JVC 2000 Annual Report Download - page 21
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 21 of the 2000 JVC annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
JVC 2000 19
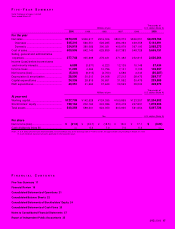
Sales of Components & Devices were down 9.4% to
¥66,791 million (US$630.1 million), making up 7.7% of net
sales, a decline of 0.1 percentage point from a year earlier.
Domestic sales dropped 25.3% as demand for deflection
yokes fell sharply, adversely affected by a decrease in orders
as customers shifted manufacturing overseas. Overseas
sales, which grew 6% on a local currency basis due to large
gains in “VIL” PWBs, declined 3.8% due to the adverse ef-
fects of currency fluctuations.
Sales in the Entertainment business decreased 16.0%
to ¥125,173 million (US$1,180.9 million), a 1.3 percentage
point decrease to 14.4% of net sales. Although new singers
debuted in music operations, domestic sales were down
18.2%, as there were no runaway hit movies like Titanic last
year. Overseas sales increased 5.7%, despite currency fluctu-
ations, on substantial growth in music CDs, especially in the
United States.
JVC advanced efforts to improve cost of sales and reduce
inventory. Adversely affected by a decline in prices, however,
cost of sales was 69.0% of net sales, an increase of 1.2 per-
centage points. Selling, general and administrative (SG&A) ex-
penses to net sales increased 0.4 percentage point to 31.9%,
owing to reductions in selling and personnel expenses. An op-
erating loss of ¥8,019 million (US$75.7 million) was recorded,
partially due to the rise in cost of sales to net sales.
In other income and expenses, expenses were recorded
for restructuring subsidiaries, including the liquidation of pro-
jector operations at a subsidiary in the United States, a
switchover to high-value-added TV models at a plant in the
United Kingdom, and investment to strengthen the structure
of a sales subsidiary in Brazil. An unrealized gain from appre-
ciation of trading securities possessed by a subsidiary in the
United States substantially contributed to other income.
Net interest expense (interest expense plus interest and divi-
dend income) was ¥3,770 million (US$35.6 million), a decrease
of ¥2,515 million owing to reductions in interest-bearing debt.
Income before income taxes and minority interests
amounted to ¥6,088 million (US$57.4 million). Income taxes
totaling ¥11,295 million (US$106.6 million) led to a net loss of
¥5,341 million (US$50.4 million). Net loss per share was
¥21.0 (US$0.20). In consideration of performance during the
fiscal year under review, management decided to suspend
cash dividends for the year.
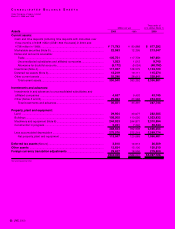
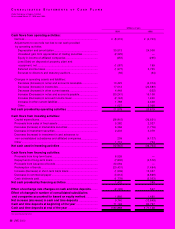
Cash Flow Analysis Purchases of property, plant and
equipment during the year were ¥23,121 million (US$218.1
million), with investment concentrated on digital and
networking operations. Purchases of property, plant and
equipment were lower than depreciation and amortization of
¥28,953 million (US$273.1 million). The Company prepared
the 2000 consolidated statement of cash flows in accordance
with new accounting regulations. The 1999 and 1998
consolidated statements of cash flows have not been
restated.
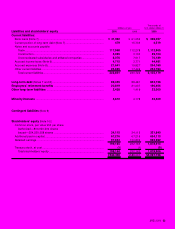
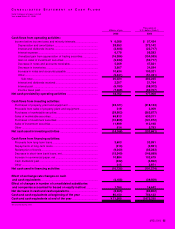
Net cash provided by operating activities totaled ¥18,762
million (US$177.0 million). This was the result of an increase in
income before income taxes and minority interests, decrease
in inventories and notes and accounts receivable, as well as
an increase in notes and accounts payable.
Net cash used in investing activities amounted to ¥14,168
million (US$133.7 million). Sales of marketable securities par-
tially offset purchases of property, plant and equipment.
Net cash used in financing activities was ¥10,735 million
(US$101.3 million). Major uses of cash were for the redemption
of bonds and a decrease in short-term bank loans, net, which
was partially offset by an increase in commercial paper, net.