Konica Minolta 2012 Annual Report Download - page 32
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 32 of the 2012 Konica Minolta annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
31
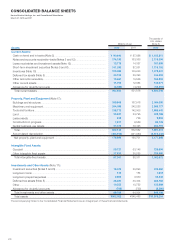
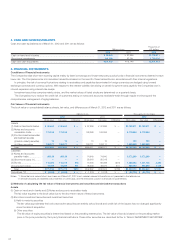
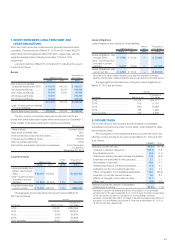
4. CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS
Cash and cash equivalents as of March 31, 2012 and 2011 are as follows:
Millions of yen
Thousands of
U.S. dollars
2012 2011 2012
Cash on hand and in banks ............................................................................ ¥ 90,640 ¥ 87,886 $1,102,811
Short-term investments .................................................................................. 141,293 87,261 1,719,102
Cash and cash equivalents ............................................................................. ¥231,933 ¥175,148 $2,821,913
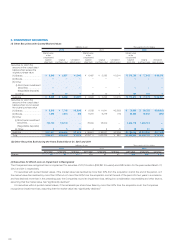
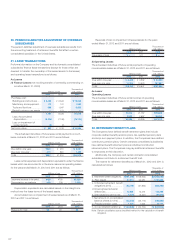
5. FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
Conditions of Financial Instruments
The Companies raise short-term working capital mainly by bank borrowings and invest temporary surplus funds in fi nancial instruments deemed to have
lower risk. The Companies enter into derivative transactions based on the need for these transactions in accordance with their internal regulations.
In principle, the risk of currency fl uctuations relating to receivables and payables denominated in foreign currencies are hedged using forward
exchange contracts and currency options. With respect to the interest volatility risk arising on certain long-term loans payable, the Companies lock in
interest expenses using interest-rate swaps.
Investment securities comprise mainly stocks, and the market values of listed stocks are determined on a quarterly basis.
The Companies try to reduce the credit risk of customers arising on notes and accounts receivable–trade through regular monitoring and the
comprehensive management of aging balances.
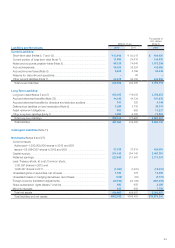
Fair Values of Financial Instruments
The book value on consolidated balance sheets, fair value, and difference as of March 31, 2012 and 2011 are as follows:
Millions of yen Thousands of U.S. dollars
2012 2011 2012
Book value Fair value Difference Book value Fair value Difference Book value Fair value Difference
Assets
(1)
Cash on hand and in banks
... ¥ 90,640 ¥ 90,640 ¥ — ¥ 87,886 ¥ 87,886 ¥ — $1,102,811 $1,102,811 $ —
(2) Notes and accounts
receivable–trade ............. 174,193 174,193 — 163,363 163,363 — 2,119,394 2,119,394 —
(3)
Short-term investment securities
and investment securities
(i)
Held-to-maturity securities
.. 10 10 — 10 10 — 122 122 —
(ii) Other securities .......... 156,977 156,977 — 103,111 103,111 — 1,909,928 1,909,928 —
Total ............................... ¥421,820 ¥421,820 ¥ — ¥354,371 ¥354,371 ¥ — $5,132,255 $5,132,255 $ —
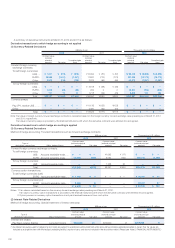
Liabilities
(1) Notes and accounts
payable–trade ................. 88,129 88,129 — 74,640 74,640 — 1,072,259 1,072,259 —
(2) Short-term loans (*1) ........ ———50,018 50,018 — —
(3) Bonds ........................... 110,000 110,278 278 70,000 69,469 (531) 1,338,362 1,341,745 3,382
(4) Long-term loans .............. 73,025 73,366 341 48,033 48,374 341 888,490 892,639 4,149
Total .............................. ¥271,154 ¥271,773 ¥619 ¥242,692 ¥242,502 ¥(189) $3,299,112 $3,306,643 $7,531
Derivatives (*2) .................... ¥ (2,032) ¥ (2,032) ¥ — ¥ (1,318) ¥ (1,318) ¥ — $ (24,723) $ (24,723) $ —
Notes: *1. Since the book value of short-term loans as of March 31, 2012 is not material, relevant information is not presented in the table above.
*2. Derivative assets and liabilities are presented on a net basis, and the net liability position is enclosed in parentheses.
(i) Methods of calculating the fair value of fi nancial instruments and securities and derivatives transactions
Assets
(1) Cash on hand and in banks and (2) Notes and accounts receivable–trade
The fair value equates to the book value due to the short-term nature of these instruments.
(3) Short-term investment securities and investment securities
(i) Held-to-maturity securities
The fair value approximates the book value as the securities are entirely school bonds and credit risk of the issuers has not changed signifi cantly
since the date of acquisition.
(ii) Other securities
The fair value of equity securities is determined based on the prevailing market price. The fair value of bonds is based on the prevailing market
price or the price provided by third-party fi nancial institutions. These other securities are described further in ‘Note 6. INVESTMENT SECURITIES’.