Xcel Energy 2012 Annual Report Download - page 34
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 34 of the 2012 Xcel Energy annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.24
Renewable Energy Sources
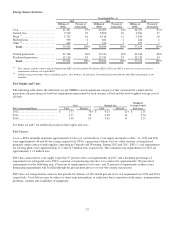
SPS’ renewable energy portfolio includes wind and solar power from both owned generating facilities and PPAs. As of Dec. 31,
2012, SPS is in compliance with mandated RPS, which require generation from renewable resources of approximately 4 percent
and 10 percent of Texas and New Mexico electric retail sales, respectively. Renewable energy comprised 7.9 percent and 8.2
percent of SPS’ total owned and purchased energy for 2012 and 2011, respectively. Wind energy comprised 7.4 percent and 7.8
percent of SPS’ total owned and purchased energy for 2012 and 2011, respectively. Solar power comprised approximately 0.5
percent and 0.4 percent of renewable energy for 2012 and 2011, respectively.
SPS also offers customer-focused renewable energy initiatives. Windsource, one of the nation’s largest voluntary renewable
energy programs, allows customers in New Mexico to purchase a portion or all of their electricity from renewable sources.
Approximately 1,100 and 1,200 customers purchased 5,000 MWh and 7,000 MWh of electricity under the Windsource program
in 2012 and 2011, respectively. Additionally, to encourage the growth of solar energy on the system in New Mexico, customers
are offered incentives to install solar panels on their homes and businesses under the Solar*Rewards program. Over 80 PV
systems with approximately 4.5 MW of aggregate capacity and over 70 PV systems with approximately 5 MW of aggregate
capacity have been installed in New Mexico under this program as of Dec. 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively.
SPS acquires its wind energy from long-term PPAs with wind farm owners, primarily in the Texas Panhandle area of Texas and
New Mexico. SPS currently has six of these agreements in place, with facilities ranging in size from under 2 MW to 161 MW for
a total capacity greater than 600 MW. In late 2012, the 161 MW Spinning Spur Wind Ranch began commercial operations. SPS
will purchase the entire output of this 161 MW facility. In addition to receiving purchased wind energy under these agreements,
SPS also typically receives wind RECs, which are used to meet state renewable resource requirements. Additionally, SPS is
currently purchasing an additional 250 MW of wind energy from qualified generating facilities, as defined in the PURPA. The
average cost per MWh of wind energy under the PPA and QF contracts was approximately $26 for each of 2012 and 2011. The
cost per MWh of wind energy varies by contract and may be influenced by a number of factors including regulation, state specific
renewable resource requirements and the year of contract execution. Generally, contracts executed in 2012 benefited from
improvements in technology, excess capacity among manufacturers, and motivation to complete new construction prior to the
anticipated expiration of the Federal PTCs in 2012. In January 2013, the Federal PTC was extended through 2013. At the end of
2012 and 2011, SPS had nearly 860 MW and 700 MW of wind energy on its system, respectively.
Wholesale Commodity Marketing Operations
SPS conducts various wholesale marketing operations, including the purchase and sale of electric capacity, energy and energy
related products. SPS uses physical and financial instruments to minimize commodity price and credit risk and hedge sales and
purchases. See Item 7 for further discussion.
Summary of Recent Federal Regulatory Developments
The FERC has jurisdiction over rates for electric transmission service in interstate commerce and electricity sold at wholesale,
hydro facility licensing, natural gas transportation, accounting practices and certain other activities of Xcel Energy Inc.’s utility
subsidiaries, including enforcement of NERC mandatory electric reliability standards. State and local agencies have jurisdiction
over many of Xcel Energy Inc.’s utility subsidiaries’ activities, including regulation of retail rates and environmental matters. In
addition to the matters discussed below, see Note 12 to the accompanying consolidated financial statements for a discussion of
other regulatory matters.
FERC Order 1000, Transmission Planning and Cost Allocation (Order 1000) —The FERC issued Order 1000 adopting new
requirements for transmission planning, cost allocation and development to be effective prospectively. The requirements for
transmission planning and cost allocation were addressed by revisions to the MISO Tariff for NSP-Minnesota and NSP-
Wisconsin as discussed below in MISO Transmission Pricing; and Xcel Energy expects the requirements will be addressed by
revisions to the SPP Tariff for SPS. PSCo submitted its compliance filing in October 2012, proposing to comply through
participation in WestConnect, a consortium of utilities in the Western Interconnection. The filing is pending FERC action.
In 2012, Minnesota’s Governor signed legislation that preserves the rights of incumbent utilities to construct and own
transmission interconnected to their systems. This legislation is similar to legislation previously passed in North Dakota and
South Dakota. Therefore, Order 1000 is expected to have limited impacts on future transmission development and ownership in
the NSP System in Minnesota, North Dakota and South Dakota. For the Wisconsin portion of the NSP System, the impacts of the
new requirements relating to future transmission development and ownership are uncertain.