Brother International 2010 Annual Report Download - page 38
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 38 of the 2010 Brother International annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
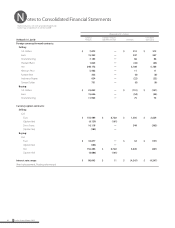
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Brother Industries, Ltd. and Consolidated Subsidiaries
For the Years ended March 31, 2010 and 2009
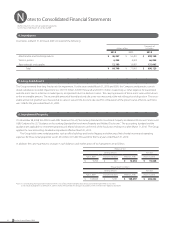
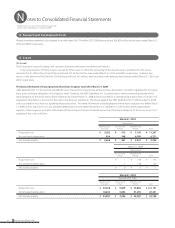
14. Financial Instruments and Related Disclosures
On March 10, 2008, the ASBJ revised ASBJ Statement No. 10, “Accounting Standard for Financial Instruments” and issued ASBJ Guidance No. 19, “Guidance
on Accounting Standard for Financial Instruments and Related Disclosures.” This accounting standard and the guidance are applicable to financial instru-
ments and related disclosures at the end of the fiscal years ending on or after March 31, 2010 with early adoption permitted from the beginning of the
fiscal years ending before March 31, 2010. The Group applied the revised accounting standard and the new guidance effective March 31, 2010.
(1) Group policy for financial instruments
The Group uses financial instruments, mainly long-term debt including bank loans and bonds, based on its capital financing plan. Cash surpluses,
if any, are invested in low risk financial assets. Short-term bank loans are used to fund its ongoing operations. Derivatives are used, not for specula-
tive purposes, but to manage exposure to financial risks as described in (2) below.
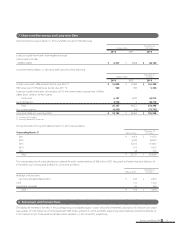
(2) Nature and extent of risks arising from financial instruments
Receivables such as trade notes and trade accounts are exposed to customer credit risk. Although receivables in foreign currencies are exposed to
the market risk of fluctuation in foreign currency exchange rates, the position, net of payables in foreign currencies, is hedged by using forward
foreign currency contracts and currency option contracts. Marketable and investment securities, mainly held-to-maturity securities and equity
instruments of customers and suppliers of the Group, are exposed to the risk of market price fluctuations.
Payment terms of payables, such as trade notes and trade accounts, are less than one year. Payables in foreign currencies are exposed to the
market risk of fluctuation in foreign currency exchange rates.
Maturities of bank loans and bonds are less than five years after the balance sheet date. Although the long-term portion of bank loans is
exposed to market risks from changes in variable interest rates, a part of those risks is mitigated by using derivatives of interest-rate swaps.
Derivatives mainly include forward foreign currency contracts, currency option contracts and interest-rate swaps, which are used to manage
exposure to market risks from changes in foreign currency exchange rates of receivables and payables, and from changes in interest rates of bank
loans. Please see Note 15 for more detail about derivatives.
(3) Risk management for financial instruments
Credit Risk Management
Credit risk is the risk of economic loss arising from a counterparty’s failure to repay or service debt according to the contractual terms. The Group
manages its credit risk from receivables on the basis of internal guidelines, which include monitoring of payment terms and balances of major
customers by each business administration department to identify the default risk of customers in the early stage. With respect to held-to-maturity
financial investments, the Group manages its exposure to credit risk by limiting its funding to high credit rating bonds in accordance with in its
internal guidelines. Please see Note 15 for the detail about derivatives.
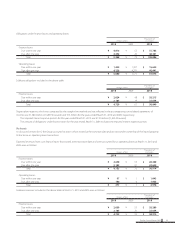
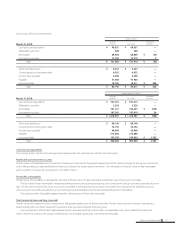
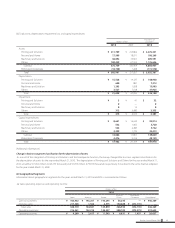
The maximum credit risk exposure of financial assets is limited to their carrying amounts as of March 31, 2010.
Market risk management (foreign exchange risk and interest rate risk)
Foreign currency trade receivables and payables are exposed to market risk resulting from fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates. Such
foreign exchange risk is hedged principally by forward foreign currency contracts and currency option contracts. In addition, when foreign cur-
rency trade receivables and payables are expected from a forecasted transaction, forward foreign currency contracts and currency option con-
tracts may be used to hedge foreign exchange risk resulting from the forecasted transaction expected to occur within one year.
Interest-rate swaps are used to manage exposure to market risks from changes in interest rates of loan payables.
The executions and administration of derivatives have been approved by those who are granted authority based on the internal guidelines
which prescribe the authority and the limit for each transaction.
Liquidity risk management
Liquidity risk comprises the risk that the Group cannot meet its contractual obligations in full on maturity dates. The Group manages its liquidity
risk with adequate financial planning by each company.
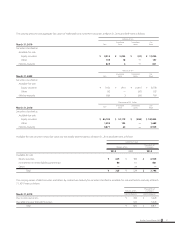
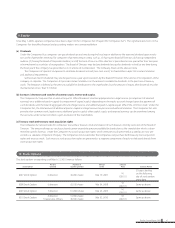
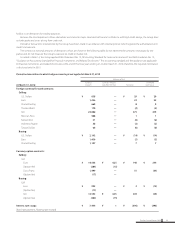
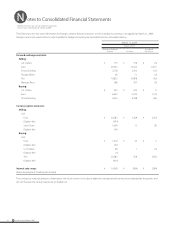
(4) Fair values of financial instruments
Fair values of financial instruments are based on quoted prices in active markets. If quoted price is not available, other rational valuation tech-
niques are used instead. Also, please see Note 15 for the detail of fair value for derivatives.
36 Brother Annual Report 2010