Proctor and Gamble 2011 Annual Report Download - page 62
Download and view the complete annual report
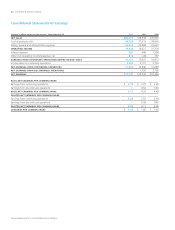
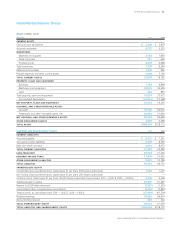
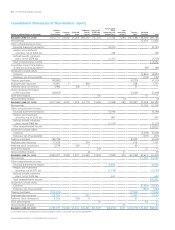
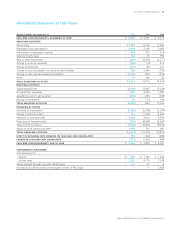
Please find page 62 of the 2011 Proctor and Gamble annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.60 The Procter & Gamble CompanyNotes to Consolidated Financial Statements
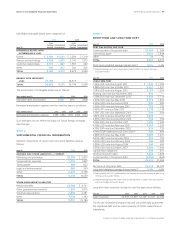
Amounts in millions of dollars except per share amounts or as otherwise specified.
NOTE 5
RISKMANAGEMENT ACTIVITIES AND
FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
As a multinational company with diverse product offerings, we are
exposed to market risks, such as changes in interest rates, currency
exchange rates and commodity prices. We evaluate exposures on a
centralized basis to take advantage of natural exposure correlation and
netting. To the extent we choose to manage volatility associated with
the net exposures, we enter into various financial transactions which we
account for using the applicable accounting guidance for derivative
instruments and hedging activities. These financial transactions are
governed by our policies covering acceptable counterparty exposure,
instrument types and other hedging practices.
At inception, we formally designate and document qualifying instruments
as hedges of underlying exposures. We formally assess, at inception and
at least quarterly, whether the financial instruments used in hedging
transactions are effective at offsetting changes in either the fair value
or cash flows of the related underlying exposure. Fluctuations in the
value of these instruments generally are offset by changes in the value
or cash flows of the underlying exposures being hedged. This offset
is driven by the high degree of effectiveness between the exposure
being hedged and the hedging instrument. The ineffective portion of
a change in the fair value of a qualifying instrument is immediately
recognized in earnings. The amount of ineffectiveness recognized is
immaterial for all years presented.
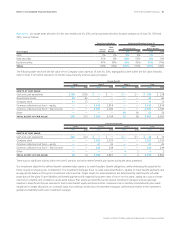
Credit Risk Management
We have counterparty credit guidelines and generally enter into
transactions with investment grade financial institutions. Counterparty
exposures are monitored daily and downgrades in counterparty credit
ratings are reviewed on a timely basis. Credit risk arising from the
inability of a counterparty to meet the terms of our financial instrument
contracts generally is limited to the amounts, if any, by which the
counterparty’s obligations to us exceed our obligations to the counter-
party. We have not incurred, and do not expect to incur, material
credit losses on our risk management or other financial instruments.
Certain of the Company’s financial instruments used in hedging
transactions are governed by industry standard netting agreements
with counterparties. If the Company’s credit rating were to fall below
the levels stipulated in the agreements, the counterparties could
demand either collateralization or termination of the arrangement.
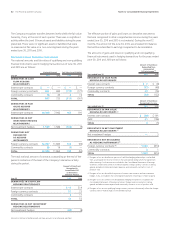
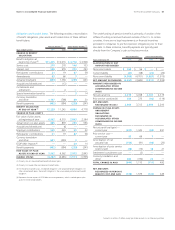
The aggregate fair value of the instruments covered by these con-
tractual features that are in a net liability position as of June30,2011,
was $143. The Company has never been required to post collateral as
a result of these contractual features.
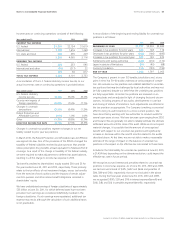
Interest Rate Risk Management
Our policy is to manage interest cost using a mixture of fixed-rate and
variable-rate debt. To manage this risk in a cost-efficient manner, we
enter into interest rate swaps whereby we agree to exchange with the
counterparty, at specified intervals, the difference between fixed and
variable interest amounts calculated by reference to a notional amount.
Interest rate swaps that meet specific accounting criteria are accounted
for as fair value or cash flow hedges. For fair value hedges, the changes
in the fair value of both the hedging instruments and the underlying
debt obligations are immediately recognized in interest expense. For
cash flow hedges, the effective portion of the changes in fair value
of the hedging instrument is reported in OCI and reclassified into
interest expense over the life of the underlying debt. The ineffective
portion for both cash flow and fair value hedges, which is not material
for any year presented, is immediately recognized in earnings.
Foreign Currency Risk Management
We manufacture and sell our products and finance operations in a
number of countries throughout the world and, as a result, are exposed
to movements in foreign currency exchange rates. The purpose of
our foreign currency hedging program is to manage the volatility
associated with short-term changes in exchange rates.
To manage this exchange rate risk, we have historically utilized a
combination of forward contracts, options and currency swaps. As of
June30,2011, we had currency swaps with maturities up to five years,
which are intended to offset the effect of exchange rate fluctuations
on intercompany loans denominated in foreign currencies. These swaps
are accounted for as cash flow hedges. The effective portion of the
changes in fair value of these instruments is reported in OCI and
reclassified into earnings in the same financial statement line item
and in the same period or periods during which the related hedged
transactions affect earnings. The ineffective portion, which is not
material for any year presented, is immediately recognized in earnings.
The change in value of certain non-qualifying instruments used to
manage foreign exchange exposure of intercompany financing
transactions and certain balance sheet items subject to revaluation
is immediately recognized in earnings, substantially offsetting the
foreign currency mark-to-market impact of the related exposure.
Net Investment Hedging
We hedge certain net investment positions in foreign subsidiaries.
To accomplish this, we either borrow directly in foreign currencies
and designate all or a portion of foreign currency debt as a hedge of
the applicable net investment position or enter into foreign currency
swaps that are designated as hedges of our related foreign net invest-
ments. Changes in the fair value of these instruments are immediately
recognized in OCI to offset the change in the value of the net
investment being hedged. Currency effects of these hedges reflected
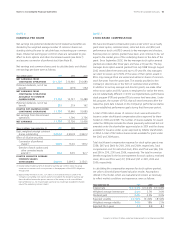
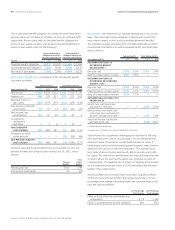
in OCI were an after-tax loss of $1,176 and an after-tax gain of $789
in 2011 and 2010, respectively. Accumulated net balances were after-
tax losses of $4,446 and $3,270 as of June30,2011 and 2010,
respectively.