Nissan 2013 Annual Report Download - page 36
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 36 of the 2013 Nissan annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
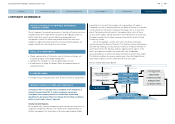
In addition, we have created an area on our intranet called
“Companywide Risk Management.” Information relating to risk management
is also distributed to subsidiaries in Japan, North America, Europe and
other overseas regions, and to important affiliated companies.
Nissan is currently engaged in meeting the goals of the Nissan Power
88 mid-term business plan. To achieve the ambitious goals of raising both
global market share and operating profit margins, we need to fully utilize
our existing production capacity in countries around the world so that new
spending can be curtailed, and we also need a highly efficient production
setup so production can be restored quickly in case a plant is forced to
shut down due to unforeseen circumstances.
To support the mid-term business plan from a risk-management
perspective, our efforts will also be expanded worldwide and throughout
the supply chain by incorporating the important lessons learned from the
March 2011 earthquake and tsunami in east Japan and the 2011 flooding
in Thailand.
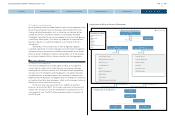
The Current State of Nissan’s Risk Management
Below we present some of our efforts to address Nissan’s corporate risks.
1 Risks Related to Financial Market
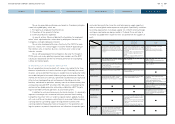
1) Automotive
1. Liquidity
An automotive business must have adequate liquidity to provide for the
working capital needs of day-to-day normal operations, capital investment
needs for future expansion and repayment of maturing debt. Liquidity can be
secured through internal cash and cash equivalents, internal cash flow
generation and external borrowings.
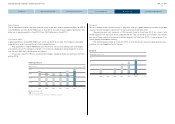
As of the end of fiscal year 2012 (March 31, 2013), Nissan’s automotive
business had ¥771 billion of cash and cash equivalents (compared with ¥781
billion as of March 31, 2012). In addition to cash, Nissan had approximately
¥480 billion of committed lines available for drawing as of March 31, 2013.
As for external borrowings, Nissan raises financing through several
sources including bond issuance in capital markets, long- and short-term
loans from banks, commercial paper issuance and committed credit lines
from banks.
Nissan has a liquidity risk management policy that is intended to ensure
adequate liquidity for the business while at the same time ensuring mitigation
of liquidity risks such as unmanageable bunched maturities of debt. In the
policy, Minimum Required Liquidity is defined, objectively considering several
factors including debt maturity, upcoming mandatory payments (such as
dividends, investments and taxes) and peak operating cash needs. We also
benchmark our liquidity targets with other major Japanese corporations and
global auto companies to ensure we are reasonable in our assumptions.
2. Financial Market
Nissan is exposed to various financial-market-related risks, such as foreign
exchange, interest rates and commodity prices. It is the general policy of
Nissan not to use derivative products as a primary tool to manage foreign
exchange and commodity price risks as it does not provide a permanent
solution to mitigate these risks. In some cases, Nissan does hedge select
currencies and commodity price risks. Nissan is taking the following measures
to minimize financial market risks.
l Foreign exchange
As a company engaged in export activities, Nissan is faced with various
foreign currency exposures that result from the currency of input cost being
different from the currency of sale to customers. In order to minimize foreign
exchange risk on a more permanent basis, Nissan is working to reduce
foreign currency exposure by such measures as shifting production to the
countries where vehicles are sold and procurement of raw materials and parts
in foreign currencies. In the short term, Nissan may hedge risks in foreign
exchange volatility within a certain range by using derivative products in
accordance with the internal policies and procedures for risk management
and operational rules regarding derivative transactions.
l Interest rates
The interest rate risk management policy is based on two principles: long-
term investments and the permanent portion of working capital are financed
at fixed interest rates while the non-permanent portion of working capital and
liquidity reserves are built at floating rates.
l Commodity prices
Nissan purchases raw materials in the form of parts provided by the suppliers,
as well as direct purchase. Nissan is exposed to the price fluctuation risks of
35
CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
NISSAN MOTOR COMPANY ANNUAL REPORT 2013
CONTENTS
MANAGEMENT MESSAGES
CORPORATE FACE TIME
PERFORMANCE
NISSAN POWER 88