Suzuki 2015 Annual Report Download - page 43
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 43 of the 2015 Suzuki annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
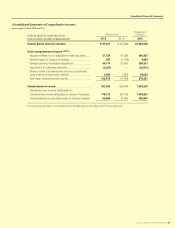
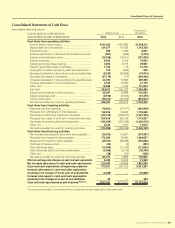
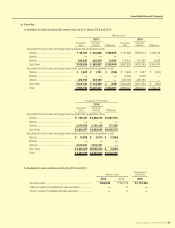
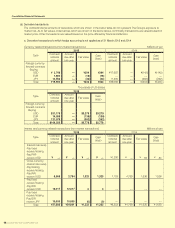
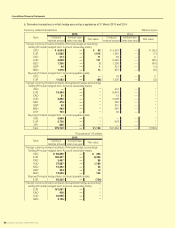
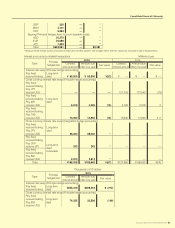
Consolidated Financial Statements
SUZUKI MOTOR CORPORATION 41
(g) Provision for disaster
Reasonably estimated amount is appropriated for anticipated loss mainly caused by relocation of plants and facilities located
in the Ryuyo Region in Iwata City, Shizuoka Prefecture where massive tsunami damages caused by Tokai and Tonankai Earth-
quake are anticipated.
(h) Provision for product liabilities
With regards to the products exported to North American market, to prepare for the payment of compensation, not covered
by “Product Liability Insurance” the anticipated amount to be borne by The Group is computed and provided on the basis of
actual results in the past.
(i) Provision for recycling expenses
The provision is appropriated for an estimated expense related to the recycle of products of The Company based on actual
sales.
(j) Short-term investment securities and Investment securities
The Company and its subsidiaries hold securities of listed companies, which have a risk of price uctuations, and non-listed
companies whose stock prices are difcult to be evaluated.
If we judge the decline in investment value is not temporary, we recognize revaluation loss based on the reasonable standard.
If the stock market falls, we may incur signicant loss on valuation of securities.
Securities have to be classied into four categories: trading securities; held-to-maturity debt securities; investments of The
Company in equity securities issued by consolidated subsidiaries and afliates; and available-for-sale securities.
According to this classication, securities held by The Company and its subsidiaries are available-for-sale securities. Avail-
able-for-sale securities for which market quotations are available are stated at market value method based on the market
values as of the consolidated account settlement date (The evaluation differences shall be reported as other comprehensive
income, and sales costs shall be calculated mainly by the moving average method).
Available-for-sale securities for which market quotations are unavailable are stated at cost by a moving average method.
(k) Hedge accounting
Gains or losses arising from changes in fair value of the derivatives designated as “hedging instruments” are deferred until the
gains and losses on the hedged items or transactions are recognized.
If foreign currency forward contracts meet certain criteria, exceptional hedge accounting is applied and these contracts are
handled together with hedged items. If interest rate swap contracts meet certain criteria, special exceptional hedge account-
ing is applied and these contracts are handled together with hedged items. If cross currency interest rate swap contracts
meet certain criteria, integration method (special exceptional method and exceptional method) is applied and these contracts
are handled together with hedged items.
The derivatives designated as hedging instruments by The Company and its subsidiaries are principally forward exchange
contracts, interest swaps and cross currency interest rate swaps. The related hedged items are foreign currency denominated
transaction and borrowings.
The Company and its subsidiaries have a policy to utilize the above hedging instruments in order to reduce our exposure to
the risk of interest rate and foreign exchange uctuation. Thus, our purchases of the hedging instruments are limited to, at
maximum, the amounts of the hedged items. The Company and its subsidiaries evaluate effectiveness of its hedging activities
by reference to the accumulated gains or losses on the hedging instruments and the related hedged items from the com-
mencement of the hedges.
(l) Foreign currency translation
All monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies, whether long-term or short-term are translated into
Japanese yen at the exchange rates prevailing at the balance sheet date. Resulting gains and losses are included in net
income or loss for the period.
Assets and liabilities of the foreign subsidiaries and afliates are translated into Japanese yen at the exchange rates pre-
vailing at the balance sheet date.
The components of net assets are translated into Japanese yen at their historical rates. Prot and loss accounts for the
scal year are translated into Japanese yen using the average exchange rate during the scal year. Differences in yen
amounts arising from the use of different rates are presented as “foreign currency translation adjustments” and “minority
interests” in the net assets.
(m) Inventories
Stated at cost mainly determined by the gross average method (Figures on the consolidated balance sheet are measured by
the method of book devaluation based on the reduction of protability).
(n) Methodofdepreciationandamortizationofsignicantdepreciableassets
a. Property, plant and equipment (excluding lease assets)
................. Mainly declining balance method for The Company and domestic subsidiaries and mainly straight-line
method for foreign subsidiaries.
Main durable years are as follows:
Buildings and structures 3 to 75 years
Machinery, equipment and vehicles 3 to 15 years