Hyundai 2001 Annual Report Download - page 46
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 46 of the 2001 Hyundai annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
December 31, 2001 and 2000
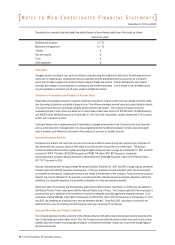
Depreciation is computed using the straight-line method based on the estimated useful lives of the assets as follows:
Intangibles
Intangible assets are stated at cost, net of amortization computed using the straight-line method over the estimated economic
useful lives of related assets. Development costs are amortized over the estimated economic useful life (not to exceed 5
years) from the date of usage of the related products using the straight-line method. Ordinary development and research
expenses are charged to current operations as selling and administrative expenses. Cost in excess of net identifiable assets
acquired (goodwill) is amortized over 20 years, using the straight-line method.
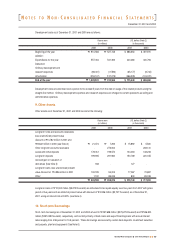
Valuation of Receivables and Payables at Present Value
Receivables and payables arising from long-term installment transactions, long-term cash loans (borrowings) and other similar
loan (borrowing) transactions are stated at present value, if the difference between nominal value and present value is material.
The present value discount is amortized using the effective interest rate method. The Company's long-term accounts
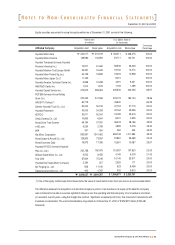
receivable included in other assets are stated net of unamortized present value discount of "4,782 million ($ 3,606 thousand)
and "8,622 million ($6,502 thousand) as of December 31, 2001 and 2000, respectively, using an interest rate of 10.0 percent
in 2001 and 11.8 percent in 2000.
If principal, interest rate or repayment period of receivables is changed unfavourably for the Company by the court imposition
such as commencement of reorganization or by mutual agreements that the difference between nominal value and present
value is material, such difference is recorded in other expense as provision for doubtful accounts.
Accrued Severance Benefits
Employees and directors with more than one year of service are entitled to receive a lump-sum payment upon termination of
their service with the Company, based on their length of service and rate of pay at the time of termination. The accrued
severance benefits which would be payable assuming all eligible employees were to resign as of December 31, 2001 and 2000
amounted to "974,775 million ($735,069 thousand) and "983,776 million ($741,857 thousand), respectively.
Actual payments of severance benefits amounted to "202,053 million ($152,366 thousand) in 2001 and "156,370 million
($117,917 thousand) in 2000.
Accrued severance benefits are approximately 60 percent funded at December 31, 2001 and 2000, through a group severance
insurance plan and individual severance insurance plan. The group severance insurance deposits under this insurance plan
are classified as other assets. Subsequent provisions are funded at the discretion of the Company. Group severance insurance
deposits may only be withdrawn for the payment of severance benefits. Individual severance insurance deposits, in which the
beneficiary is a respective employee, are presented as deduction from accrued severance benefits.
Before April 2000, the Company and the employees paid 3 percent and 6 percent, respectively, of monthly pay (as defined) to
the National Pension Fund in accordance with the National Pension Law of Korea. The Company paid half of the employees’ 6
percent portion and is paid back at the termination of service by netting the receivable against the severance payment. Such
receivables, totalling "83,681 million ($63,103 thousand) and "100,093 million ($75,479 thousand) as of December 31, 2001
and 2000, are presented as a deduction from accrued severance benefits. Since April 2000, according to a revision in the
National Pension Law, the Company and the employees each pay 4.5 percent of monthly pay.
Accrued Warranties and Product Liabilities
The Company generally provides a warranty to the ultimate consumer with each product and accrues warranty expense at the
time of sale based upon actual claims history. Also, the Company accrues potential expenses which may occur due to product
liabilities suits and voluntary recall campaign pending as of the balance sheet date. Actual costs incurred are charged against
the accrual when paid.
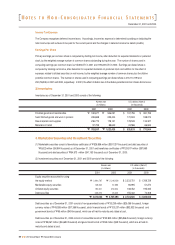
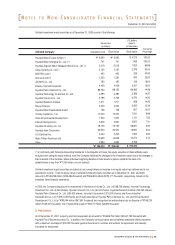
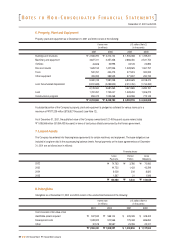
Buildings and structures
Machinery and equipment
Vehicles
Dies and moulds
Tools
Other equipment
12 - 50
12 - 15
6
6
6
6
Useful lives (years)
N
OTES TO
N
ON
-C
ONSOLIDATED
F
INANCIAL
S
TATEMENTS
48
2001 Annual Report Hyundai Motor Company