Supercuts 2003 Annual Report Download - page 44
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 44 of the 2003 Supercuts annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Table of Contents
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
The primary market risk exposure of the Company relates to changes in interest rates in connection with its debt, some of which bears interest
at floating rates based on LIBOR plus an applicable borrowing margin. To a lesser extent, the Company is also exposed to foreign currency
translation risk related to its net investments in its foreign subsidiaries.
As of June 30, 2003, the Company had $22.8 million of floating and $279.0 million of fixed rate debt outstanding. As of June 30, 2002, the
Company had $55.0 million of floating and $244.0 million of fixed rate debt outstanding. The Company manages its interest rate risk by
balancing the amount of fixed and floating rate debt. On occasion, the Company uses interest rate swaps to further mitigate the risk associated
with changing interest rates and to maintain its desired balances of fixed and floating rate debt. Generally, the terms of the interest rate swap
agreements contain quarterly settlement dates based on the notional amounts of the swap contracts. At June 30, 2002, the Company had interest
rate swap agreements covering $55.0 million of its floating rate obligations. During fiscal year 2003, the $55.0 million of interest rate swap
agreements matured. The Company also had interest rate swap agreements covering $88.5 and $111.0 million of its fixed rate obligations at
June 30, 2003 and 2002, respectively. Further discussion is contained in Note 5 to the Consolidated Financial Statements.
During fiscal year 2002, the Company entered into an interest rate swap agreement with a notional amount of $11.8 million to hedge its
variable rate operating lease obligations as discussed on the following page. During fiscal year 2003, the $11.8 million swap was redesignated
as a hedge of a portion of the interest payments associated with the Company’s long-term financing program. The redesignation was the result
of the Company exercising its right to purchase the property under the variable rate operating lease. In addition, during fiscal year 2002, the
Company entered into a $21.3 million cross currency swap to hedge its Euro foreign currency exposure in certain net investments. See the
discussion in Note 5 to the Consolidated Financial Statements for further explanation of the currency swap hedge’s effect on the Consolidated
Financial Statements.
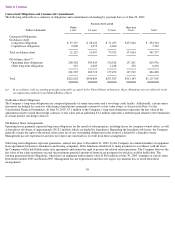
The table on the next page presents information about the Company’s debt obligations and derivative financial instruments that are sensitive to
changes in interest rates. For fixed rate debt obligations, the table presents principal amounts and related weighted-average interest rates by
fiscal year of maturity. For variable rate obligations, the table presents principal amounts and the weighted-average interest rates as of June 30,
2003. For the Company’s derivative financial instruments, the table presents notional amounts and weighted-average interest rates by expected
(contractual) maturity dates. Notional amounts are used to calculate the contractual payments to be exchanged under the contract.
41