Proctor and Gamble 2000 Annual Report Download - page 23
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 23 of the 2000 Proctor and Gamble annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
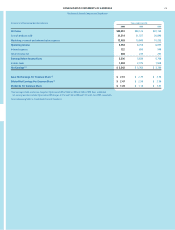
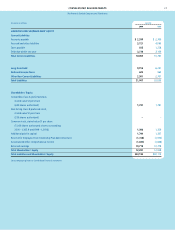
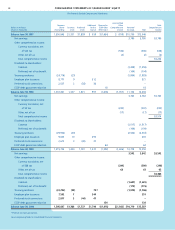
FINANCIAL REVIEW (CONTINUED)
The Procter & Gamble Company and Subsidiaries
21
Based on the Company’s overall currency rate exposure as
of and during the year ended June 30, 2000, including
derivative and other instruments sensitive to foreign
currency movements, a near-term change in currency
rates, at a 95% confidence level based on historical
currency rate movements, would not materially affect the
Company’s financial statements.
COMMODITY PRICE EXPOSURE
Raw materials used by the Company are subject to price
volatility caused by weather, supply conditions, political
and economic variables and other unpredictable factors.
The Company uses futures and options contracts, pri-
marily in food and beverage products, to manage the
volatility related to certain of these exposures. Commodity
hedging activity is not material to the Company’s financial
statements.
ORGANIZATION 2005
As also discussed in Note 2 to the consolidated finan-
cial statements, effective July 1, 1999, the Company
reorganized its operations, moving from a geographic
structure to product-based Global Business Units.
This Organization 2005 program is designed to realign the
organizational structure, work processes and culture to
commercialize innovations faster and drive growth. This
involves Global Business Units streamlining decision
making to quickly flow innovation across categories and
geographies, Market Development Organizations getting
initiatives to market faster and more efficiently, and
Global Business Services leveraging scale to deliver ser-
vices at significantly lower cost.
To achieve this, changes are required to administrative
and manufacturing operations. As announced in June
1999, the Company has undertaken a multi-year program
to consolidate and standardize manufacturing opera-
tions, reduce enrollment and effect other actions integral
to the Organization 2005 objectives.
The cost of this program is estimated to be $2.1 billion
after tax over a six year period. Based on the nature
and duration of the Organization 2005 program, costs
incurred in future years are subject to varying degrees of
estimation for key assumptions, such as normal
employee attrition levels, the actual timing of the execu-
tion of plans and other variables. The estimated cost
of the program has increased approximately $200 mil-
lion after tax since its announcement, primarily due to
refinement of estimates associated with the legal and
organizational restructuring of the Company and expan-
sion of certain manufacturing consolidation plans.
Significant savings are expected to begin accruing next
fiscal year, reaching going annual levels of approximately
$1.2 billion after tax by fiscal 2004. This annual savings
estimate has increased by approximately $300 million
since announcement of the program, primarily due to
the savings associated with the legal and organiza-
tional restructuring, which yields substantial tax and
other savings.