Qantas 2004 Annual Report Download - page 78
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 78 of the 2004 Qantas annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
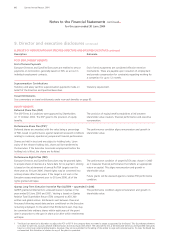
10. International Financial Reporting Standards continued
KEY DIFFERENCES BETWEEN AUSTRALIAN GAAP AND IFRS
The potential implications of the conversion to IFRS on the Qantas Group are outlined below. The summary should not be taken as
an exhaustive list of all the differences between Australian GAAP and IFRS. The impact on future years will depend on the particular
circumstances prevailing in those years. Accordingly, there can be no assurances that the consolidated statements of financial performance
and financial position would not be significantly different if determined in accordance with IFRS.
Frequent Flyer
Qantas is considering the application of AASB 118 “Revenue” to the accounting for the frequent flyer program. Australian GAAP and
IFRS do not specifically address accounting for frequent flyer/loyalty schemes. Under both GAAP’s there are two acceptable accounting
treatments including the Deferral and Incremental Cost approaches.
The Deferral approach results in the deferral of frequent flyer revenue until earned points are redeemed. The Incremental Cost approach
recognises revenue when points are allocated to individuals participating in the scheme, with the recognition of a corresponding provision
for the incremental cost of providing the service at a later date.
Both approaches are used by airlines globally and the most appropriate accounting policy is dependent upon factors such as the size of
the program, the mechanism for managing redemptions and the potential for frequent flyers to displace fare-paying passengers. Under
Australian GAAP, Qantas has adopted the Incremental Cost approach, as historically it has best reflected the commercial operation of
the program.
AASB 1 “First Time Adoption of Australian Equivalents to International Financial Reporting Standards”, requires that all accounting policies
be reconsidered having regard to both their current and future suitability.
As part of the Qantas IFRS transition project, the company is considering changing to the Deferral approach. Future growth in the scheme
and a desire to make redemptions easier, may require changes to the current marginal management of the scheme. Should a decision to
change to the Deferral method be approved, revenue previously recognised would be deferred and retained earnings reduced. In future
periods, deferred revenue would be released to the Statement of Financial Performance as points are redeemed. This treatment would no
longer necessitate the raising of a provision for future incremental costs.
The quantification of the financial impact of the possible change in treatment is complex and requires the calculation of the fair value of
unredeemed frequent flyer points, breakage rates and a detailed analysis of revenues previously brought to account. To date, the financial
effect of the change being considered has not been determined. It is anticipated that should it be adopted, a reduction in retained
earnings will be made. The impact on future profits is largely dependent on the extent to which the program grows and as such cannot
be quantified at this time.
Defined Benefit Superannuation Plans
Qantas is considering the application of AASB 119 “Employee Benefits” to the recognition of the funding surplus or deficit of the Qantas
sponsored defined benefit superannuation plans. Under the requirements of IFRS, any surpluses and deficits in the defined benefit
superannuation plans within the consolidated entity will be recognised in the Statement of Financial Position and movements in the surplus
or deficit recognised in the Statement of Financial Performance.
Actuarial valuations of the Plans will be conducted as at 30 June 2004. The expected impact is likely to be a one-off reduction in retained
earnings and the corresponding recognition of a retirement liability.
Leases
Qantas is considering the application of AASB 117 “Leases” to the classification of lease transactions. Under IFRS some leases currently
classified as operating may require recognition in the Statement of Financial Position. To date the financial effect of the change has not
been determined, however, it is not expected to have a significant impact on the Statement of Financial Performance in future years.
Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement
1. Fuel Hedging
Qantas is considering the application of AASB 139 “Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement” to aviation fuel hedging
transactions. Extensive hedge effectiveness testing and documentation is required under IFRS in order to apply hedge accounting to
these transactions. The potential application and impact of this accounting standard on aviation fuel hedging has not been determined.
2. Revenue Hedging
Qantas is considering the application of AASB 139 “Financial Instruments: Recognition and Measurement” to revenue hedging
transactions. The potential application and impact of this accounting standard on revenue hedging has not been completed. It is
anticipated that, after initial adoption adjustments are made, the existing accounting treatment will continue under IFRS, although
it will be subject to increased effectiveness testing and documentation requirements.
76 Qantas Annual Report 2004
Notes to the Financial Statements continued
for the year ended 30 June 2004