Nissan 2013 Annual Report Download - page 37
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 37 of the 2013 Nissan annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
raw materials, no matter whether purchased directly or indirectly.
For precious metals, which are used in catalysts, Nissan is making
continuous efforts to reduce its usage by technological innovation in order to
minimize commodity price risk. In the short term, Nissan manages commodity
price volatility exposure through the use of fixed-rate purchase contracts in
which commodity prices are fixed for a period of time; Nissan may also hedge
risks in commodity price volatility within a certain range by the use of
derivative products in accordance with the internal policies and procedures for
risk management and operational rules regarding derivative transactions.
l Marketable securities
The Company may hold marketable securities for certain reasons including
strategic holding, relationship management and cash management. There are
risks of price fluctuation for these securities. Therefore, price fluctuations in
the stock and bond markets could adversely affect the company’s business
performance and financial position. The Company defines the authority for
decision concerning such transactions within the internal policies and
procedures for risk management. The company also takes measures for
these risks including mandatory periodical reporting with fair value of such
financial transactions.
3. Counterparties
The Group does business with a variety of local counterparties including
suppliers, sales companies and financial institutions in different regions
around the world. Should unprecedented conditions such as bankruptcies be
triggered by a global economic crisis, the resulting interruption to business
operations from production interruption and/or troubles on any other
production activity at the procurement side, and any significant default by a
counterparty at the sales side or financial institutions, would adversely affect
the Group’s financial position and business performance.
The Group assesses its own counterparty credit risks by conducting
comprehensive ongoing reviews of suppliers’, sales companies’ and financial
institutions’ financial condition based on their latest available financial
information. Based on such assessment, the Group is prepared to take
necessary actions for risk avoidance or mitigation in a prompt manner.
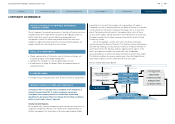
4. Pensions
Nissan has defined benefit pension plans mainly in Japan, the United States
and the United Kingdom. The funding policy for pension plans is to make
periodic contributions as required by applicable regulations. Benefit
obligations and pension costs are calculated using many different drivers,
such as the discount rate and rate of salary/wage increase.
Plan assets are exposed to financial market risks as they are invested in
various types of financial assets including bonds and stocks. When the fair
value of these assets declines, the amount of the unfunded portion of pension
plans increases, which could materially increase required cash pension
contributions and pension expenses.
As countermeasures to manage such risks, the investment policy of
these pension plans is based upon the liability profile of the plans, long-term
investment views and benchmark information regarding asset allocation of
other global corporations’ pension plans.
In addition, Nissan holds Global Pension Committee meetings on a
periodic basis to review investment performance, manager performance
and asset allocations and to discuss other issues related to pension assets
and liabilities.
2) Sales Finance
1. Liquidity
Nissan operates captive sales finance companies in Japan, the United States,
Canada, Mexico, China, Australia and Thailand. In these countries, banks and
other financial institutions also provide financing solutions to Nissan’s
customers and dealers.
Additionally, in Europe and other regions, RCI Banque and several other
banks/financial institutions are providing financing to Nissan’s customers and
dealers.
We monitor the liquidity of sales finance companies on an ongoing basis
to ensure we have adequate liquidity to meet maturing debt and continue
operations. As a policy, we target to match maturity of liabilities with maturity
of assets wherever possible. In some of the countries where we operate,
long-term capital markets are not developed and thus it is not always possible
to be perfectly match-funded. Match-funding policy allows us to meet
maturing debt obligations even in an environment in which we cannot raise
additional debt due to the state of capital markets.
In addition to match-funding, we manage liquidity risk in sales financing
36
CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
NISSAN MOTOR COMPANY ANNUAL REPORT 2013
CONTENTS
MANAGEMENT MESSAGES
CORPORATE FACE TIME
PERFORMANCE
NISSAN POWER 88