Columbia Sportswear 2003 Annual Report Download - page 46
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 46 of the 2003 Columbia Sportswear annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.COLUMBIA SPORTSWEAR COMPANY
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
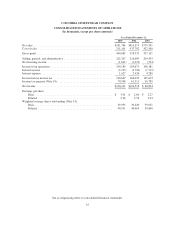
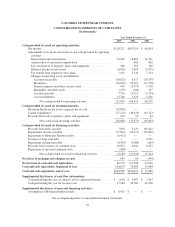
Selling, general and administrative expense:
Selling, general and administrative expense consists of commissions, advertising, other selling costs,
personnel related costs, planning, receiving finished goods, warehousing, depreciation and other general
operating expenses.
Shipping and handling costs:
Shipping and handling fees billed to customers are recorded as revenue. The direct costs associated with
shipping goods to customers are recorded as cost of sales. Inventory planning, receiving and handling costs are
recorded as a component of selling, general, and administrative expenses. Handling costs were $22,461,000,
$16,798,000 and $16,341,000 for the years ended 2003, 2002 and 2001, respectively. Inventory planning and
receiving costs were $11,073,000, $9,979,000 and $8,781,000 for the years ended 2003, 2002 and 2001,
respectively.
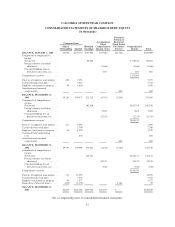
Foreign currency translation:
The assets and liabilities of the Company’s foreign subsidiaries have been translated into U.S. dollars using
the exchange rates in effect at period end, and the net sales and expenses have been translated into U.S. dollars
using average exchange rates in effect during the period. The foreign currency translation adjustments are
included as a separate component of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) in shareholders’ equity and
are not currently adjusted for income taxes as they relate to indefinite net investments in non-U.S. operations.
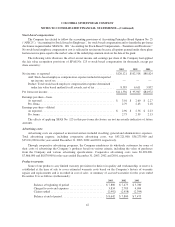
Fair value of financial instruments:
Based on borrowing rates currently available to the Company for bank loans with similar terms and
maturities, the fair value of the Company’s long-term debt approximates the carrying value. Furthermore, the
carrying value of all other financial instruments potentially subject to valuation risk (principally consisting of
cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable and accounts payable) also approximate fair value because of
their short-term maturities.
Derivatives:
The Company accounts for derivatives in accordance with SFAS No. 133, “Accounting for Derivative
Instruments and Hedging Activities,” as amended by SFAS No. 137, “Accounting for Derivative Instruments and
Hedging Activities – Deferral of the Effective Date of SFAS No. 133” and SFAS No. 138, “Accounting for
Certain Derivative Instruments and Certain Hedging Activities – an Amendment of SFAS No. 133.”
Substantially all foreign currency derivatives entered into by the Company qualify for and are designated as
foreign-currency cash flow hedges, including those hedging foreign currency denominated firm commitments.
Changes in fair values of outstanding cash flow hedge derivatives that are highly effective are recorded in
other comprehensive income, until earnings are affected by the variability of cash flows of the hedged
transaction. In most cases amounts recorded in other comprehensive income will be released to earnings some
time after maturity of the related derivative. The consolidated statement of operations classification of effective
hedge results is the same as that of the underlying exposure. Results of hedges of product costs are recorded in
cost of sales when the underlying hedged transaction affects earnings. Unrealized derivative gains and losses
recorded in current and non-current assets and liabilities and amounts recorded in other comprehensive income
are non-cash items and therefore are taken into account in the preparation of the consolidated statement of cash
flows based on their respective balance sheet classifications.
41