss)
Swap contracts:
Receive floating/pay fixed ¥8,013 ¥(530) ¥(530)
Thousands of
Millions of yen U.S. dollars
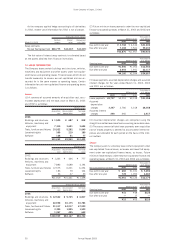
2003 2002 2001 2003
Severance and retirement benefits expenses:
Service costs ¥ 7,103 ¥ 8,200 ¥ 7,044 $ 59,192
Interest costs on projected benefit obligation 6,383 8,884 8,923 53,192
Expected return on plan assets (3,080) (4,499) (4,499) (25,667)
Amortization of net transition obligation 1,994 2,779 2,779 16,617
Amortized actuarial differences 3,151 1,610 — 26,258
Amortized prior service costs (297) (890) — (2,475)
Severance and retirement benefits expenses 15,254 16,084 14,247 127,117
Gain on return of substitutional portion of
Employees’ Pension Insurance 3,456 ——28,800
Total ¥11,798 ¥16,084 ¥14,247 $ 98,317