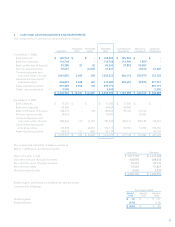
Blackberry 2008 Annual Report Download - page 59
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 59 of the 2008 Blackberry annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.57
(r) Government assistance
The Company has received no government assistance in fiscal
2008, 2007 and 2006.
Assistance related to the acquisition of capital assets used
for research and development is credited against the cost
of related capital assets and all other assistance is credited
against related expenses as incurred.
(s) Statements of comprehensive income (loss)
SFAS 130 Reporting Comprehensive Income, establishes
standards for the reporting and display of comprehensive
income and its components in general-purpose financial
statements. Comprehensive income is defined as the change
in net assets of a business enterprise during a period from
transactions and other events and circumstances from
non-owner sources, and includes all changes in equity
during a period except those resulting from investments by
owners and distributions to owners. The reportable items of
comprehensive income are cash flow hedges as described
in note 18, and changes in the fair value of investments
available-for-sale as described in note 4. Realized gains or
losses on available-for-sale investments are reclassified into
earnings using the specific identification basis.
(t) Earnings per share
Earnings per share is calculated based on the weighted
average number of shares outstanding during the year.
The treasury stock method is used for the calculation of the
dilutive effect of stock options.
(u) Stock-based compensation plans
The Company has stock-based compensation plans, which
are described in note 11(b).
Effective March 5, 2006, the Company adopted the
provisions of SFAS 123(R) Share-Based Payment. Under
the provisions of SFAS 123(R), stock-based compensation
expense is estimated at the grant date based on the award’s
fair value as calculated by the Black-Scholes-Merton (“BSM”)
option-pricing model and is recognized rateably over the
vesting period. The BSM model requires various judgmental
assumptions including volatility, forfeiture rates and expected
option life. If any of the assumptions used in the BSM model
change significantly, stock-based compensation expense may
differ materially in the future from that recorded in the current
period.
recurring engineering contracts is recognized as specific
contract milestones are met. The attainment of milestones
approximates actual performance.
Shipping and handling costs
Shipping and handling costs charged to earnings are
included in Cost of sales where they can be reasonably
attributed to certain revenue; otherwise they are included in
Selling, Marketing and Administration.
Multiple-element arrangements
The Company enters into transactions that represent
multiple-element arrangements which may include any
combination of hardware, service and software. These
multiple-element arrangements are assessed to determine
whether they can be separated into more than one unit
of accounting or element for the purpose of revenue
recognition. When the appropriate criteria for separating
revenue into more than one unit of accounting is met and
there is vendor specific objective evidence of fair value for
all units of accounting or elements in an arrangement, the
arrangement consideration is allocated to the separate units
of accounting or elements based on each unit’s relative fair
value. This vendor specific objective evidence of fair value is
established through prices charged for each revenue element
when that element is sold separately. The revenue recognition
policies described above are then applied to each unit of
accounting.
(q) Research and development
Research costs are expensed as incurred. Development costs
for BlackBerry devices and licensed software to be sold,
leased or otherwise marketed are subject to capitalization
beginning when a product’s technological feasibility has
been established and ending when a product is available
for general release to customers pursuant to SFAS 86
Accounting for the Costs of Computer Software to be Sold,
Leased, or Otherwise Marketed. The Company’s products
are generally released soon after technological feasibility has
been established and therefore cost incurred subsequent to
achievement of technological feasibility are not significant
and have been expensed as incurred.