Qantas 2016 Annual Report Download - page 76
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 76 of the 2016 Qantas annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Notes to the Financial Statements continued
For the year ended 30 June 2016
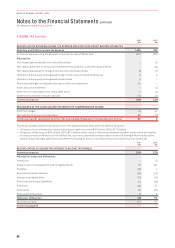
19 SHARE-BASED PAYMENTS CONTINUED
Fair Value Calculation
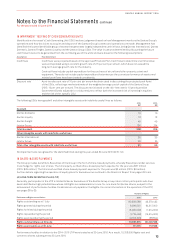
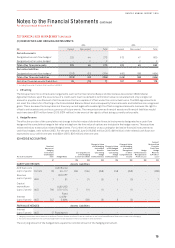
The estimated value of Rights granted was determined at grant date using a Monte Carlo model. The weighted average fair value of
Rights granted during the year was $2.17 (2015: $1.06).
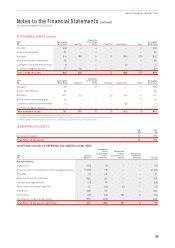
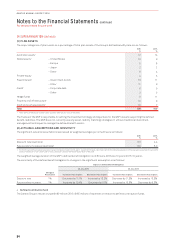
2016 2015
Inputs into the models 23 October 2015 1 September 2015 3 May 2015 24 October 2014 15 September 2014
Rights granted 1,119,500 4,967,000 2,580,500 4,688,500 57,048,000
Weighted average share value $3.86 $3.47 $3.40 $1.43 $1.48
Expected volatility 37.5% 37.5% 35% 35% 35%
Dividend yield 4.23% 4.23% 3.7% 1.2% 1.2%
Risk-free interest rate 1.84% 1.84% 2.0% 2.5% 2.5%
The expected volatility was determined having regard to the historical volatility of Qantas shares and the implied volatility on
exchange traded options. The risk-free rate was the yield on an Australian Government Bond at the grant date matching the
remaining useful lives of the plans. The yield is converted into a continuously compounded rate in the model. The expected life
assumes immediate exercise after vesting.
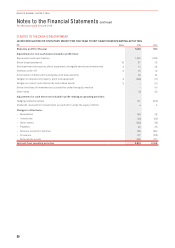
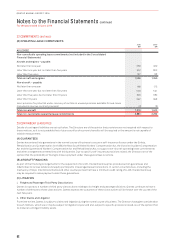
(B) SHORT TERM INCENTIVE PLAN (STIP)
For details on the operation of the STIP, see pages 37 to 38. There were 735,442 awards of Qantas shares made under the STIP during
the year ended 30 June 2016 (2015: nil).
(C) MANAGER INCENTIVE PLAN (MIP)
The MIP is the annual incentive plan for the broader management group. Each year, to the extent that the plan’s performance
conditions are achieved, this group may receive an award that is a combination of cash and restricted shares. The MIP outcome is
based on individual performance (50 per cent) and scorecard performance (50 per cent). The scorecard performance outcomes are
the same as those for STIP. For scorecard performance outcomes, refer to the details of the operation of the STIP on pages 37 to 42.
There were 1,519,286 awards of Qantas shares made under the MIP during the year ended 30 June 2016 (2015: nil).
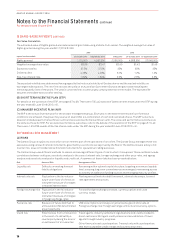
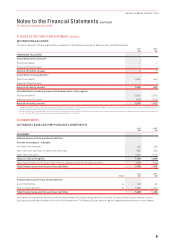
20 FINANCIAL RISK MANAGEMENT
(A) RISKS
The Qantas Group is subject to risks which are an inherent part of the operations of an airline. The Qantas Group manages these risk
exposures using various financial instruments, governed by a set of policies approved by the Board. The Qantas Group’s policy is not
to enter into, issue or hold derivative financial instruments for speculative trading purposes.
The Qantas Group uses different methods to assess and manage different types of risk to which it is exposed. These methods include
correlations between risk types, sensitivity analysis in the case of interest rate, foreign exchange and other price risks, and ageing
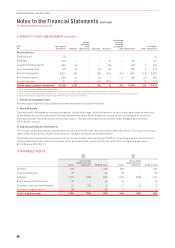
analysis and sensitivity analysis for liquidity and credit risk. A summary of these risks has been presented below:
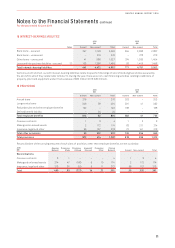
Risk Nature of Risk Management of Risk
Liquidity risk Difficulty in meeting financial
liability obligations
Remaining within optimal capital structure, targeting a minimum liquidity
level, ensuring long-term commitments are managed, maintaining access
to a variety of additional funding sources and managing maturity profiles.
Interest rate risk Fluctuation in the fair value or
future cash flows of a financial
instrument because of changes
in market interest rates
Floating versus fixed rate debt framework, interest rate swaps, forward
rate agreement and options.
Foreign exchange risk Fluctuation in the fair value or
future cash flows of a financial
instrument because of changes
in foreign exchange rates
Forward foreign exchange contracts, currency options and cross
currency swaps.
Fuel price risk Exposure of future AUD fuel to
unfavourable USD denominated
price movements
USD price: Options and swaps on jet kerosene, gasoil and crude oil
Foreign exchange risk: Foreign exchange contracts and currency options.
Credit risk Potential loss from a transaction
in the event of a default by a
counterparty during the term or
on settlement of a transaction
Travel agents, industry settlement organisations and credit provided to
direct customers: Stringent credit policies and accreditation of travel
agents through industry programs.
Other financial asset counterparties: Transact only with counterparties
that have acceptable credit ratings and counterparty limits.
74
QANTAS ANNUAL REPORT 2016