TomTom 2009 Annual Report Download - page 66
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 66 of the 2009 TomTom annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
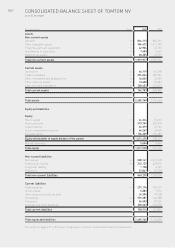
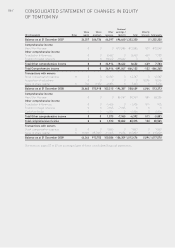
64 / NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
OF TOMTOM NV
2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (continued)
Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost and net realisable value. The cost of inventories comprises costs of
purchase, assembly and conversion to finished products. Borrowing costs are excluded. The cost of inventories is
determined using the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method, net of reserves for obsolescence and any excess stock. Net
realisable value represents the estimated selling price less an estimate of the costs of completion and direct
selling costs.
Trade receivables
Trade receivables are initially recognised at fair value, and subsequently measured at amortised cost (if the time
value is material), using the effective interest method, less provision for impairment. A provision for impairment
of trade receivables is established when there is objective evidence that the group will not be able to collect all
amounts due, according to the original terms of the receivables. Significant financial difficulties of the debtor,
probability that the debtor will enter bankruptcy or financial reorganisation, and default or delinquency in payments
(more than 30 days overdue) are considered indicators that the trade receivable is impaired. The amount of the
provision is the difference between the asset’s carrying amount and the present value of estimated future cash
flows, discounted at the original effective interest rate. The carrying amount of the asset is reduced through the
use of an allowance account and the amount of the loss is recognised in the income statement within ‘cost of
sales’. When a trade receivable is uncollectible, it is written off against the allowance account for trade receivables.
Subsequent recoveries of amounts previously written off are credited against ‘cost of sales’ in the income statement.
Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents are stated at face value and comprise cash on hand, deposits held on call with banks,
and other short-term highly liquid investments that are readily convertible to a known amount of cash and are
subject to an insignificant risk of changes in value.
Financial liabilities and equity instruments
Financial liabilities and equity instruments issued by the group are classified according to the substance of the
contractual arrangements entered into, and the definitions of a financial liability and an equity instrument. An
equity instrument is any contract that evidences a residual interest in the assets of the group after deducting all
of its liabilities. Equity instruments are recorded at the proceeds received, net of direct issue costs.
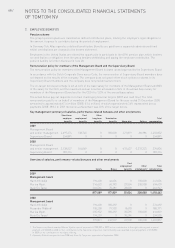
Share capital
Ordinary shares are classified as equity. Incremental costs directly attributable to the issue of new shares or
options are shown in equity as a deduction, net of tax, from the proceeds.
Preference shares
Reference is made to the corporate governance section on page 39.
Share premium
The share premium represents the amount by which the fair value of the consideration received exceeds the
nominal value of shares issued. Incremental costs directly attributable to the issue of new shares or options are
shown in equity as a deduction, net of tax, from the proceeds.
Provisions
Provisions are recognised when the group has a present obligation as a result of a past event and it is probable
that the group will be required to settle that obligation. Provisions are measured at management’s best estimate
of the expenditure required to settle the obligation at the balance sheet date, and are discounted to present value
where the effect is material.
Provisions for warranty costs are recognised at the date of sale of the relevant products, at management’s best
estimate of the expenditure required to settle the group’s obligation. Warranty costs are recorded within cost of sales.
Other provisions are recorded for probable liabilities that can be reasonably estimated. The provisions include legal
claims and tax risks for which it is probable that an outflow of resources will be required to settle the obligation.
Borrowings
Borrowings are recognised initially at fair value, net of transaction costs incurred. Subsequently, amounts are
stated at amortised cost with the difference being recognised in the income statement over the period of the
borrowings using the effective interest rate method.
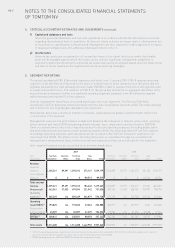
3. FINANCIAL RISK MANAGEMENT
The Business Risk report included in this Annual Report, contains auditable parts comprising ‘Credit’, ‘Liquidity’,
‘Loan covenants’, ‘Foreign currencies’ and ‘Interest rates’. Management policies have been established to identify,
analyse and monitor these risks, and to set appropriate risk limits and controls. Risk management is carried out
in accordance with the Treasury policy which has been approved by the Supervisory Board. The written principles
and policies are reviewed periodically to reflect changes in market conditions and the activities of the business.