Qantas 2016 Annual Report Download - page 78
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 78 of the 2016 Qantas annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Notes to the Financial Statements continued
For the year ended 30 June 2016
20 FINANCIAL RISK MANAGEMENT CONTINUED
ii. Interest Rate Risk
Nature of the Risk:
Interest rate risk refers to the risk that the fair value or future cash flows of a financial instrument will fluctuate because of changes
in market interest rates. The Qantas Group has exposure to movements in interest rates arising from its portfolio of interest rate
sensitive assets and liabilities which are predominantly in AUD and USD currencies. These principally include corporate debt,
leases and cash.
Management of Interest Rate Risk:
The Qantas Group manages interest rate risk by using a floating versus fixed rate debt framework. The relative mix of fixed and
floating interest rate funding is managed by using interest rate swaps, forward rate agreements and options. For the year ended
30June 2016, interest-bearing liabilities amounted to $4,862 million (2015: $5,562 million). The fixed/floating split is 46 per cent and
54 per cent respectively (2015: 37 per cent and 63 per cent). For the year ended 30 June 2016, other financial assets and liabilities
included derivative financial instruments relating to debt obligations and future interest payments totalling $56 million (liability)
(2015: $5 million (asset)). These are recognised at fair value in accordance with AASB 9.
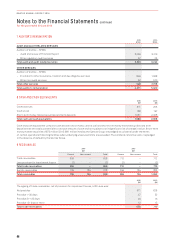
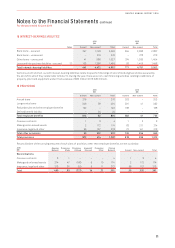
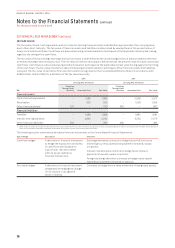
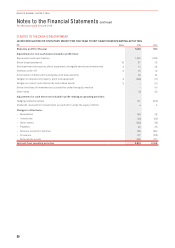
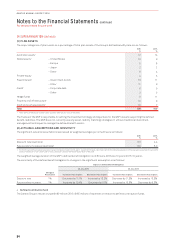
Sensitivity to Interest Rate Risk:
Profit Before Tax Equity (Before Tax)
$M 2016 2015 2016 2015
100bps increase in interest rates1
Variable rate interest-bearing instruments (net of cash) (9) (10) – –
Derivatives designated in a cash flow hedge relationship – – 17 21
100bps decrease in interest rates1
Variable rate interest-bearing instruments (net of cash) 910 – –
Derivatives designated in a cash flow hedge relationship – – (18) (22)
1 Sensitivity analysis assumes hedge designations as at 30 June 2016 remain unchanged and that all designations are effective.
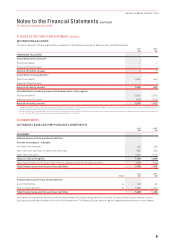
iii. Foreign Exchange Risk (Revenue and Capital Expenditure)
Nature of the Risk:
Foreign exchange risk is the risk that the fair value of future cash flows of a financial instrument will fluctuate because of changes in
foreign exchange rates. The source and nature of this risk arise from operations, capital expenditures and translation risks.
Management of Foreign Exchange Risk:
Cross-currency swaps are used to convert long-term foreign currency borrowings to currencies in which the Qantas Group has
forecast sufficient surplus net revenue to meet the principal and interest obligations under the swaps. Where long-term borrowings
are held in foreign currencies in which the Qantas Group derives surplus net revenue, offsetting forward foreign exchange contracts
have been used to match the timing of cash flows arising under the borrowings with the expected revenue surpluses. These foreign
currency borrowings have a maturity of between one and 12 years. To the extent a foreign exchange gain or loss is incurred, and the
cash flow hedge is deemed effective, this is deferred until the net revenue is realised. As at 30 June 2016, total unrealised exchange
gains on hedges of net revenue designated to service long-term debt was $1 million (2015: $12 million gain).
Forward foreign exchange contracts and currency options are used to hedge a portion of remaining net foreign currency revenue or
expenditure in accordance with Qantas Group policy. Net foreign currency revenue and expenditure out to two years may be hedged
within specific parameters, with any hedging outside these parameters requiring approval by the Board. Purchases and disposals
of property, plant and equipment denominated in a foreign currency may be hedged out to two years using a combination of forward
foreign exchange contracts and currency options. For the year ended 30 June 2016, other financial assets and liabilities included
derivative financial instruments used to hedge foreign currency, including hedging of future capital expenditure payments, totalling
$4 million (net liability) (2015: $54 million (net asset)). These are recognised at fair value in accordance with AASB 9.
76
QANTAS ANNUAL REPORT 2016