Bed, Bath and Beyond 2006 Annual Report Download - page 17
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 17 of the 2006 Bed, Bath and Beyond annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
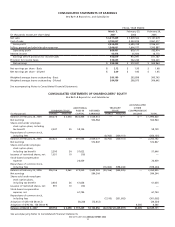
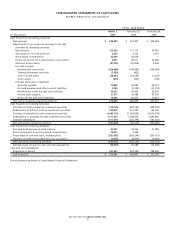
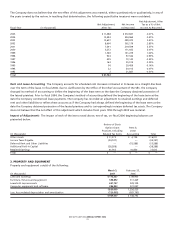
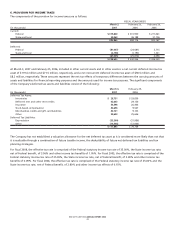
BED BATH& BEYOND ANNUAL REPORT 2006
15
1. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND RELATED MATTERS
A. Nature of Operations
Bed Bath & Beyond Inc. and subsidiaries (the “Company”) is a nationwide chain of retail stores, operating under the names
Bed Bath & Beyond (“BBB”), Christmas Tree Shops (“CTS”) and Harmon. The Company sells a wide assortment of merchandise
principally including domestics merchandise and home furnishings as well as food, giftware and health and beauty care items.
As the Company operates in the retail industry, its results of operations are affected by general economic conditions and
consumer spending habits.
B. Principles of Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its subsidiaries, all of which are
wholly owned.
All significant intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
C. Fiscal Year
The Company’s fiscal year is comprised of the 52 or 53 week period ending on the Saturday nearest February 28. Accordingly, fiscal
2006 represented 53 weeks and ended on March 3, 2007; fiscal 2005 and fiscal 2004 represented 52 weeks and ended on February
25, 2006 and February 26, 2005, respectively.
D. Segments
The Company accounts for its operations as one operating segment.
E. Use of Estimates
The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles requires the
Company to establish accounting policies and to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets and
liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities as of the date of the consolidated financial statements and the report-
ed amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. The Company bases its estimates on historical experience and
on other assumptions that it believes to be relevant under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judg-
ments about the carrying value of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. In particular, judgment is
used in areas such as inventory valuation, impairment of long-lived assets, goodwill and other indefinitely lived intangible assets,
accruals for self insurance, litigation, store opening, expansion, relocation and closing costs, the provision for sales returns, vendor
allowances, stock-based compensation and income taxes. Actual results could differ from these estimates.
F. Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In February 2007, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Statement of Financial Accounting Standards (“SFAS”)
No. 159, “The Fair Value Option for Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities-Including an amendment of FASB Statement No. 115.”
SFAS No. 159 permits companies to choose to measure certain financial assets and liabilities at fair value (the “fair value option”).
If the fair value option is elected, any upfront costs and fees related to the item must be recognized in earnings and cannot be
deferred, e.g. debt issue costs. The fair value election is irrevocable and may generally be made on an instrument-by-instrument
basis, even if a company has similar instruments that it elects not to fair value. At the adoption date, unrealized gains and losses
on existing items for which fair value has been elected are reported as a cumulative adjustment to beginning retained earnings.
SFAS No. 159 is effective for fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2007. The Company is currently assessing the impact of
SFAS No. 159 on its consolidated financial statements.
In September 2006, the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) issued Staff Accounting Bulletin (“SAB”) No. 108, “Consider-
ing the Effects of Prior Year Misstatements when Quantifying Misstatements in Current Year Financial Statements.” SAB 108
provides guidance on the consideration of effects of the prior year misstatements in quantifying current year misstatements for
the purpose of a materiality assessment. The SEC staff believes registrants must quantify errors using both a balance sheet and
income statement approach and evaluate whether either approach results in quantifying a misstatement that, when all relevant
quantitative and qualitative factors are considered, is material. SAB 108 is effective for the first annual period ending after
November 15, 2006 with early application encouraged. The Company adopted SAB 108 in its fiscal fourth quarter. (See “Staff
Accounting Bulletin No. 108, Considering the Effects of Prior Year Misstatements When Quantifying Misstatements in Current Year
Financial Statements,” Note 2).
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Bed Bath & Beyond Inc. and Subsidiaries