Nissan 2013 Annual Report Download - page 43
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 43 of the 2013 Nissan annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
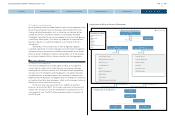
Policy and Principles in Case of Earthquake:
1. The first priority is human life (utilization of employee safety
confirmation system)
2. Prevention of secondary disaster (in-house firefighting organization,
stockpiling, provision of disaster information)
3. Speedy disaster recovery and business continuity (measures for
hardware, improvement of contingency plan and development of BCP)
4. Contribution to local society (cooperation/mutual aid with neighboring
communities, companies, local and central governments)
The Global Disaster Headquarters and Regional Disaster Headquarters
conduct simulation training assuming a large earthquake to prepare for a
catastrophe. The drills test the effectiveness of this organization and
contingency plan and clarify the issues to be improved. The contingency plan
is reviewed based on the feedback.
In the aftermath of the March 11, 2011, disaster, our periodic simulation
training helped to ensure the smooth launch of our Global Disaster
Headquarters and Regional Disaster Headquarters on the initiative of the First
Response Team. This also helped to complete confirmation of employees’
safety and checks on the extent of the damage.
Additionally, based on the policy of contribution to local society, we
reacted rapidly to provide rest space to people who could not return home on
March 11 and to support damaged areas.
At the stage of business recovery, the Disaster Headquarters and the
project teams of each function continuously shared up-to-date information
and were addressing the issues for production and business recovery with
companywide cooperation. It was effective for the quick recovery of our total
supply chain, including parts supply, production, logistics, sales and services.
The response to the March 2011 disaster was reviewed during fiscal
2011 to identify issues that came to light on a function-by-function basis and
to consider countermeasures. In March 2012, simulation training was
conducted based on a new scenario incorporating the review findings, and the
new measures were verified.
Simulation training continued in fiscal 2012 in an effort to enhance our
response to earthquake damage. Based on a scenario of a consolidated Tokai,
Tonankai and Nankai earthquake, we confirmed our preparedness for issues
that came to light during drills held the preceding fiscal year, such as
responses to wide-area disruptions to our logistics network and fuel
shortages. During the fiscal year, we also worked to enhance responsiveness
to earthquake disasters through advance risk estimates carried out by each of
the Company's divisions.
In the face of our expanding global operations and the need to enhance
the natural disaster response of our overseas facilities, we are undertaking
horizontal development of best practices at each facility and inviting overseas
personnel to observe the simulation training held in Japan. In addition, we
conducted communication training (four times during fiscal 2012) among our
overseas facilities based on a scenario of a major disaster in various regions
of the world.
Utilizing the PDCA cycle, disaster measures will be advanced to
address additional issues raised during training and in response to recent
changes in the government’s anticipated seismic scale announcements. The
Global Headquarters building, where the Disaster Headquarters has been
set up (built in August 2009), has an earthquake-resistant structure using
vibration-controlling brace dampers. Safety is assured even in the case of a
maximum-level earthquake at the site. Inspections after the March 2011
earthquake confirmed that the building had no problems whatsoever with its
safety and functions.
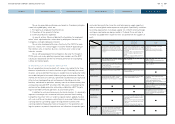
2) Pandemic
In response to the outbreak of H1N1 type influenza in April 2009, Nissan
established a global policy for infection prevention. Each region has organized
a response team and has promoted concrete countermeasures based on the
policy. Infection status can be monitored globally thanks to firmly developed
reporting lines between the global response team and each regional team.
42
CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
NISSAN MOTOR COMPANY ANNUAL REPORT 2013
CONTENTS
MANAGEMENT MESSAGES
CORPORATE FACE TIME
PERFORMANCE
NISSAN POWER 88