NetFlix 2014 Annual Report Download - page 35
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 35 of the 2014 NetFlix annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Table of Contents
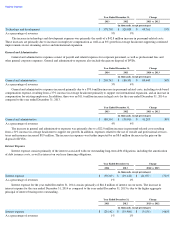
likely than not that substantially all deferred tax assets recorded on our Consolidated Balance Sheets will ultimately be realized. In the event we
were to determine that we would not be able to realize all or part of our net deferred tax assets in the future, an adjustment to the deferred tax
assets would be charged to earnings in the period in which we make such determination.
We did not recognize certain tax benefits from uncertain tax positions within the provision for income taxes. We may recognize a tax
benefit only if it is more likely than not the tax position will be sustained on examination by the taxing authorities, based on the technical merits
of the position. The tax benefits recognized in the financial statements from such positions are then measured based on the largest benefit that
has a greater than 50% likelihood of being realized upon settlement. At December 31, 2014 , our estimated gross unrecognized tax benefits
were $34.8 million of which $29.2 million, if recognized, would favorably impact our future earnings. Due to uncertainties in any tax audit
outcome, our estimates of the ultimate settlement of our unrecognized tax positions may change and the actual tax benefits may differ
significantly from the estimates. See Note 10 of Item 8, Financial Statements and Supplementary Data for further information regarding
income taxes.
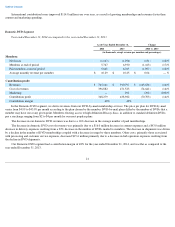
Stock
-Based Compensation
Stock-based compensation expense at the grant date is based on the total number of options granted and an estimate of the fair value of
the awards expected to vest and is recognized as expense ratably over the requisite service period, which is the vesting period.
We calculate the fair value of our stock option grants using a lattice-binomial model. This model requires the input of highly subjective
assumptions. Changes in the subjective input assumptions can materially affect the estimate of fair value of options granted and our results of
operations could be impacted.
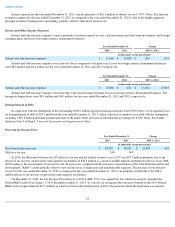
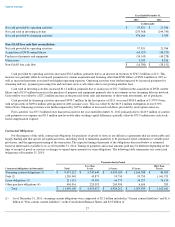
We are exposed to market risks related to interest rate changes and the corresponding changes in the market values of our investments,
debt and foreign currency fluctuations.
Interest Rate Risk
The primary objective of our investment activities is to preserve principal, while at the same time maximizing income we receive from
investments without significantly increased risk. To achieve this objective, we follow an established investment policy and set of guidelines to
monitor and help mitigate our exposure to interest rate and credit risk. The policy sets forth credit quality standards and limits our exposure to
any one issuer, as well as our maximum exposure to various asset classes. We maintain a portfolio of cash equivalents and short-term
investments in a variety of securities. These securities are classified as available-for-sale and are recorded at fair value with unrealized gains
and losses, net of tax, included in “Accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income” within Stockholders' equity in the Consolidated Balance
Sheets.
For the year ended December 31, 2014 , we had no material impairment charges associated with our short-term investment portfolio.
Although we believe our current investment portfolio has very little risk of material impairment, we cannot predict future market conditions or
market liquidity and can provide no assurance that our investment portfolio will remain materially unimpaired. Some of the securities we invest
in may be subject to market risk due to changes in prevailing interest rates which may cause the principal amount of the investment to fluctuate.
For example, if we hold a security that was issued with a fixed interest rate at the then-prevailing rate and the prevailing interest rate later rises,
the value of our investment will decline. At December 31, 2014 , our cash equivalents were generally invested in money market funds, which
are not subject to market risk because the interest paid on such funds fluctuates with the prevailing interest rate. Our short-term investments
were comprised of corporate debt securities, government and agency securities and asset backed securities.
30
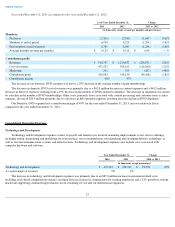
•
Expected Volatility:
Our computation of expected volatility is based on a blend of historical volatility of our common stock and
implied volatility of tradable forward call options to purchase shares of our common stock. Our decision to incorporate implied
volatility was based on our assessment that implied volatility of publicly traded options in our common stock is more reflective of
market conditions and, therefore, can reasonably be expected to be a better indicator of expected volatility than historical volatility of
our common stock. Low trade volume of our tradable forward call options prior to 2011 precluded sole reliance on implied volatility,
and as such we include historical volatility in our computation of expected volatility. An increase/decrease of 10% in our
computation of expected volatility would increase/decrease the total stock-based compensation expense by approximately $10.9
million for the year ended December 31, 2014 .
• Suboptimal Exercise Factor: Our computation of the suboptimal exercise factor is based on historical option exercise behavior and
is determined for both executives and non-executives. An increase/decrease in the suboptimal exercise factor of 10% would
increase/decrease the total stock-based compensation expense by approximately $2.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 .
Item 7A.
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk