Proctor and Gamble 2000 Annual Report Download - page 22
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 22 of the 2000 Proctor and Gamble annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
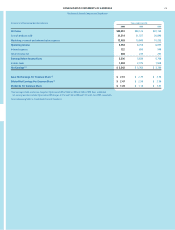
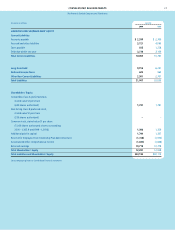
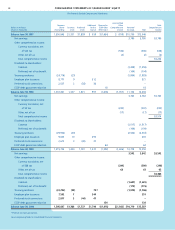
FINANCIAL REVIEW (CONTINUED)
The Procter & Gamble Company and Subsidiaries
20
HEDGING AND DERIVATIVE FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
The Company is exposed to market risks, such as changes
in interest rates, currency exchange rates and commodity
prices. To manage the volatility relating to these expo-
sures, the Company nets the exposures on a consolidated
basis to take advantage of natural offsets. For the resid-
ual portion, the Company enters into various derivative
transactions pursuant to the Company’s policies in areas
such as counterparty exposure and hedging practices.
The financial impacts of these hedging instruments are
offset in part or in whole by corresponding changes in the
underlying exposures being hedged. The Company does
not hold or issue derivative financial instruments for trad-
ing purposes. Note 6 to the consolidated financial state-
ments includes a discussion of the Company’s accounting
policies for financial instruments.
Derivative positions are monitored using techniques
including market value, sensitivity analysis and value at
risk modeling. The tests for interest rate and currency
rate exposures discussed below are based on a variance/
co-variance value at risk model using a one year horizon
and a 95% confidence level. The model incorporates
the impact of correlation and diversification from hold-
ing multiple currency and interest rate instruments,
assumes that financial returns are normally distributed
and approximates the financial return for options and
other non-linear instruments. Estimates of volatility
and correlations of market factors are drawn from
the RiskMetrics™ dataset as of June 30, 2000. In cases
where data is unavailable in RiskMetrics™ a reason-
able proxy is included.
The Company’s market risk exposures relative to interest
and currency rates, as discussed below, have not changed
materially versus the previous reporting period. In
addition, the Company is not aware of any facts or
circumstances that would significantly impact such expo-
sures in the near term.
INTEREST RATE EXPOSURE
Interest rate swaps are used to hedge underlying debt
obligations. Certain currency interest rate swaps are
designated as hedges of the Company’s foreign net
investments.
Based on the Company’s overall interest rate exposure as
of and during the year ended June 30, 2000, including
derivative and other instruments sensitive to interest
rates, a near-term change in interest rates, at a 95%
confidence level based on historical interest rate move-
ments, would not materially affect the Company’s finan-
cial statements.
CURRENCY RATE EXPOSURE
The Company manufactures and sells its products in a
number of countries throughout the world and, as
a result, is exposed to movements in foreign currency
exchange rates. The Company’s major foreign cur-
rency exposures involve the markets in Western and
Eastern Europe, Asia and Mexico. The primary purpose
of the Company’s foreign currency hedging activities is to
manage the volatility associated with foreign currency
purchases of materials and other assets and liabilities
created in the normal course of business. Corporate
policy prescribes the range of allowable hedging activity.
The Company primarily utilizes forward exchange con-
tracts and purchased options with maturities of less
than eighteen months.
In addition, the Company enters into certain foreign
currency swaps to hedge intercompany financing trans-
actions. The Company also utilizes purchased foreign
currency options with maturities of generally less than
eighteen months and forward exchange contracts to
hedge against the effect of exchange rate fluctuations
on royalties and income from international operations.