Dell 2004 Annual Report Download - page 46
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 46 of the 2004 Dell annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.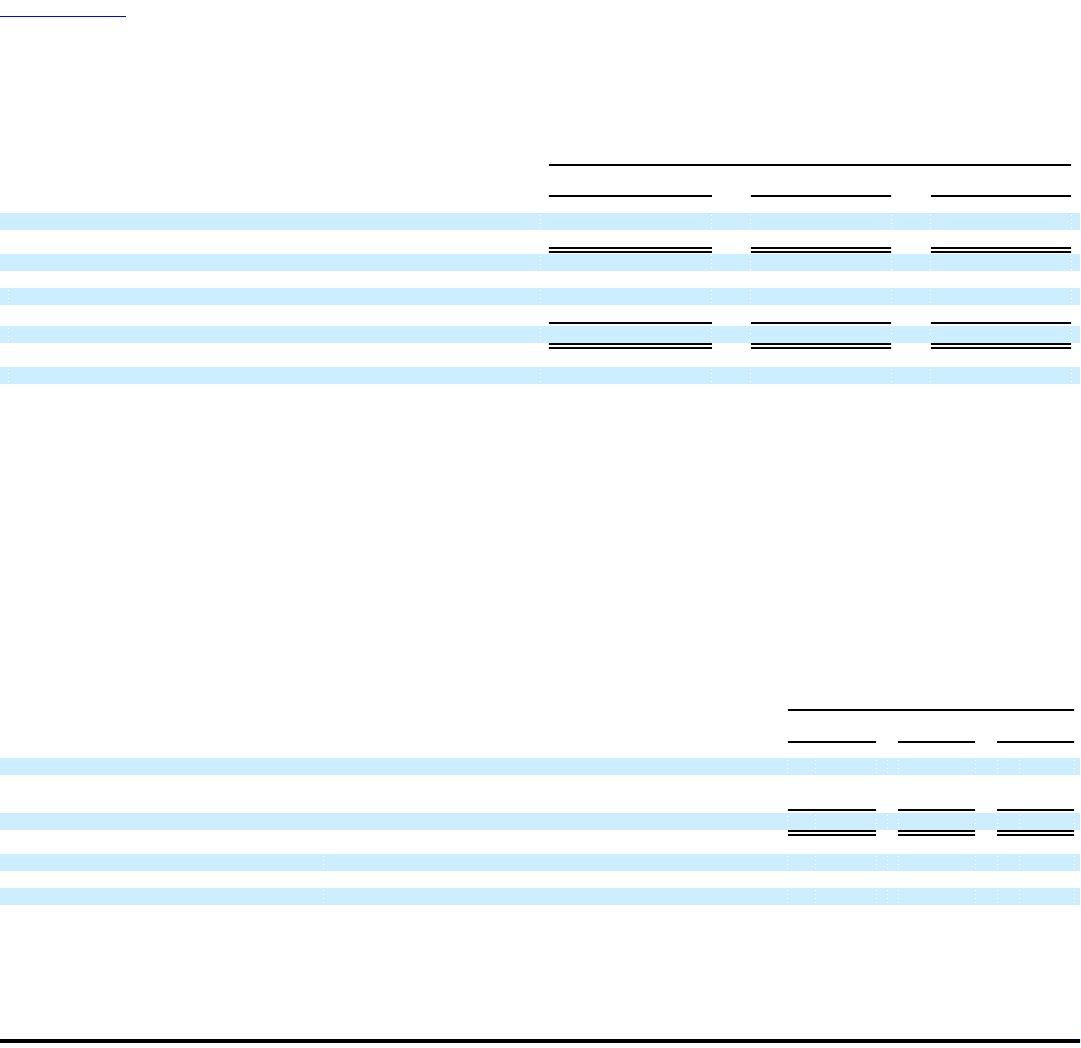
Table of Contents
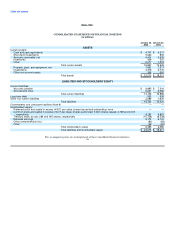
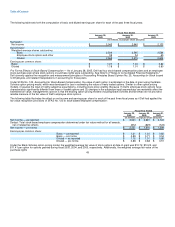
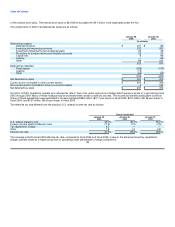
The following table sets forth the computation of basic and diluted earnings per share for each of the past three fiscal years:
Fiscal Year Ended
January 28, January 30, January 31,
2005 2004 2003
(in millions, except per share amounts)
Numerator:
Net income $ 3,043 $ 2,645 $ 2,122
Denominator:
Weighted average shares outstanding:
Basic 2,509 2,565 2,584
Employee stock options and other 59 54 60
Diluted 2,568 2,619 2,644
Earnings per common share:
Basic $ 1.21 $ 1.03 $ 0.82
Diluted $ 1.18 $ 1.01 $ 0.80
Pro Forma Effects of Stock-Based Compensation — As of January 28, 2005, Dell had four stock-based compensation plans and an employee
stock purchase plan where stock options or purchase rights were outstanding. See Note 5 of "Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements."
Dell currently applies the recognition and measurement principles of Accounting Principles Board Opinion No. 25, Accounting for Stock Issued
to Employees, and related Interpretations in accounting for those plans.
Under SFAS No. 123, Accounting for Stock-Based Compensation, the value of each option is estimated on the date of grant using the Black-
Scholes option pricing model, which was developed for use in estimating the value of freely traded options. Similar to other option pricing
models, it requires the input of highly subjective assumptions, including stock price volatility. Because (1) Dell's employee stock options have
characteristics significantly different from those of traded options and (2) changes in the subjective input assumptions can materially affect the
estimated fair value, management's opinion is that the existing option pricing models (including Black-Scholes and Binomial) do not provide a
reliable measure of the fair value of Dell's employee stock options.
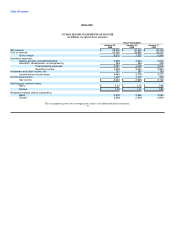
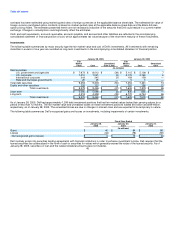
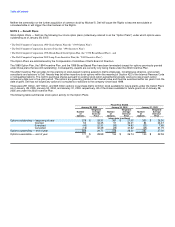
The following table illustrates the effect on net income and earnings per share for each of the past three fiscal years as if Dell had applied the
fair value recognition provisions of SFAS No. 123 to stock-based employee compensation:
Fiscal Year Ended
January 28, January 30, January 31,
2005 2004 2003
(in millions, except per share amounts)
Net income — as reported $ 3,043 $ 2,645 $ 2,122
Deduct: Total stock-based employee compensation determined under fair value method for all awards,
net of related tax effects (812) (829) (723)
Net income — pro forma $ 2,231 $ 1,816 $ 1,399
Earnings per common share:
Basic — as reported $ 1.21 $ 1.03 $ 0.82
Basic — pro forma $ 0.89 $ 0.71 $ 0.54
Diluted — as reported $ 1.18 $ 1.01 $ 0.80
Diluted — pro forma $ 0.88 $ 0.68 $ 0.51
Under the Black-Scholes option pricing model, the weighted average fair value of stock options at date of grant was $10.72, $10.25, and
$11.41 per option for options granted during fiscal 2005, 2004, and 2003, respectively. Additionally, the weighted average fair value of the
purchase rights 43