Lenovo 2008 Annual Report Download - page 100
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 100 of the 2008 Lenovo annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (CONTINUED)
4 Critical accounting estimates and judgments (continued)
(b) Income taxes (continued)
Deferred tax assets are mainly recognized for temporary differences such as warranty provision, accrued sales rebates,
bonus accruals, and other accrued expenses, and unused tax losses carried forward to the extent it is probable that future
taxable profits will be available against which deductible temporary differences and the unused tax losses can be utilized,
based on all available evidence. Recognition primarily involves judgment regarding the future financial performance of the
particular legal entity or tax group in which the deferred tax asset has been recognized. A variety of other factors are also
evaluated in considering whether there is convincing evidence that it is probable that some portion or all of the deferred
tax assets will ultimately be realized, such as the existence of taxable temporary differences, group relief, tax planning
strategies and the periods in which estimated tax losses can be utilized. The carrying amount of deferred tax assets and
related financial models and budgets are reviewed at each balance sheet date and to the extent that there is insufficient
convincing evidence that sufficient taxable profits will be available within the utilization periods to allow utilization of the
carry forward tax losses, the asset balance will be reduced and the difference charged to the income statement.
Where the final tax outcome of these matters is different from the amounts that were initially recorded, such differences
will impact the income tax and deferred tax provisions and deferred tax assets in the period in which such determination
is made.
(c) Warranty provision
Warranty provision is based on the estimated cost of product warranties when revenue is recognized. Factors that affect
the Group’s warranty liability include the number of sold units currently under warranty, historical and anticipated rates
of warranty claims on those units, and cost per claim to satisfy our warranty obligation. The estimation basis is reviewed
on an on-going basis and revised where appropriate. Certain of these costs are reimbursable from the suppliers in
accordance with the terms of relevant arrangement with the suppliers. These amounts are recognized as a seperate
asset, to the extent of the amount of the provision made, when it is virtually certain that reimbursement will be received
if the Group settles the obligation.
(d) Future billing adjustments
Estimates that further impact revenue recognition relate primarily to customer sales returns and allowance for future
volume discounts and price rebates. Both estimates are relatively predictable based on historical experience. The primary
factors affecting the Group’s accrual for estimated customer returns include estimated return rates as well as the number
of units shipped that still have a right of return as of the balance sheet date.
(e) Retirement benefits
Pension and other post-retirement benefit costs and obligations are dependent on various assumptions. The Group’s major
assumptions primarily relate to discount rate, expected return on assets, and salary growth. In determining the discount
rate, the Group references market yields at the balance sheet date on high quality corporate bonds. The currency and term
of the bonds are consistent with the currency and estimated term of the benefit obligations being valued. The expected
return on plan assets is based on market expectations for returns over the life of the related assets and obligations. The
salary growth assumptions reflect the Group’s long-term actual experience and future and near-term outlook. Actual
results that differ from the assumptions are generally recognized in the year they occur.
(f) Fair value of derivatives and other financial instruments
The fair value of financial instruments that are not traded in an active market (for example, over-the-counter derivatives)
is determined by using valuation techniques. The Group uses its judgment to select a variety of methods and make
assumptions that are mainly based on market conditions existing at each balance sheet date. The Group has used
discounted cash flow analysis for various available-for-sale financial assets that are not traded in active markets.
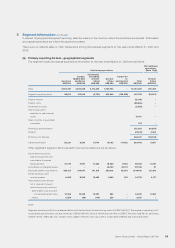
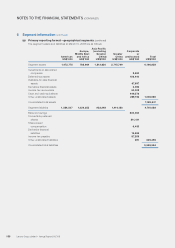
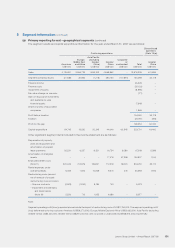
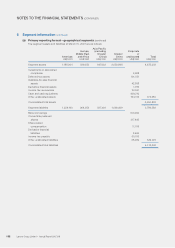
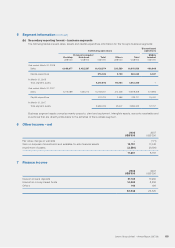
5 Segment information
In accordance with the Group’s internal financial reporting, the Group has adopted geographical segments as the primary
reporting format and business segments as the secondary reporting format.
Segment assets consist primarily of inventories and accounts receivable, and exclude assets not dedicated to a particular
segment, including mainly deferred tax assets, available-for-sale financial assets and centrally managed cash and cash
equivalents and inventories. Segment liabilities comprise mainly accounts payable and exclude liabilities not dedicated to a
particular segment, including mainly long-term bank borrowings, convertible preferred shares and income tax payable. Capital
expenditure mainly comprises additions to property, plant and equipment, intangible assets and construction-in-progress.
Lenovo Group Limited • Annual Report 2007/08
98