3M 2013 Annual Report Download - page 89
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 89 of the 2013 3M annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.83
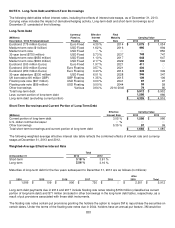
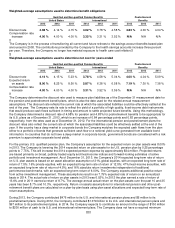
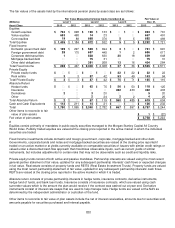
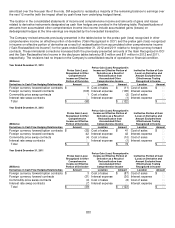
Fixed income includes derivative instruments such as credit default swaps, interest rate swaps and futures contracts that
are used to help manage risks. U.S. government and government agency bonds and notes are valued at the closing price
reported in the active market in which the individual security is traded. Corporate bonds and notes, asset backed
securities and collateralized mortgage obligations are valued at either the yields currently available on comparable
securities of issuers with similar credit ratings or valued under a discounted cash flows approach that maximizes
observable inputs, such as current yields of similar instruments, but includes adjustments for certain risks that may not be
observable such as credit and liquidity risks. Private placements are valued by the custodian using recognized pricing
services and sources. Swaps and derivative instruments are valued by the custodian using closing market swap curves
and market derived inputs.
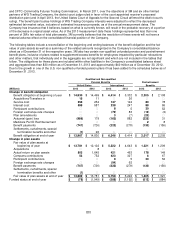
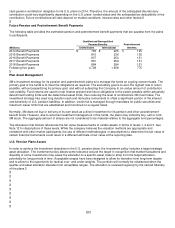
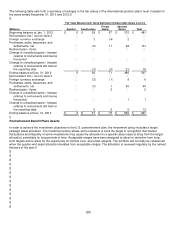
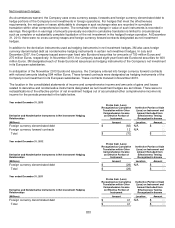
The private equity portfolio is a diversified mix of direct investments, derivative instruments and partnership interests
including buyouts, distressed debt, growth equity, mezzanine, real estate and venture capital investments. Partnership
interests are valued using the most recent general partner statement of fair value, updated for any subsequent partnership
interests’ cash flows or expected changes in fair value. Direct investments are equity co-investments in private companies
and projects, the majority of which are power infrastructure investments, which are valued by an independent valuation
agent.
Absolute return consists primarily of private partnership interests in hedge funds, hedge fund of funds and bank loan
funds. Partnership interests are valued using the NAV as determined by the administrator or custodian of the fund. Hedge
fund partnership interests, which have a redemption right and are past any lock-up redemption period, are classified as
level 2. A hedge fund was restructured during 2012, extending the lock-up redemption period, and therefore was moved to
level 3 during 2012.
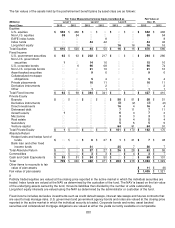
Commodities consist of commodity-linked notes and commodity-linked derivative contracts designed to deliver investment
returns similar to the Goldman Sachs Commodities Index (GSCI) or Dow Jones UBS Commodity index returns.
Commodities are valued at closing prices determined by calculation agents for outstanding transactions.
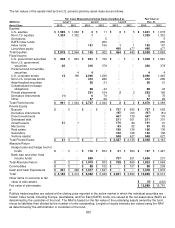
Other items to reconcile to fair value of plan assets include the net of insurance receivables for WG Trading Company,
interest receivables, amounts due for securities sold, amounts payable for securities purchased and interest payable.