Samsung 1999 Annual Report Download - page 65
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 65 of the 1999 Samsung annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
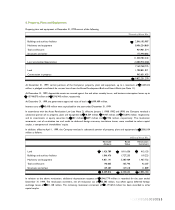
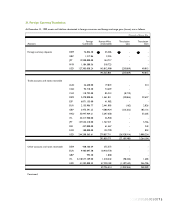
In addition, at December 31, 1999, the Company has entered into lease agreements that were recognized as operating leases.
Related rental payments were charged to operations as incurred. Rental expense under operating lease agreements amounts to
544 million for the year ended December 31, 1999, and future rental payments are as follows:
Thousands of U.S. Dollars
2000 US$ 323
2001 107
US$ 430
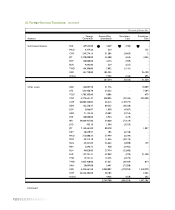
As of December 31, 1999, the Company has entered into thirteen forward exchange contracts and two currency swap
contracts with various foreign and Korean financial institutions to hedge currency risk on foreign currency long-term debt. In
addition the Company has entered into twelve interest rate swap contracts with various foreign and Korean financial
institutions to hedge interest rate risk on floating-rate foreign currency long-term debt.
For the year ended December 31, 1999, the Company recognized gains of 9,407 million and losses of 1,954 million from the
valuation of forward exchange contracts, and losses of 24,182 million from the valuation of currency swap contracts. In
addition, the Company recognized gains of 395 million, losses of 1,650 million and deferred losses of 3,794 million as capital
adjustment from the valuation of interest rate swap contracts entered to hedge future cash flow, of which 1,913 million is
estimated to be realized by December 31, 2000.
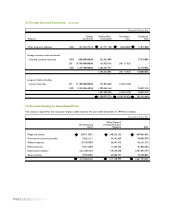
As of December 31, 1999, the Company has entered into an agreement to issue asset backed securities based on export
accounts and notes receivable with Atlantic Asset Securitization Corporation amounting up to US$100 million and an
agreement to discount trade notes receivable with two Korean banks amounting up to 200,000 million (see Note 6).
At December 31, 1999 the Company is a defendant in seven legal actions for alleged patent infringement, two legal actions for
breach of contract and one environmental legal action brought against the Company in a foreign country. In addition, the
Company is party to various other legal claims and proceedings in Korea, all of which are pending as of December 31, 1999.
The Company’s management believes that, although the outcome of these matters is uncertain, the resolution of these matters
will not have a material adverse effect on the operations or financial position of the Company.
On September 1, 1999, the Company and the other 33 affiliated companies of Samsung Group entered into an agreement with
16 creditor financial institutes of Samsung Motors Inc., currently in court receivership. The agreement forces the Company and
the other 33 affiliates to assume the deficit or excess arising from the disposal of the shares of Samsung Life Insurance Co., Ltd.
valued at 2,450,000 million, donated by the Chairman of Samsung Group.
In connection with the Asian financial crisis which began in 1997, the Korean economy as well as other economies in the Asia
Pacific region experienced economic contractions, a reduction in the availability of credit, increased interest rates, increased
inflation, negative fluctuations in currency exchange rates, increased numbers of bankruptcies, increased unemployment and
labor unrest. Such conditions had a significant adverse effect on the operations of the Company and other companies in Korea
and in the Asia Pacific region.
Recently, economic conditions in the Republic of Korea have improved as evidenced by an increased trade surplus, increases in
foreign exchange reserves, record levels of foreign investment and economic growth, lower inflation and interest rates and
stabilized foreign exchange rates. Notwithstanding the current recovery, significant uncertainties still exist related to the economy
in Korea and in the Asia Pacific region. The accompanying financial statements reflect management’s current assessment of the
impact to date of the economic situation on the financial position of the Company. Actual results may differ materially from
management’s current assessment.
10101001010010065