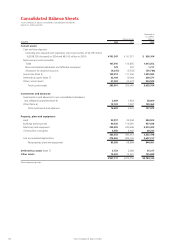
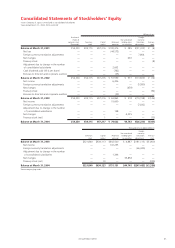
JVC 2004 Annual Report Download - page 45
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 45 of the 2004 JVC annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Annual Report 2004 43.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Victor Company of Japan, Limited and its consolidated subsidiaries
Years ended March 31, 2004, 2003 and 2002
1. BASIS OF PRESENTING CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL
STATEMENTS
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been
prepared in accordance with the provisions set forth in the
Japanese Securities and Exchange Law and its related accounting
regulations, and in conformity with accounting principles generally
accepted in Japan, which are different in certain respects as to
application and disclosure requirements of International Financial
Reporting Standards.
The accounts of overseas subsidiaries are based on their account-
ing records maintained in conformity with generally accepted
accounting principles prevailing in the respective countries of
domicile. The accompanying consolidated financial statements
have been restructured and translated into English (with some
expanded descriptions and the inclusion of consolidated state-
ments of stockholders’ equity) from the consolidated financial
statements of the Company prepared in accordance with Japanese
GAAP and filed with the appropriate Local Finance Bureau of the
Ministry of Finance as required by the Securities and Exchange
Law. Some supplementary information included in the statutory
Japanese language consolidated financial statements, but not
required for fair presentation, is not presented in the accompanying
consolidated financial statements.
The translation of the Japanese yen amounts into U.S. dollars
are included solely for the convenience of readers outside Japan,
using the prevailing exchange rate at March 31, 2004, which was
¥106 to U.S. $1.00. The convenience translations should not be
construed as representations that the Japanese yen amounts have
been, could have been, or could in the future be, converted into
U.S. dollars at this or any other rate of exchange.
2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Principles of consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the
Company and its significant subsidiaries. All significant inter-
company transactions, account balances and unrealized profits
have been eliminated.
Investments in certain non-consolidated subsidiaries and affiliated
companies (20% to 50% owned and certain others 15% to 20%
owned) are, with minor exceptions, stated at their underlying net
equity value after elimination of unrealized inter-company profits.
The Company’s investments in its remaining subsidiaries and
affiliated companies are immaterial in the aggregate, and are
stated at cost or less.
The differences between acquisition cost and underlying net
equity at the time of acquisition are generally being amortized on
the straight-line method over five years.
Foreign currency translation
Assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies are translated
into Japanese yen at exchange rates prevailing at the balance
sheet dates except for those hedged by foreign currency forward
contracts, which are recorded at contract rates.
Balance sheets of consolidated overseas subsidiaries are translated
into Japanese yen at the year-end rate except for stockholders’
equity accounts, which are translated at the historical rates.
Statements of operations of consolidated overseas subsidiaries
are translated at average rates except for transactions with the
Company, which are translated at the rates used by the Company.
The Company reports foreign currency translation adjustments
in the stockholder’s equity and minority interests.
Cash and cash equivalents
In preparing the consolidated statements of cash flows for the
years ended March 31, 2004, 2003 and 2002, cash on hand,
readily available deposits and short-term highly liquid investments
with maturities not exceeding three months at the time of purchase
are considered to be cash and cash equivalents.
Inventories
Inventories are stated at cost, which is determined primarily by the
average- cost method.
Securities
Securities are classified as (a) securities held for trading purposes
(hereafter, “trading securities”), (b) debt securities intended to be
held to maturity (hereafter, “held-to-maturity debt securities”),
(c) equity securities issued by subsidiaries and affiliated companies,
and (d) for all other securities that are not classified in any of the
above categories (hereafter, “available-for-sale securities”).
Trading securities are stated at fair market value. Gains and
losses realized on disposal and unrealized gains and losses from
market value fluctuations are recognized as gains or losses in the
period of the change. The Company and its consolidated subsid-
iaries (“the Companies”) had no held-to-maturity debt securities.
Equity securities issued by subsidiaries and affiliated companies
which are not consolidated or accounted for by the equity
method, are stated at moving-average cost. Available-for-sale
securities with available fair market values are stated at fair market
value. Unrealized gains and losses on these securities are reported,
net of applicable income taxes, as a separate component of stock-
holders’ equity. Realized gains and losses on sale of such securities
are computed using moving-average cost. Other securities with no
available fair market value are stated at moving-average cost.
If the market value of equity securities issued by non-consolidated
subsidiaries and affiliated companies, and available-for-sale
securities, declines significantly, such securities are stated at fair
market value and the difference between fair market value and
the carrying amount is recognized as loss in the period of the
decline. If the fair market value of equity securities issued by
non-consolidated subsidiaries and affiliated companies not accounted
for by the equity method is not readily available, such securities
should be written down to net asset value with a corresponding
charge in the income statement in the event net asset value
declines significantly.
Derivatives and hedge accounting
The Companies state derivative financial instruments at fair value
and recognize changes in the fair value as gains or losses unless
derivative financial instruments are used for hedging purposes.
If derivative financial instruments are used as hedges and meet
certain hedging criteria, the Companies defer recognition of gains
or losses resulting from changes in fair value of derivative financial
instruments until the related losses or gains on the hedged items
are recognized.
Property, plant and equipment
Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost. Depreciation is
computed primarily by the declining-balance method based on the
estimated useful lives of the assets. Certain consolidated overseas
subsidiaries use the straight-line method.