Under Armour 2013 Annual Report Download - page 75
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 75 of the 2013 Under Armour annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
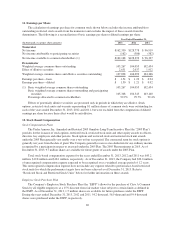
outstanding shares of Class B Convertible Common Stock will automatically convert into shares of Class A
Common Stock on a one-for-one basis upon the death or disability of Mr. Plank or on the record date for any
stockholders’ meeting upon which the shares of Class A Common Stock and Class B Convertible Common Stock
beneficially owned by Mr. Plank is less than 15% of the total shares of Class A Common Stock and Class B
Convertible Common Stock outstanding. Holders of the Company’s common stock are entitled to receive
dividends when and if authorized and declared out of assets legally available for the payment of dividends.
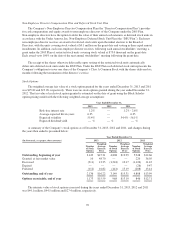
During the year ended December 31, 2013, 1.3 million shares of Class B Convertible Common Stock were
converted into shares of Class A Common Stock on a one-for-one basis in connection with stock sales.
9. Fair Value Measurements
Fair value is defined as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an
orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date (an exit price). The fair value
accounting guidance outlines a valuation framework, creates a fair value hierarchy in order to increase the
consistency and comparability of fair value measurements and the related disclosures, and prioritizes the inputs
used in measuring fair value as follows:
Level 1: Observable inputs such as quoted prices in active markets;
Level 2: Inputs, other than quoted prices in active markets, that are observable either directly or indirectly; and
Level 3: Unobservable inputs for which there is little or no market data, which require the reporting entity to
develop its own assumptions.
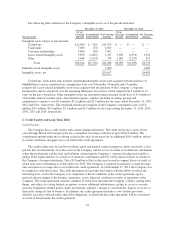
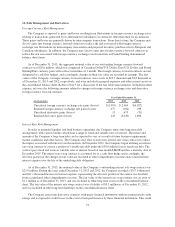
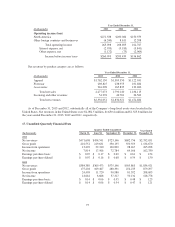
Financial assets and (liabilities) measured at fair value are set forth in the table below:
December 31, 2013 December 31, 2012
(In thousands) Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 1 Level 2 Level 3
Derivative foreign currency forward contracts (see Note 14) $ — $ 12 $ — $ — $ 5 $ —
Interest rate swap contract (see Note 14) — 1,087 — — (141) —
TOLI policies held by the Rabbi Trust (see Note 13) — 4,625 — — 4,250 —
Deferred Compensation Plan obligations (see Note 13) — (3,338) — — (2,837) —
Fair values of the financial assets and liabilities listed above are determined using inputs that use as their
basis readily observable market data that are actively quoted and are validated through external sources,
including third-party pricing services and brokers. The foreign currency forward contracts represent gains and
losses on derivative contracts, which is the net difference between the U.S. dollar value to be received or paid at
the contracts’ settlement date and the U.S. dollar value of the foreign currency to be sold or purchased at the
current forward exchange rate. The interest rate swap contract represents gains and losses on the derivative
contract, which is the net difference between the fixed interest to be paid and variable interest to be received over
the term of the contract based on current market rates. The fair value of the trust owned life insurance (“TOLI”)
policies held by the Rabbi Trust is based on the cash-surrender value of the life insurance policies, which are
invested primarily in mutual funds and a separately managed fixed income fund. These investments are initially
made in the same funds and purchased in substantially the same amounts as the selected investments of
participants in the Under Armour, Inc. Deferred Compensation Plan (the “Deferred Compensation Plan”), which
represent the underlying liabilities to participants in the Deferred Compensation Plan. Liabilities under the
Deferred Compensation Plan are recorded at amounts due to participants, based on the fair value of participants’
selected investments.
The carrying value of the Company’s long term debt approximated its fair value as of December 31, 2013
and 2012. The fair value of the Company’s long term debt was estimated based upon quoted prices for similar
instruments (Level 2 input).
65