Singapore Airlines 2013 Annual Report Download - page 109
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 109 of the 2013 Singapore Airlines annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
107
ANNUAL REPORT 2012/13
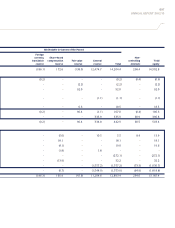
2 Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
(e) Intangible assets
(i) Computer software
Computer software acquired separately is measured initially at cost. Following initial acquisition, computer
software is stated at cost less accumulated amortisation and accumulated impairment losses, if any. These costs
are amortised using the straight-line method over their estimated useful lives of 3 to 10 years and assessed for
impairment whenever there is an indication that the computer software may be impaired. Advance and progress
payments are not amortised. The amortisation period and method are reviewed at least annually.
(ii) Deferred engine development cost
This relates to the Group’s share of engine development payments made in connection with its participation in
aircraft engine development projects with other companies. Amortisation of such intangibles begins only when
the aircraft engines are available for sale. These deferred engine development costs are amortised on a straight-
line basis over the period of expected sales of the aircraft engines, which is estimated to be over a period of 20
years. The amortisation period and amortisation method would be reviewed annually in light of experience and
changing circumstances, and adjusted prospectively, as appropriate at the end of each reporting period.
(iii) Others
Purchased landing slots are measured initially at cost. Following initial recognition, landing slots are measured at cost
less accumulated impairment losses, if any. Landing slots based within the European Union are not amortised, as
regulations provide that these landing slots have an indefinite useful life, and are tested for impairment annually.
Licences were acquired in business combinations. These intangible assets are amortised on a straight-line basis
over an estimated useful life of 3 years.
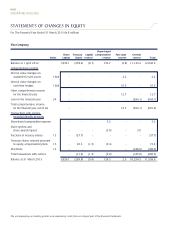
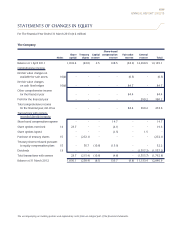
(f) Foreign currencies
The management has determined the currency of the primary economic environment in which the Company operates
i.e., functional currency, to be SGD. Sales prices and major costs of providing goods and services including major
operating expenses are primarily influenced by fluctuations in SGD.
Foreign currency transactions are converted into SGD at exchange rates which approximate bank rates prevailing at
dates of transactions.
All foreign currency monetary assets and liabilities are translated into SGD using year-end exchange rates. Non-
monetary assets and liabilities that are measured in terms of historical cost in a foreign currency are translated using
the exchange rates as at the dates of the initial transactions. Non-monetary assets and liabilities measured at fair value
in a foreign currency are translated using the exchange rates at the date when the fair value was determined.
Gains and losses arising from conversion of monetary assets and liabilities are taken to the profit and loss account.