Konica Minolta 2006 Annual Report Download - page 43
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 43 of the 2006 Konica Minolta annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.41
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Konica Minolta Holdings, Inc. and Consolidated Subsidiaries
For the fiscal years ended March 31, 2006 and 2005
1. Basis of Presenting Financial Statements
Konica Minolta Holdings, Inc., (the “Company”) and its con-
solidated subsidiaries in Japan maintain their records and pre-
pare their financial statements in accordance with accounting
principles generally accepted in Japan while its foreign sub-
sidiaries maintain their records and prepare their financial
statements in conformity with accounting principles generally
accepted in their respective country of domicile.
The accompanying consolidated financial statements of
the Company and its consolidated subsidiaries and affiliates
are prepared on the basis of accounting principles generally
accepted in Japan, which are different in certain respects as
to application and disclosure requirements of International
Financial Reporting Standards, and are compiled from the
consolidated financial statements prepared by the Company
as required by the Securities and Exchange Law of Japan.
The accompanying consolidated financial statements
incorporate certain reclassifications and rearrangements in
order to present them in a form that is more familiar to read-
ers outside Japan. In addition, the notes to the consolidated
financial statements include information that is not required
under generally accepted accounting principles in Japan, but
which is provided here in as additional information.
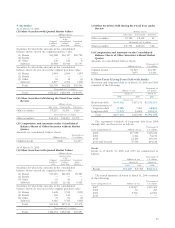
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
(a) Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts
of the Company and, with certain exceptions which are
not material, those of its 124 subsidiaries in which it has
control. All significant intercompany transactions balances
and unrealized profits among the Companies are eliminated
on consolidation.
Investments in 11 unconsolidated subsidiaries and 3 sig-
nificant affiliates are accounted for using the equity method.
Investments in other unconsolidated subsidiaries and affili-
ates are stated at cost, since they have no material effect on
the consolidated financial statements.
The excess of cost over the underlying investments in
subsidiaries is recognized as consolidation goodwill and is
amortized on a straight-line basis over a period not exceeding
20 years.
(b) Translation of Foreign Currencies
Translation of Foreign Currency Transactions
All monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign
currencies, whether long-term or short-term, are translated
into Japanese yen at the exchange rates prevailing at the bal-
ance sheet date and revenues and costs are translated using
the average exchange rate for the period.
Translation of Foreign Currency Financial Statements
The translations of foreign currency financial statements
of overseas consolidated subsidiaries and affiliates into
Japanese yen are made by applying the exchange rates pre-
vailing at the balance sheet dates for balance sheet items,
except common stock, additional paid-in capital and retained
earnings accounts, which are translated at the historical rates,
and the statements of income and retained earnings which
are translated at average exchange rates.
(c) Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents in the consolidated statements of
cash flows consist of cash on hand, bank deposits able to be
withdrawn on demand and short-term investments with an
original maturity of three months or less, which represent
aminor risk of fluctuation in value.
(d) Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
The allowance for doubtful accounts is provided from the
amount of possible losses from uncollectible receivables
based on the management’s estimate.
(e) Inventories
The company and its domestic consolidated subsidiaries’
inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market value,
where cost is primarily determined using the weighted aver-
age cost method. Overseas consolidated subsidiaries’ inven-
tories are stated at the lower of cost or market value, where
cost is determined using the first-in, first-out method.
(f) Property, Plant and Equipment
Depreciation of property, plant and equipment for the
Company and domestic consolidated subsidiaries is com-
puted using the declining balance method, except for depre-
ciation of buildings acquired after April 1, 1998, based on
the estimated useful lives of the assets.
Depreciation of buildings acquired after April 1, 1998 is
computed using the straight-line method. Depreciation for
foreign subsidiaries is computed using the straight-line
method.
Ordinary maintenance and repairs are charged to income
as incurred. Major replacements and improvements are
capitalized. When properties are retired or otherwise dis-
posed of, the property and related accumulated depreciation
accounts are relieved of the applicable amounts and any
differences are charged or credited to income.
(g) Accounting Standard for Impairment
of Fixed Assets
On August 9, 2002, the Business Accounting Council of
Japan issued new accounting standards entitled “Statement
of Opinion on the Establishment of Accounting Standards for
Impairment of Fixed Assets”. Further, on October 31, 2003,
the Accounting Standards Board of Japan issued Financial
Accounting Standards Implementation Guidance No. 6 –
“Application Guidance on Accounting Standards for
Impairment of Fixed Assets”. These standards are effective
from the fiscal years beginning April 1, 2005.
The company and its subsidiaries adopted these stan-
dards in the fiscal year ended March 31, 2006. As a result,
operating income increased by ¥3,018 million and loss
before income taxes and minority interest increased by
¥29,483 million, as compared with the amount which would
have been reported if the previous standards had been
applied consistently. The accumulated impairment loss is
deducted from net book value of each asset.
(h) Income Taxes
The income taxes of the Company and its domestic sub-
sidiaries consist of corporate income taxes, local inhabitants’
taxes and enterprise taxes. Deferred income taxes are pro-
vided for based on temporary differences between the tax
basis of assets and liabilities and those as reported in the
consolidated financial statements.
(i) Research and Development Costs
Research and development costs are expensed as incurred.
(j) Financial Instruments
Derivatives
All derivatives are stated at fair value, with changes in fair
value included in net profit or loss for the period in which
they arise, except for derivatives that are designated as
“hedging instruments” (see Hedge Accounting below).