Sharp 2014 Annual Report Download - page 54
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 54 of the 2014 Sharp annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
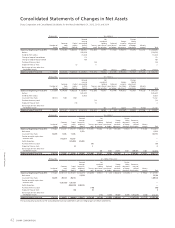
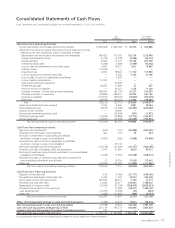
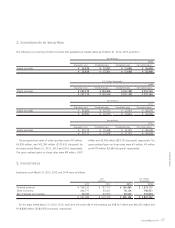
52 SHARP CORPORATION
Financial Section
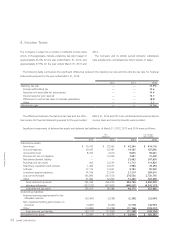
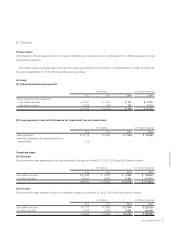
(a) Qualitative information on financial instruments
(1) Policies for financial instruments
The Company and its consolidated subsidiaries obtain neces-
sary funds mainly through bank loans and issuing bonds ac-
cording to its capital investment plan for its main business
of manufacturing and distributing electronic communica-
tion equipment, electronic equipment, electronic application
equipment and electronic components.
Short-term operating funds are obtained through bank loans.
Transactions involving such financial instruments are con-
ducted with creditworthy financial institutions. The Company
utilizes derivative transactions for minimizing risk and not for
speculative or dealing purposes.
(2) Description and risks of financial instruments
Notes and accounts receivable are exposed to customer credit
risk. Some notes and accounts receivable are denominated in
foreign currencies because the Company has business rela-
tions globally and therefore are exposed to foreign currency
risk. Notes and accounts payable (excluding other accounts
payable) are payable within one year. Some notes and ac-
counts payable arising from the import of raw materials are
denominated in foreign currencies and therefore are exposed
to foreign currency risk. The Company offsets foreign currency
denominated notes and accounts receivable with notes and
accounts payable, and uses forward exchange contracts to
hedge foreign currency risk exposure.
Other securities are held for the long term to construct bet-
ter business alliances and relations with Company customers
and suppliers. Other securities are exposed to market price
fluctuation risk. Long-term borrowings (included in long-term
debt) and bonds (included in short-term borrowings and long-
term debt) are mainly in preparation for capital investments.
The longest redemption date for bonds is five and a half years
after March 31, 2014.
Derivative transactions consist primarily of forward ex-
change contracts, and currency swap contracts are used to
hedge foreign currency risk exposure. Interest swap contracts
are used to hedge interest rate risk exposure. For hedging
instruments, hedged items, hedging policies and assessment
methods of effectiveness of hedging instruments, please see
Note 1.
(3) Risk management of financial instruments
[1] Management of credit risk
For notes and accounts receivable, the Company periodi-
cally reviews the status of its key customers, monitoring
their respective payment deadlines and remaining out-
standing balances.
The Company strives to recognize and reduce irrecover-
able risks, due to deteriorating financial conditions or other
factors at an early stage. The Company’s consolidated sub-
sidiaries also follow the same monitoring and administra-
tion process.
[2] Management of market risk
The Company decides basic policy for derivative transac-
tions at the Foreign Exchange Administration Committee
meeting which is held monthly and the Finance Adminis-
tration Committee meeting which is required by the Com-
pany’s internal procedure.
The Finance Unit of Corporate Management Group ex-
ecutes transactions and reports the result of such trans-
actions to the Accounting and Control Unit of Corporate
Management Group on a daily basis. The Accounting and
Control Unit has set up a specialized section for transaction
results and position management and reports the result of
transactions to the Chief officer of Accounting and Cost
Structural Reform, Corporate Management Group on a
daily basis.
In addition, the Finance Unit reports the result of trans-
actions to the Foreign Exchange Administration Committee
and the Finance Administration Committee on a periodic
basis. Its consolidated subsidiaries also manageforward
foreign exchange transactions in accordance with the
rules established by the Company and report the content
of such transactions to the Company on a monthly basis.
For interest swap contracts and currency swap contracts,
its consolidated subsidiaries execute transactions after the
7. Financial Instruments