Energizer 2002 Annual Report Download - page 41
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 41 of the 2002 Energizer annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
exercise of the Rights. If the threshold is reduced it cannot be lowered to a
percentage that is less than 10% or, if any shareholder holds 10% or more
of the outstanding ENR stock at that time, the reduced threshold must be
greater than the percentage held by that shareholder. The Rights will
expire on April 1, 2010.
At September 30, 2002, there were 300 million shares of ENR stock
authorized, of which approximately 8.9 million shares were reserved for
issuance under the 2000 Incentive Stock Plan.
In September 2000, Energizer’s Board of Directors approved a share
repurchase plan authorizing the repurchase of up to 5 million shares of
Energizer’s common stock, which was completed in May 2002. At that
time, the Board approved a new share repurchase plan authorizing the
repurchase of up to an additional 5 million shares of common stock, of
which no shares have been repurchased as of the date of this report. In
addition, in August 2002, pursuant to a modified Dutch Auction tender
offer, and under a separate Board authorization, Energizer acquired
approximately 2.6 million shares of its common stock at a cost of $77.0.
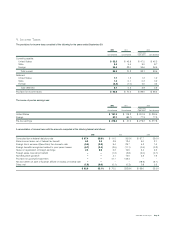
18. Financial Instruments and Risk
Management
Foreign Currency Contracts Energizer enters into foreign exchange for-
ward contracts and, to a lesser extent, purchases options and enters into
zero-cost option collars to mitigate potential losses in earnings or cash
flows on foreign currency transactions. Energizer has not designated any
financial instruments as hedges for accounting purposes. Foreign currency
exposures are primarily related to anticipated intercompany purchase
transactions and intercompany borrowings. Other foreign currency transac-
tions to which Energizer is exposed include external purchase transactions
and intercompany receivables, dividends and service fees.
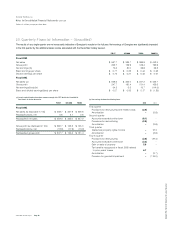
The table below summarizes, by instrument and by major currency, the
contractual amounts of Energizer’s forward exchange contracts and pur-
chased currency options in U.S. dollar equivalents at year-end. These
contractual amounts represent transaction volume outstanding and do
not represent the amount of Energizer’s exposure to credit or market
loss. Foreign currency contracts are generally for one year or less.
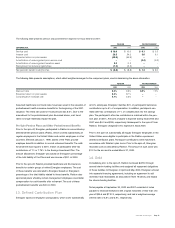
2002 2001
Instrument
Options $ 25.8 $ 16.0
Forwards 8.7 121.3
Currency
Euro 25.8 27.5
Australian dollar 8.6 –
Swiss franc –105.7
Other currencies 0.1 4.1
Prepaid Share Option Transaction A portion of Energizer’s deferred
compensation liabilities is based on Energizer stock price and is subject
to market risk. In May 2002, Energizer entered into a prepaid share option
transaction with a financial institution to mitigate this risk. Energizer invest-
ed $22.9 in the prepaid share option transaction and recorded it in other
current assets. The change in fair value of the prepaid share option is
recorded in selling, general and administrative expenses. Changes in
value of the prepaid share option should substantially offset changes in
the deferred compensation liabilities tied to the Energizer stock price. The
change in fair value of the prepaid share option for the year ended
September 30, 2002 resulted in income of $2.6.
Concentration of Credit Risk The counterparties to foreign currency
contracts consist of a number of major international financial institutions
and are generally institutions with which Energizer maintains lines of
credit. Energizer does not enter into foreign exchange contracts through
brokers nor does it trade foreign exchange contracts on any other
exchange or over-the-counter markets. Risk of currency positions and
mark-to-market valuation of positions are strictly monitored at all times.
Energizer continually monitors positions with, and credit ratings of,
counterparties both internally and by using outside rating agencies.
Energizer has implemented policies that limit the amount of agreements
it enters into with any one party. While nonperformance by these coun-
terparties exposes Energizer to potential credit losses, such losses are
not anticipated due to the control features mentioned.
Energizer sells to a large number of customers primarily in the retail trade,
including those in mass merchandising, drugstore, supermarket and other
channels of distribution throughout the world. Energizer performs ongoing
evaluations of its customers’ financial condition and creditworthiness, but
does not generally require collateral. While the competitiveness of the
retail industry presents an inherent uncertainty, Energizer does not believe
a significant risk of loss from a concentration of credit risk exists with
respect to accounts receivable.
Financial Instruments Energizer’s financial instruments include cash and
cash equivalents, short-term and long-term debt, foreign currency con-
tracts, and interest rate swap agreements. Due to the nature of cash and
cash equivalents and short-term borrowings, including notes payable, car-
rying amounts on the balance sheet approximate fair value.
At September 30, 2002 and 2001, the fair market value of long-term debt
was $200.0 and $242.2, respectively, compared to its carrying value of
$175.0 and $225.0, respectively. The fair value of the long-term debt is
estimated using yields obtained from independent pricing sources for simi-
lar types of borrowing arrangements.
The fair value of foreign currency contracts is the amount that Energizer
would receive or pay to terminate the contracts, considering first, quoted
market prices of comparable agreements, or in the absence of quoted
market prices, such factors as interest rates, currency exchange rates and
ENR 2002 Annual Report Page 39