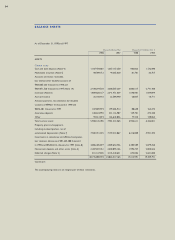
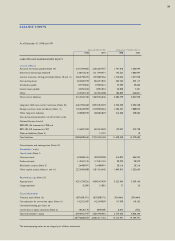
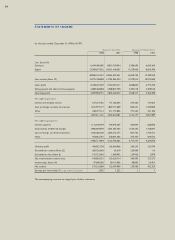
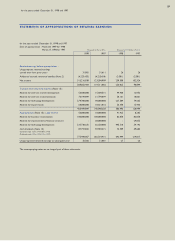
Samsung 1998 Annual Report Download - page 42
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 42 of the 1998 Samsung annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
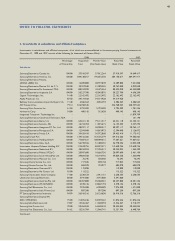
ued assets (see Note 7).Depreciation is computed using the
straight-line method, based on the estimated useful lives of the
assets as described below.
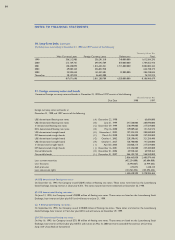
Estimated Useful Lives-years
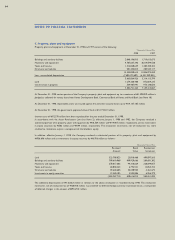
Buildings and auxiliary facilities 7 - 60
Machinery and equipment 2 - 10
Tools and fixtures 2 - 10
Structures and vehicles 2 - 40
Pursuant to revised Korean Corporate Income Tax Law, the resid-
ual value of assets acquired on or before December 31, 1994, is
depreciated over three years following the year in which 90% of
the cost is fully depreciated. During 1998, depreciation expense
charged to operations for the residual value amounted ₩41,013
million. No residual salvage value is provided for assets acquired
after December 31, 1994.
In conformity with Korean accounting practices, the Company
recognizes special accelerated depreciation expense on certain
plant and equipment acquired on or before December 31, 1994
which are used in operations more than 12 hours a day on aver-
age. During 1998 and 1997, the Company recognized special depre-
ciation expense of £‹38,190 million and ₩2,650 million, respec-
tively.
The Company capitalizes interest as part of the cost of constructing
major facilities and equipment (see Note 7).
Maintenance and Repairs -
Routine maintenance and repairs are charged to expense as
incurred. Expenditures which enhance the value or extend the
useful life of the related assets are capitalized.
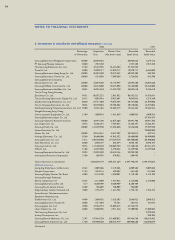
Investments in Subsidiaries and Affiliated Companies -
Investments in subsidiaries and affiliated companies and non-mar-
ketable equity securities are reported at cost, except where mar-
ket value or net book value declines significantly compared to acqui-
sition cost and is not expected to recover, in which case the
investment is reduced to the market value or net book value.
Under generally accepted financial accounting standards in the
Republic of Korea, neither consolidation of subsidiaries nor the
equity method of accounting for minority owned companies is
applied in the primary financial statements of the Company.
Equity investments in publicly traded companies excluding sub-
sidiaries and affiliated companies, classified as noncurrent deposits
and other assets, are reported at market value and the differences
between the market value and the acquisition cost are treated
as unrealized holding gain or loss on the valuation of investments
in equity securities, a component of shareholders’ equity.
The Company is required to prepare, in addition to these non-
consolidated financial statements, audited financial statements that
are consolidated with those of certain domestic and overseas sub-
sidiaries as defined by Consolidation Financial Accounting Standards.
Such audited consolidated financial statements for 1998 are
required to be prepared by April 30, 1999.
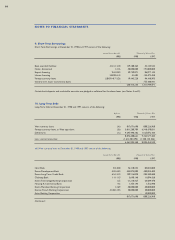
Deferred Charges -
Research and development costs, as well as stock and debenture
issuance costs are charged to operations as incurred.
Deferred foreign exchange losses are amortized over the terms
of the related debt using the straight-line method.
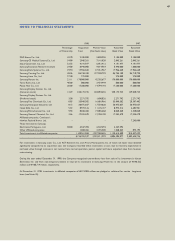
Accrued Severance Benefits -
Employees and directors with more than one year of service are
entitled to receive a lump-sum payment upon termination of their
employment with the Company, based on their length of service
and rate of pay at the time of termination. Accrued severance ben-
efits which would be payable assuming all eligible employees
terminated their employment as of December 31, 1998 and
1997 are ₩264,043 million and ₩777,358 million, respectively.
Severance pay expense is calculated based on the net change in
the accrued severance benefit liability assuming the termination
of all eligible employees as of the beginning and end of the
accounting period.
Under prevailing generally accepted accounting standards, as of
December 31, 1990, accrued severance benefits were underac-
crued by approximately ₩42,254 million. The Company is adjust-
ing the underaccrued severance benefits over 10 years beginning
in 1991 in accordance with the provisions of the Addendum of
the Financial Accounting Standards of the Republic of Korea.
Accordingly, for the year ended December 31, 1998, the Company
deducted ₩4,225 million from retained earnings for additional
accrued severance benefits.
Accrued severance benefits are funded approximately 68% and
45% as of December 31, 1998 and 1997, respectively, through
a group severance insurance plan with Samsung Life Insurance
Company, Ltd. The amounts funded under this insurance plan are
classified as noncurrent deposits and other assets. Subsequent accru-
als are to be funded at the discretion
of the Company.
In accordance with the National Pension Act, a certain portion
of accrued severance benefits is deposited with the National Pension
Fund and deducted from the accrued severance benefits liabili-
ty. The contributed amount shall be refunded from the National
Pension Fund to employees on their retirement.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
41