Energizer 2009 Annual Report Download - page 43
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 43 of the 2009 Energizer annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
ENERGIZER HOLDINGS INC. 2009 ANNUAL REPORT PAGE 41
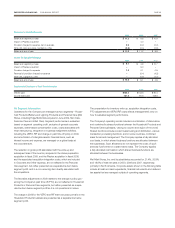
14. Financial Instruments and Risk Management
The market risk inherent in the Company’s financial instruments and
positions represents the potential loss arising from adverse changes in
currency rates, commodity prices, interest rates and the Company’s
stock price. Company policy allows derivatives to be used only for
identifiable exposures and, therefore, the Company does not enter
into hedges for trading purposes where the sole objective is to
generate profits.
Concentration of Credit Risk The counterparties to derivative
contracts consist of a number of major multinational and interna-
tional financial institutions and are generally institutions with which
the Company maintains lines of credit. The Company does not enter
into derivative contracts through brokers nor does it trade derivative
contracts on any other exchange or over-the-counter markets. Risk
of currency positions and mark-to-market valuation of positions are
strictly monitored at all times.
The Company continually monitors positions with, and credit ratings
of, counterparties both internally and by using outside rating agencies.
The Company has implemented policies that limit the amount of agree-
ments it enters into with any one party. While nonperformance by these
counterparties exposes the Company to potential credit losses, such
losses are not anticipated although the current economic environment
makes such assessments more challenging.
The Company sells to a large number of customers primarily in the
retail trade, including those in mass merchandising, drugstore, super-
market and other channels of distribution throughout the world. The
Company performs ongoing evaluations of its customers’ financial
condition and creditworthiness, but does not generally require
collateral. The Company’s largest customer had obligations to the
Company with a carrying value of $114.2 at September 30, 2009.
While the competitiveness of the retail industry presents an inherent
uncertainty, the Company does not believe a significant risk of
loss from a concentration of credit risk exists with respect to
accounts receivable.
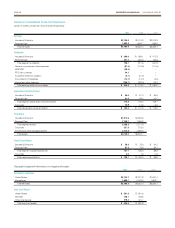
Commodity Price Risk The Company uses raw materials that are
subject to price volatility. At times, hedging instruments are used by
the Company to reduce exposure to variability in cash flows associated
with future purchases of zinc or other commodities. The fair market
value of the Company’s outstanding hedging instruments included
in Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income was an unrealized
pre-tax gain of $6.1 and an unrealized pre-tax loss of $9.8 at
September 30, 2009 and 2008, respectively. Over the next twelve
months, approximately $5.2 of the gain recognized in Accumulated
Other Comprehensive Income will be included in earnings. Contract
maturities for these hedges extend into fiscal year 2011. There were
14 open contracts at September 30, 2009.
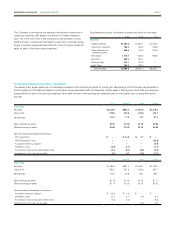
Foreign Currency Risk A significant portion of Energizer’s product
cost is more closely tied to the U.S. dollar than to the local curren-
cies in which the product is sold. As such, a weakening of currencies
relative to the U.S. dollar results in margin declines unless mitigated
through pricing actions, which are not always available due to the com-
petitive environment. Conversely, a strengthening in currencies relative
to the U.S. dollar can improve margins. As a result, the Company
has entered into a series of forward currency contracts to hedge the
cash flow uncertainty of forecasted inventory purchases due to short
term currency fluctuations. The Company’s primary foreign affiliates,
which are exposed to U.S. dollar purchases, have the Euro, the Yen,
the British pound, the Canadian dollar and the Australian dollar as
their local currencies. At September 30, 2009, the Company had an
unrecognized loss on these forward currency contracts accounted
for as cash flow hedges of $15.3 recognized in Accumulated Other
Comprehensive Income. Assuming foreign exchange rates versus the
U.S. dollar remains at September 30, 2009 levels, over the next twelve
months, approximately $11.7 of the loss included in Accumulated
Other Comprehensive Income will be included in earnings. Contract
maturities for these hedges extend into fiscal year 2012. There were
27 open contracts at September 30, 2009.
Interest Rate Risk The Company has interest rate risk with respect
to interest expense on variable rate debt. At September 30, 2009,
the Company had $628.6 variable rate debt outstanding. During the
second quarter, the Company entered into interest rate swap agree-
ments with two major multinational financial institutions that fixed the
variable benchmark component (LIBOR) of the Company’s interest rate
on $300 of the Company’s variable rate debt for the next four years. At
September 30, 2009, the Company had an unrecognized pre-tax gain
on these interest rate swap agreements of $3.4 included in Accumu-
lated Other Comprehensive Income.