Suzuki 2013 Annual Report Download - page 43
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 43 of the 2013 Suzuki annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Consolidated Financial Statements
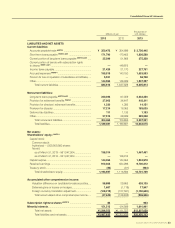
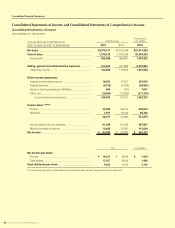
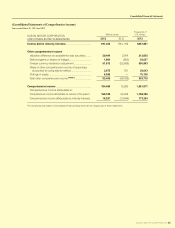
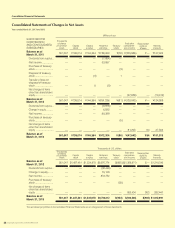
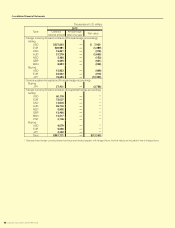
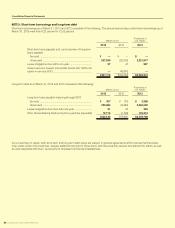
SUZUKI MOTOR CORPORATION 41
NOTE 3:ChangesinAccountingPrinciplesandAccountingEstimates
ChangeinAccountingPrincipleswhichisdifculttobedistinguishedfromChangesinAccountingEstimates
In accordance with revisions of the Corporation Tax Act, The Company and its domestic consolidated subsidiaries have
revised the method of depreciation which is based on the revised Corporation Tax Act for property, plant and equipment ac-
quired on or after April 1, 2012 from this scal year.
The impact of this change on operating income, ordinary income and income before income taxes was immaterial.
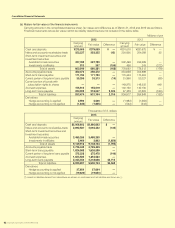
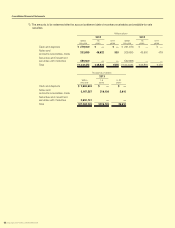
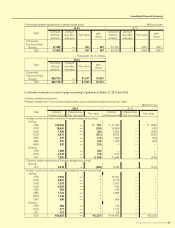
NOTE 4:FinancialInstruments
(a) Mattersforconditionsofnancialinstruments
a.Policyfornancialinstruments
As for the fund management, The Group uses short-term deposits and short-term investment securities, and as for
the fund-raising, The Group uses borrowings from nancial institutions such as banks and issuance of bonds. The
Group uses derivatives to hedge and manage the risks of interest-rates and exchange-rates uctuations, and does
not use derivatives for speculation purposes.
b.Typeofnancialinstruments,risksandriskmanagement
With respect to customers’ credit risks from operating receivables such as notes and accounts receivables-trade,
in order to mitigate the risks, The Group identies credit standing of major counterparties and manages due date
and receivable balance of each counterparty in line with our rules and regulations for credit control. The Group
hedges risks of exchange-rate uctuations from operating receivables denominated in foreign currency by forward
exchange contract in principle.
Investment securities are mainly stocks of companies with which The Group has business relationship, and as for
listed stocks, The Group quarterly identies those fair values and reports them to the Board of Directors.
Most of accounts payable-trade are due within one year.
Applications of borrowings are fund for operating capital (mainly short-term) and capital expenditures (long-term),
and The Group uses interest-rate swaps for the interest rate risks of some long-term borrowings to x interest ex-
penses. Also, The Group uses cross currency interest rate swaps for uctuation of exchange rate in repayment of
principle and interest rate risk to x cash ow.
Objectives of derivative transactions are foreign currency forward contracts to hedge the risks of exchange-rate
uctuations related to receivables denominated in foreign currencies, interest rate swaps to hedge the risks of uc-
tuations in interest rate related to borrowings, and cross currency interest rate swaps to hedge the risk of uctuation
in exchange rate and interest rate related to borrowings. The Group executes and manages derivatives within the
actual demand in line with our rules and regulations which set out the authority to trade. In addition, in using deriva-
tives, The Group deals with nancial institutions which have high credit grade in order to reduce credit risks. With
respect to hedge accounting, also please see Note 2 (g).
In addition, each of The Group company manages liquidity risk related to accounts payable and borrowings by
making a nancial plan.
c.Supplementtofairvaluesofnancialinstruments
Fair values of nancial instruments include values based on quoted prices in active markets and values assessed
by rational valuation techniques in case quoted prices are not available. Because the rational valuation techniques
include variable factors, the results of valuation may differ when different assumption is applied.