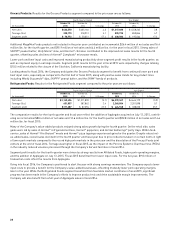
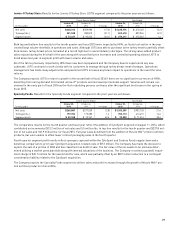
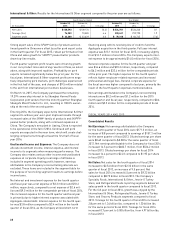
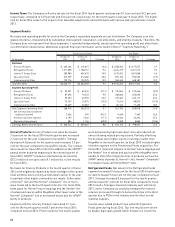
Hormel Foods 2015 Annual Report Download - page 32
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 32 of the 2015 Hormel Foods annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.30
has limited or no prior experience. Any or all of these risks
could impact the Company’s fi nancial results and business
reputation. In addition, acquisitions outside the United States
may present unique challenges and increase the Company’s
exposure to the risks associated with foreign operations.
The Company’s operations are subject to the general risks
of litigation. The Company is involved on an ongoing basis in
litigation arising in the ordinary course of business. Trends
in litigation may include class actions involving employees,
consumers, competitors, suppliers, shareholders, or injured
persons, and claims relating to product liability, contract
disputes, intellectual property, advertising, labeling, wage and
hour laws, employment practices, or environmental matters.
Litigation trends and the outcome of litigation cannot be
predicted with certainty and adverse litigation trends and out-
comes could adversely affect the Company’s fi nancial results.
The Company is subject to the loss of a material contract.
The Company is a party to several supply, distribution,
contract packaging, and other material contracts. The loss
of a material contract could adversely affect the Company’s
fi nancial results.
Government regulation, present and future, exposes the
Company to potential sanctions and compliance costs
that could adversely affect the Company’s business. The
Company’s operations are subject to extensive regula-
tion by the U.S. Department of Homeland Security, the
U.S. Department of Agriculture, the U.S. Food and Drug
Administration, federal and state taxing authorities, and other
state and local authorities that oversee workforce immigration
laws, tax regulations, animal welfare, food safety standards,
and the processing, packaging, storage, distribution, advertis-
ing, and labeling of the Company’s products. The Company’s
manufacturing facilities and products are subject to continu-
ous inspection by federal, state, and local authorities. Claims
or enforcement proceedings could be brought against the
Company in the future. The availability of government inspec-
tors due to a government furlough could also cause disruption
to the Company’s manufacturing facilities. Additionally, the
Company is subject to new or modifi ed laws, regulations, and
accounting standards. The Company’s failure or inability to
comply with such requirements could subject the Company
to civil remedies, including fi nes, injunctions, recalls, or sei-
zures, as well as potential criminal sanctions.
The Company is subject to stringent environmental regu-
lation and potentially subject to environmental litigation,
proceedings, and investigations. The Company’s past and
present business operations and ownership and operation
of real property are subject to stringent federal, state, and
local environmental laws and regulations pertaining to the
discharge of materials into the environment and the handling
and disposition of wastes (including solid and hazardous
& Respiratory Syndrome (PRRS), Foot-and-Mouth Disease
(FMD), Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus (PEDv), and Highly
Pathogenic Avian Infl uenza (HPAI). The outbreak of disease
could adversely affect the Company’s supply of raw mate-
rials, increase the cost of production, reduce utilization
of the Company’s harvest facilities, and reduce operating
margins. Additionally, the outbreak of disease may hinder
the Company’s ability to market and sell products both
domestically and internationally. Most recently, HPAI has
impacted the Company’s Jennie-O Turkey Store operations
and several of the Company’s independent turkey suppliers.
The impact of HPAI in the industry will reduce volume through
the Company’s turkey facilities through the fi rst part of fi scal
2016. The Company has developed business continuity plans
for various disease scenarios and will continue to update
these plans as necessary. There can be no assurance given,
however, that these plans will be effective in eliminating the
negative effects of any such diseases on the Company’s oper-
ating results.
Market demand for the Company’s products may fl uctuate.
The Company faces competition from producers of alternative
meats and protein sources, including pork, beef, turkey,
chicken, fi sh, peanut butter, and whey. The bases on which the
Company competes include:
• price;
• product quality and attributes;
• brand identifi cation;
• breadth of product line; and
• customer service.
Demand for the Company’s products is also affected by
competitors’ promotional spending, the effectiveness of the
Company’s advertising and marketing programs, and con-
sumer perceptions. Trends within the food industry change
often, and failure to identify and react to changes in these
trends could lead to, among other things, reduced demand
and price reductions for the Company’s brands and products.
The Company may be unable to compete successfully on any
or all of these bases in the future.
The Company’s operations are subject to the general risks
associated with acquisitions. The Company has made several
acquisitions in recent years, most recently the acquisitions
of Applegate Farms, LLC and CytoSport Holdings, Inc., and
regularly reviews opportunities for strategic growth through
acquisitions. Potential risks associated with acquisitions
include the inability to integrate new operations successfully,
the diversion of management’s attention from other business
concerns, the potential loss of key employees and custom-
ers of the acquired companies, the possible assumption
of unknown liabilities, potential disputes with the sellers,
potential impairment charges if purchase assumptions are not
achieved or market conditions decline, and the inherent risks
in entering markets or lines of business in which the Company