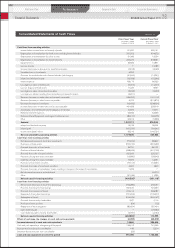
Nissan 2011 Annual Report Download - page 39
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 39 of the 2011 Nissan annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Maintaining Trust Through Transparency
As described above, Nissan is implementing thorough quality checks before new model launches.
Nissan is advancing quality improvement activities also after launch by gathering quality information
from markets and promptly deploying countermeasures. In case of occurrence of safety or
compliance issues, necessary actions such as recalls are implemented with close cooperation with
market side team based on a management decision reached by an independent process. Incidents
are thoroughly investigated, analyzed and fed back to models on the way of production or
development for prevention of recurrence. In addition to the above described activities, such as
quality assurance at new model project and quality improvement activities on daily basis, the “Quality
Risk Management” framework has been newly developed from fiscal 2009. This is a high-level
system to ensure successful quality management for on-going and future projects. This includes
assessment of quality related risks, evaluation of risk level, assignment of responsible persons based
on the level and clarification of an organization for follow up. These processes are implemented by
the Quality Risk Management Committee, chaired by an EVP twice a year.
3) Environment, Climate Change
The automotive industry is affected globally by various regulations related to the environment and
safety, such as exhaust emissions, CO2/fuel efficiency, noise and recycling, and these regulations
are getting more stringent year by year. In this environment, one effective solution from a long-term
perspective will be widespread use of zero-emission vehicles. Nissan has started sales of the Nissan
LEAF, the world’s first affordable, mass-produced EV, in 2010. As the Renault-Nissan Alliance, we
have promoted partnership formation to develop a zero-emission society with national and local
governments.
Additionally, Nissan will reduce CO2 emissions by continuously developing technologies to
improve fuel efficiency in internal combustion engines and bringing them widely into the market. In
particular, we will promote low CO2 output technologies named PURE DRIVE, such as our hybrid
system, fuel efficient direct injection engine and continuously variable transmission (CVT).
Stricter controls on the environmental impact of substances are being sought in countries around
the world. Nissan has steadily advanced efforts to meet these requirements. In an effort to reduce
the potential release of environment-impacting substances, we have established voluntary standards
to meet the environmental regulations enacted in countries where we do businesses.
Demand for natural resources such as metals and oil is skyrocketing in response to the rapid
economic growth of emerging countries. In addition to promoting reduced use of virgin natural
resources through resource-saving and resource-recycling measures, it is becoming important to
procure natural resources that have a lower impact on the Earth’s ecosystems, not only from the
standpoint that these resources are limited, but also considering the wide-ranging effects that
resource extraction has on ecosystems. Nissan has targeted 100% resource recovery for end-of-life
vehicles (ELVs), while also promoting design centered on the vehicle life cycle, waste reduction and
promotion of expanded use of recycled materials.
The issue of water resources is becoming ever more serious with the retreat of glaciers and
rainfall fluctuation due to climate change in addition to increasing water use due to the growing
world population and economic development. Nissan, which uses water resources in its production
process, deeply recognizes the importance of this issue and is working to preserve water resources,
such as by reducing consumption and recycling water discharged in the production process.
The purchasing divisions of Nissan and Renault carry out supply-chain management in a manner
consistent with The Renault-Nissan Purchasing Way, a booklet outlining policies for dealing with
suppliers, and the Renault-Nissan CSR Guidelines for Suppliers. With respect to environmental
issues, we have set standards for the efforts of our automobile parts and material suppliers in the
form of the Nissan Green Purchasing Guidelines. Through these purchasing guidelines we seek to
share our environmental principles and action plans with our suppliers and to promote the reduction
of environmental impact throughout the entire supply chain.
Thus, Nissan is working to achieve autonomous guidelines and targets as part of its corporate
social responsibility as well as to comply with laws and regulations. In order to promote this
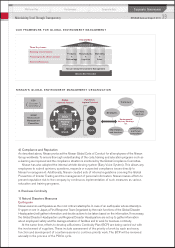
environmental management on a global basis, the Global Environment Management Committee
(G-EMC) chaired by the COO makes decisions on general direction and proposals to the Executive
Committee. The Global Environmental Planning Office decides concrete actions for each function
and conducts effective follow up of the progress based on PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) management.
Corporate Governance
Performance Corporate DataMid-term Plan
38
NISSAN Annual Report 2011