Mazda 2012 Annual Report Download - page 21
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 21 of the 2012 Mazda annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.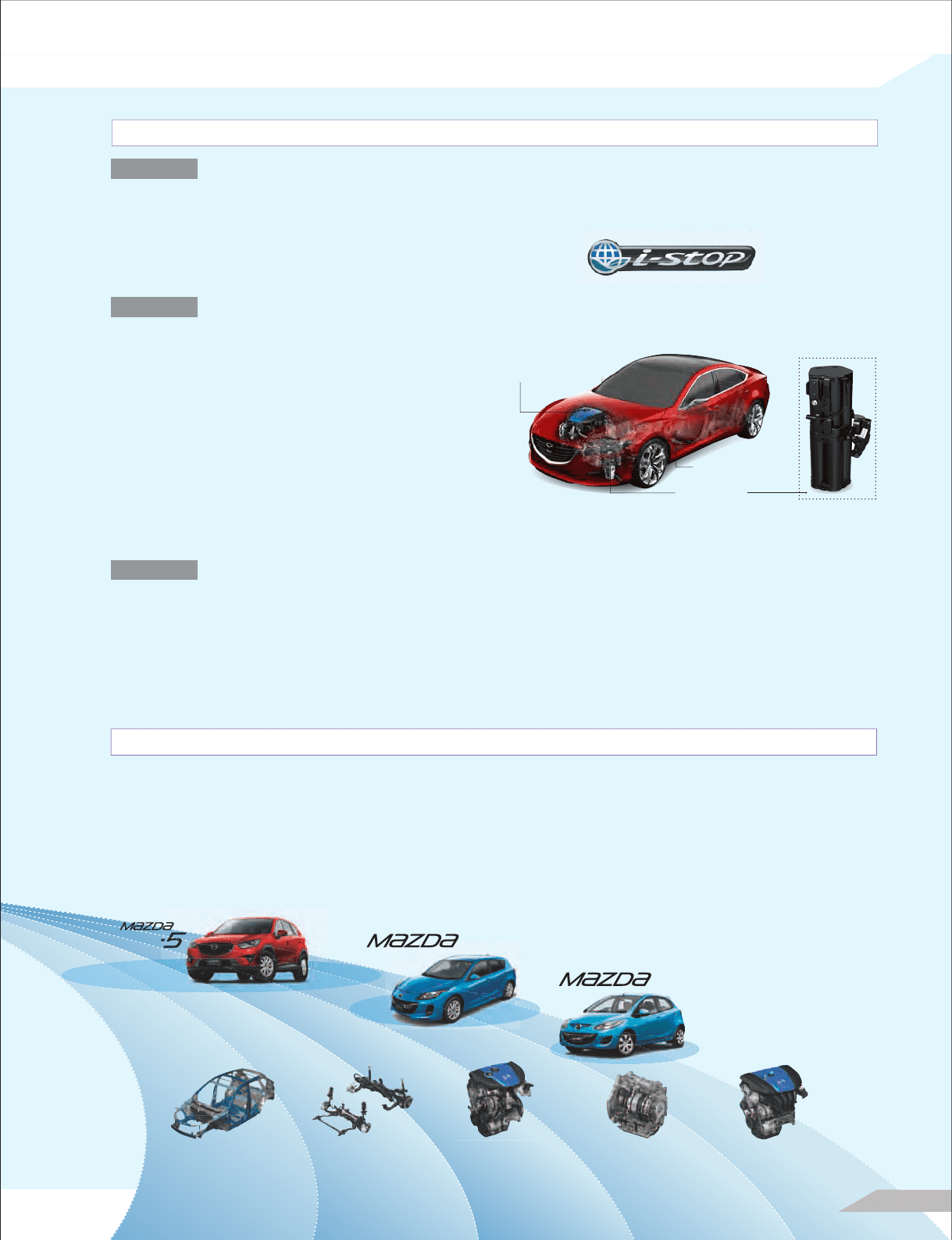
Development of Products Using SKYACTIV Technology
Step-3
Step-2
Motor Drive Technology (Hybrid Systems)
This type of system improves overall energy efficiency using
an electric motor to assist gasoline engines at times when
energy efficiency is low, such as when a vehicle is running at
low engine speeds or during low-load operation. The combina-
tion of this hybrid system with the systems mentioned in steps
1 and 2 can produce a substantial boost in overall efficiency.
Mazda has obtained a license for hybrid systems from
Toyota Motor, with the aim of beginning to sell hybrid vehicles
in Japan in the fiscal year March 2014.
The new Mazda Demio (overseas name: Mazda2), released in
Japan in 2011, was our first product equipped with SKYACTIV-G,
followed by the new Mazda3 (Japanese name: Mazda Axela),
equipped with SKYACTIV-G and SKYACTIV-DRIVE.
The new Mazda CX-5, fully equipped with SKYACTIV
technology in the body and chassis in addition to the engine
and transmission, was released in 2012 and is receiving high
praise around the world.
We will gradually launch the new Mazda6 (Japanese name:
Mazda Atenza), globally starting in the second half of 2012, as
our second vehicle fully equipped with SKYACTIV technology.
Step-1
Regenerative Braking Technology (Regenerative Braking System “i-ELOOP*1”)
For the second step in our Building Block Strategy, we have
developed the “i-ELOOP” regenerative braking system for cars
that do not have electric motors. This is the first use anywhere
in the world*2 of a capacitor*3 to store electricity in a regen-
erative braking system, and can be expected to increase fuel
efficiency in actual driving conditions. Capacitors can store
large volumes of electricity with quick charging and discharging,
and can be used repeatedly without losing capacity. Mazda has
been rolling out this technology in cars without electric motors
from 2012.
Regenerative Braking System “i-ELOOP”
12–25 V variable
voltage alternator
Electric double
layer capacitor
skyactiv-body
Lightweight,
Rigid New-Generation
Vehicle Body
skyactiv-chassis
New-Generation,
High-Performance
Lightweight Chassis
skyactiv-D
New-Generation,
Clean Diesel Engine
skyactiv-Drive
New-Generation,
High-Efficiency Automatic
Transmission
skyactiv-g
New-Generation,
Highly Efficient Direct-Injection
Gasoline Engine
Battery Management Technology (Idling Stop System “i-stop”)
The i-stop system automatically shuts the engine off when the
vehicle makes a temporary stop, to reduce unnecessary fuel
consumption. This alone can improve fuel efficiency by 7% to
10% (as measured in Japanese models). Mazda installed i-stop
in the Mazda3 (Japanese name: Mazda Axela) in 2009 and has
been steadily rolling out this feature in other models.
Successively Implementing Electric Device Technologies
CX-5
*1. Intelligent Energy Loop
*2. As of November 2011, based on Mazda’s research
*3. A storage cell that is able to store and release electricity as electricity, unlike in lead
and lithium-ion batteries where the energy undergoes a chemical reaction
DC-DC converter
3
2
Mazda Annual Report 2012 19