Mazda 2012 Annual Report Download - page 41
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 41 of the 2012 Mazda annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Allowance for doubtful receivables
Allowance for doubtful receivables provides for the losses from bad debt. The amount estimated to be uncollectible
is recognized. For receivables of ordinary risk, the amount is estimated based on the past default ratio.
For receivables of high risk and receivables from debtors under bankruptcy proceedings, the amount is estimated
based on the financial standing of the debtor.
Investment valuation allowance
Investment valuation allowance provides for losses from investments. The amount is estimated in light of the
financial standings of the investee companies.
Reserve for warranty expenses
In order to match the recognition of after-sales expenses to product (vehicle) sales revenues, an amount estimated
based on product warranty provisions and actual costs incurred in the past, taking future prospects into
consideration, is recognized.
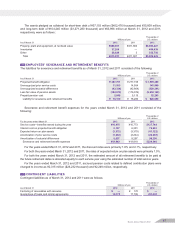
Employees’ severance and retirement benefits
The Domestic Companies provide various types of post-employment benefit plans, including lump-sum plans,
defined benefit pension plans, and defined contribution pension plans, under which all eligible employees are enti-
tled to benefits based on the level of wages and salaries at the time of retirement or termination, length of service,
and certain other factors. Also, consolidated foreign subsidiaries provide defined benefit and/or contribution plans.
The liabilities and expenses for severance and retirement benefits are determined based on the amounts actuari-
ally calculated using certain assumptions.
Employees’ severance and retirement benefits are provided based on the estimated amounts of projected benefit
obligation and the fair value of the plan assets. Prior service costs are recognized in expenses in equal amounts
mainly over 12 years, which is within the average of the estimated remaining service periods of employees, and
actuarial gains and losses are recognized in expenses using the straight-line basis mainly over 13 years, which is
within the average of the estimated remaining service periods, commencing with the following period.
(Additional Information)
Effective from October 2011, some consolidated domestic subsidiaries changed their post-employment benefit plans
and such changes were accounted for in accordance with the Accounting Standards Board of Japan (“ASBJ”)
Guidance No.1 “Guidance on Accounting Standard for Transfer between Retirement Benefit Plans” and the Practical
Issue Task Force (“PITF”) No.2 “Practical Solution on Accounting for Transfer between Retirement Benefit Plans”. As
a result, transition losses of ¥1,044 million ($12,732 thousand) were posted in “Other, net” item in Other income/
(expenses) in the consolidated statements of operations for the year ended March 31, 2012.
Reserve for loss from business of affiliates
Reserve for loss from business of affiliates provides for losses from affiliates’ businesses. The amount of loss
estimated to be incurred by the Company is recognized.
Reserve for environmental measures
Reserve for environmental measures provides for expenditure aimed at environmental measures. The amount of
future expenditure estimated as of the end of the current fiscal year is recognized.
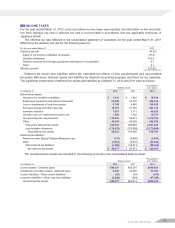
Income taxes
Income taxes are comprised of corporation, enterprise, and inhabitants taxes. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are
recognized to reflect the estimated tax effects attributable to temporary differences and carryforwards. Deferred tax
assets and liabilities are measured using the enacted tax rates that will be in effect when the temporary differences
are expected to reverse. The measurement of deferred tax assets is reduced by a valuation allowance, if necessary,
by the amount of any tax benefits that are not expected to be realized.
Mazda Annual Report 2012 39