Sharp 2013 Annual Report Download - page 25
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 25 of the 2013 Sharp annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
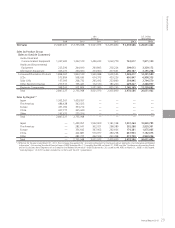
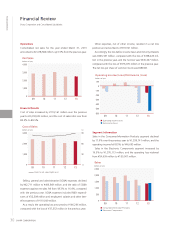
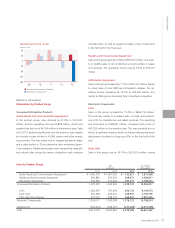
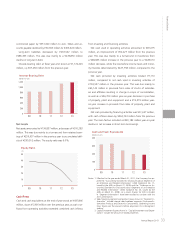
Annual Report 2013 23
Risk Factors
of an increase in expenses due to rising interest rates. Moreover,
Sharp has possibility of increase in fund procurement costs as
well as limitations on fund procurement. This may be that neces-
sary funds cannot be obtained at required time with adequate
conditions, including for the refinancing of existing debt. These
factors may affect Sharp’s business results and financial posi-
tion. Sharp has borrowing agreements with multiple financial
institutions, and such agreements entail financial covenants. If
its consolidated net assets, operating income or net income fall
below the levels specified under such financial covenants, Sharp
may forfeit the benefit of time at the lender’s request. Moreover,
Sharp may also forfeit the benefit of time on bonds and other
borrowings if it violates the relevant financial covenants. In ad-
dition, dependence on borrowings, a credit ratings reduction
caused by it, or deterioration of Sharp’s financial position may
work to its disadvantage with respect to competition with other
companies with robust financial positions, and contract-related
issues could also arise between Sharp and its lenders or business
partners.
(8) Technological Innovation
New technologies are emerging rapidly in the markets where
Sharp operates. Resultant changes in social infrastructure, in-
tensified market competition, changes in technology standards,
obsolescence of technologies, or the appearance of substitute
technologies may lead to an increase in inventories or the inabil-
ity to recover product development costs. These and other fac-
tors may impact Sharp’s business results and financial position.
(9) Intellectual Property Rights
Sharp strives to protect its proprietary technologies by acquir-
ing patents, trademarks, and other intellectual property rights
in Japan and in other countries, and by concluding contracts
with other companies. However, there is a risk that rights may
not be granted, or a third party may demand invalidation of an
application, such that Sharp may be unable to obtain sufficient
legal protection of its proprietary technologies. In addition, intel-
lectual property that Sharp holds may not result in a superior
competitive advantage, or Sharp may not be able to make effec-
tive use of such intellectual property, such as when a third party
infringes on the intellectual property rights of Sharp. There may
also be instances where a third party launches litigation against
Sharp, claiming infringement of intellectual property rights. Res-
olution of such cases may place a significant financial burden on
Sharp. Furthermore, if such a third-party claim against Sharp is
recognized, Sharp may have to pay a large amount of compen-
sation, and may incur further damage by having to cease using
the technology in question. Also, as a result of an M&A, a third
party previously unlicensed to use Sharp’s intellectual property
may acquire such license, with the result that Sharp’s intellec-
tual property may lose its superiority. Alternatively, an M&A with
a third party could result in Sharp’s business becoming subject
to new restrictions to which it had not previously been subject,
the resolution of which may require Sharp to pay additional
compensation. Furthermore, although compensation is given
to employees for innovations that they make in the course of
their work pursuant to a patent reward system governed by in-
ternal regulations, an employee may consider such payment in-
adequate and initiate legal action. If any of the above problems
related to intellectual property were to occur, it could impact
Sharp’s business results and financial position.
(10) Long-Term Investments and Agreements
Sharp actively invests in manufacturing equipment and the like
and has a large amount of noncurrent assets. Various factors re-
lated to such manufacturing equipment may prevent Sharp from
securing anticipated income and require it to book impairment
losses, which could impact its business results and financial posi-
tion. These factors include equipment not functioning as expect-
ed and difficulty converting for other products due to equipment
performance problems or contractual limitations. Sharp also has
goodwill and other noncurrent assets. Sharp may be required
to apply impairment treatment to such assets if its profitability
declines or if the market prices of its asset holdings decline sig-
nificantly. Such factors may affect Sharp’s business results and
financial position. In addition, Sharp has a large number of long-
term contractual agreements in place, and fluctuations in prices
and costs during the periods of such agreements may have a
major negative effect on Sharp’s business. In particular, there are
such agreements covering raw materials for solar panels. These
include a contract that obligates Sharp to purchase a total of
25,775 tons of polysilicon by the end of 2020 at a rate substan-
tially higher than recent market prices (the weighted average
price under the contracts exceeded the market price as of June
19, 2013 by around ¥2,500 per kilogram). Sharp’s Medium-Term
Management Plan, announced on May 14, 2013, incorporates
the assumption that Sharp is obligated to purchase polysilicon
at higher than market rates throughout the period covered by
the plan.
(11) Product Liability
Sharp manufactures products in accordance with strict quality
control standards to ensure the utmost in quality. In order to
fulfill its responsibility as a manufacturer in case product defects
do arise, Sharp has taken out insurance to cover compensations
based on product liability. Nonetheless, there is still a risk of a
large-scale product recall or litigation caused by unforeseen
events, which may adversely affect Sharp’s brand image or influ-
ence its business results and financial position.