Bed, Bath and Beyond 2007 Annual Report Download - page 18
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 18 of the 2007 Bed, Bath and Beyond annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
BED BATH& BEYOND ANNUAL REPORT 2007
16
1. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND RELATED MATTERS
A. Nature of Operations
Bed Bath & Beyond Inc. and subsidiaries (the “Company”) is a chain of retail stores, operating under the names Bed Bath &
Beyond (“BBB”), Christmas Tree Shops (“CTS”), Harmon and Harmon Face Values (“Harmon”) and buybuy BABY, which was
acquired on March 22, 2007. (See “Acquisition,” Note 2). The Company sells a wide assortment of merchandise principally includ-
ing domestics merchandise and home furnishings as well as food, giftware, health and beauty care items and infant and toddler
merchandise. As the Company operates in the retail industry, its results of operations are affected by general economic conditions
and consumer spending habits.
B. Fiscal Year
The Company’s fiscal year is comprised of the 52 or 53 week period ending on the Saturday nearest February 28. Accordingly, fiscal
2007 and fiscal 2005 represented 52 weeks and ended on March 1, 2008 and February 25, 2006, respectively; fiscal 2006 represent-
ed 53 weeks and ended on March 3, 2007.
C. Principles of Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its subsidiaries, all of which are
wholly owned.
All significant intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
D. Use of Estimates
The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles requires
the Company to establish accounting policies and to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets
and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities as of the date of the consolidated financial statements and
the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. The Company bases its estimates on historical
experience and on other assumptions that it believes to be relevant under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis
for making judgments about the carrying value of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. In
particular, judgment is used in areas such as impairment of auction rate securities, inventory valuation, impairment of long-lived
assets, goodwill and other indefinitely lived intangible assets, accruals for self insurance, litigation, store opening, expansion,
relocation and closing costs, the provision for sales returns, vendor allowances, stock-based compensation and income taxes.
Actual results could differ from these estimates.
E. Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid instruments purchased with original maturities of three months or less to be cash
equivalents. Included in cash and cash equivalents are credit and debit card receivables from banks, which typically settle within
5 business days, of $49.3 million and $44.3 million as of March 1, 2008 and March 3, 2007, respectively.
F. Investment Securities
Investment securities primarily consist of auction rate securities, U.S. Government Agency debt securities and municipal debt
securities. Auction rate securities are securities with interest rates that reset periodically through an auction process. Auction rate
securities are classified as available-for-sale and are stated at fair value, which had historically been consistent with cost or par
value due to interest rates which reset periodically, typically every 7, 28 or 35 days. As a result, there generally were no cumulative
gross unrealized holding gains or losses relating to these auction rate securities. However, due to current market conditions,
the auction process for the Company’s auction rate securities has recently failed beginning in mid-February 2008. These failed
auctions result in a lack of liquidity in the securities, and affect their estimated fair values at March 1, 2008, but do not affect the
underlying collateral of the securities. (See “Investment Securities,” Note 6). All income from these investments is recorded as
interest income.
Those investment securities which the Company has the ability and intent to hold until maturity are classified as held-to-maturity
investments and are stated at amortized cost. Those investment securities which are bought and held principally for the purpose
of selling them in the near term are classified as trading securities and are stated at fair market value.
Premiums are amortized and discounts are accreted over the life of the security as adjustments to interest income using the
effective interest method. Dividend and interest income are recognized when earned.
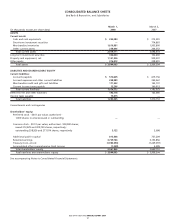
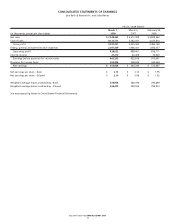
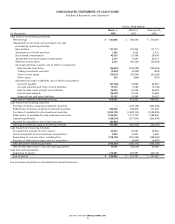
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Bed Bath & Beyond Inc. and Subsidiaries