Konica Minolta 2005 Annual Report Download - page 51
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 51 of the 2005 Konica Minolta annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
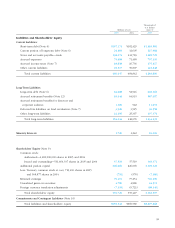
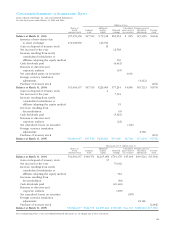
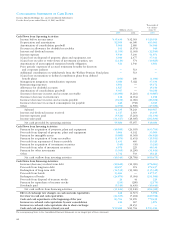
49
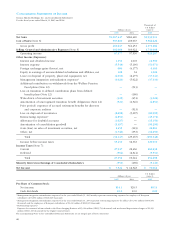
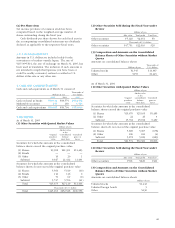
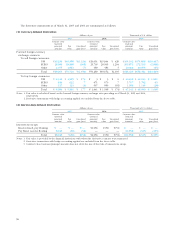
Net retirement benefit costs for the years ended March
31, 2005 and 2004 are as follows:
Thousands of
Millions of yen U.S. dollars
2005 2004 2005
a. Service costs ¥7,426 ¥ 5,645 $69,150
b. Interest costs 2,947 2,670 27,442
c. Expected return on
plan assets (736) (358) (6,854)
d. Amortization of
transition amounts 521 1,540 4,851
e. Actuarial differences
that are accounted
for as expenses 2,042 1,968 19,015
f. Prior service costs
that are accounted
for as expenses (1,233) (519) (11,482)
g. Retirement benefit costs
(a+b+c+d+e+f) 10,968 10,946 102,132
h. Loss on the transition to
defined contribution
plans from defined
benefit plans (160) 180 (1,490)
i. Contribution to defined
contribution pension
plans 1,257 1,488 11,705
Total (g+h+i) ¥12,065 ¥12,615 $112,348
Note: Retirement benefit costs of consolidated subsidiaries using a
simplified method are included in “a. Service costs.”
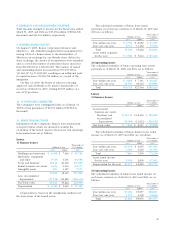
Assumptions used in the calculation of the above
information are as follows:
2005 2004
a. Method of attributing Periodic allo- Periodic allo-
the retirement benefits cation method cation method
to periods of service for projected for projected
benefit benefit
obligations obligations
b. Discount rate Mainly Mainly
2.5% 2.5%
c. Expected rate of return Mainly Mainly
on plan assets 1.25% 1.25%
d. Amortization of Mainly Mainly
unrecognized prior 10 years 10 years
service cost
e. Amortization of Mainly Mainly
unrecognized actuarial 10 years 10 years
differences
f. Amortization of Mostly Mostly
transition amount 5 years for 5 years for
due to changes in subsidiaries subsidiaries
accounting standards
13. DERIVATIVES
The Companies enter into derivative instruments including
forward foreign currency exchange contracts, interest rate
swaps and commodity swaps, to hedge against the adverse
effects of fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates,
interest rates and material prices. The Companies utilize
these derivatives as hedges to effectively reduce the risks
inherent in their assets and liabilities. These transactions are
not likely to have a material impact on the performance of
the Companies. Additionally, the Companies have a policy
of limiting the purpose to hedging identified exposures
only and not for speculative or trading purposes.
Risks associated with derivative instruments
Although the Companies are exposed to credit-related risks
and risks associated with the changes in interest rates and
foreign exchange rates, such derivative instruments are
limited to hedging purposes only and the risks associated
with these transactions are limited. All derivative contracts
entered into by the Companies are with selected major
financial institutions based upon their credit ratings and
other factors. Such credit-related risks are not anticipated
and would not be expected to have a significant impact on
the Companies results.
Risk control system on derivative instruments
In order to manage the market and credit risks, the Finance
Division of the Company is responsible for setting or
managing the position limits and credit limits under the
Company’s internal policies for derivative instruments.
The resources are principally assigned to the functions,
including transaction execution, administration, and risk
management, independently, in order to clarify the
responsibility and the role of each function.
The principal policies on foreign currency exchange
instruments and other derivative instruments at the
Company and its major subsidiaries are approved by
the Management Committee of the Company. Additionally,
the Expert Committee, which consists of management from
the Company and its major subsidiaries meets regularly, at
which time the principal policies on foreign currency
exchange instruments and other derivative instruments are
reaffirmed and the market risks are assessed. All derivative
instruments are reported monthly to the respective officers.
Market risks and credit risks for other subsidiaries are
controlled and assessed based on the internal rules, and
the derivative instruments are approved by the respective
President of each subsidiary.
Interest rate swap contracts are approved by the
Finance Manager of the President of the Company and
other subsidiaries, respectively.
Commodity swap contracts are approved by the
respective President of each subsidiary based on
internal rules.