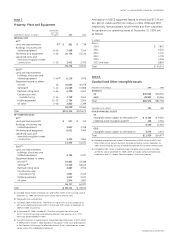
GE 2009 Annual Report Download - page 74
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 74 of the 2009 GE annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.72 GE 2009 ANNUAL REPORT
INVESTMENTS IN SUBSIDIARIES AND FORMERLY CONSOLIDATED
SUBSIDIARIES. Upon a change in control that results in either
consolidation or deconsolidation of a subsidiary, the fair value
measurement of our previous equity investment or retained
noncontrolling stake in the former subsidiary, respectively, are
valued using an income approach, a market approach, or a com-
bination of both approaches as appropriate. In applying these
methodologies, we rely on a number of factors, including actual
operating results, future business plans, economic projections,
market observable pricing multiples of similar businesses and
comparable transactions, and possible control premium. These
investments are included in Level 3.
Accounting Changes
The FASB has made the Accounting Standards Codification (ASC)
effective for financial statements issued for interim and annual
periods ending after September 15, 2009. The ASC combines all
previously issued authoritative GAAP into one codified set of
guidance organized by subject area. In these financial statements,
references to previously issued accounting standards have been
replaced with the relevant ASC references. Subsequent revisions
to GAAP by the FASB will be incorporated into the ASC through
issuance of Accounting Standards Updates (ASU).
We adopted ASC 820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures,
in two steps; effective January 1, 2008, we adopted it for all
financial instruments and non-financial instruments accounted
for at fair value on a recurring basis and effective January 1,
2009, for all non-financial instruments accounted for at fair value
on a non-recurring basis. This guidance establishes a new frame-
work for measuring fair value and expands related disclosures.
See Note 21.
Effective January 1, 2008, we adopted ASC 825, Financial
Instruments. Upon adoption, we elected to report $172 million of
commercial mortgage loans at fair value in order to recognize
them on the same accounting basis (measured at fair value
through earnings) as the derivatives economically hedging these
loans. See Note 21.
On January 1, 2009, we adopted an amendment to ASC 805,
Business Combinations. This amendment significantly changed the
accounting for business acquisitions both during the period of the
acquisition and in subsequent periods. Among the more signifi-
cant changes in the accounting for acquisitions are the following:
• Acquired in-process research and development (IPR&D) is
accounted for as an asset, with the cost recognized as the
research and development is realized or abandoned. IPR&D
was previously expensed at the time of the acquisition.
• Contingent consideration is recorded at fair value as an element
of purchase price with subsequent adjustments recognized in
operations. Contingent consideration was previously accounted
for as a subsequent adjustment of purchase price.
• Subsequent decreases in valuation allowances on acquired
deferred tax assets are recognized in operations after the
measurement period. Such changes were previously consid-
ered to be subsequent changes in consideration and were
recorded as decreases in goodwill.
• Transaction costs are expensed. These costs were previously
treated as costs of the acquisition.
• Upon gaining control of an entity in which an equity method
or cost basis investment was held, the carrying value of that
investment is adjusted to fair value with the related gain or
loss recorded in earnings. Previously, this fair value adjustment
would not have been made.
In April 2009, the FASB amended ASC 805 and changed the
previous accounting for assets and liabilities arising from contin-
gencies in a business combination. We adopted this amendment
retrospectively effective January 1, 2009. The amendment requires
pre-acquisition contingencies to be recognized at fair value, if
fair value can be determined or reasonably estimated during
the measurement period. If fair value cannot be determined or
reasonably estimated, the standard requires measurement based
on the recognition and measurement criteria of ASC 450,
Contingencies.
On January 1, 2009, we adopted an amendment to ASC 810
that requires us to make certain changes to the presentation of
our financial statements. This amendment requires us to classify
earnings attributable to noncontrolling interests (previously
referred to as “minority interest”) as part of consolidated net
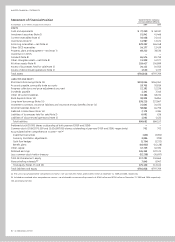
earnings ($216 million and $641 million for 2009 and 2008,
respectively) and to include the accumulated amount of noncon-
trolling interests as part of shareowners’ equity ($7,845 million
and $8,947 million at December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively).
The net earnings amounts we have previously reported are now
presented as “Net earnings attributable to the Company” and,
as required, earnings per share continues to reflect amounts
attributable only to the Company. Similarly, in our presentation
of shareowners’ equity, we distinguish between equity amounts
attributable to GE shareowners and amounts attributable to the
noncontrolling interests — previously classified as minority inter-
est outside of shareowners’ equity. Beginning January 1, 2009,
dividends to noncontrolling interests ($548 million in 2009) are
classified as financing cash flows. In addition to these financial
reporting changes, this guidance provides for significant changes
in accounting related to noncontrolling interests; specifically,
increases and decreases in our controlling financial interests in
consolidated subsidiaries will be reported in equity similar to
treasury stock transactions. If a change in ownership of a con-
solidated subsidiary results in loss of control and deconsolidation,
any retained ownership interests are remeasured with the gain
or loss reported in net earnings.
Effective January 1, 2009, we adopted ASC 808, Collaborative
Arrangements, that requires gross basis presentation of revenues
and expenses for principal participants in collaborative arrange-
ments. Our Technology Infrastructure and Energy Infrastructure
segments enter into collaborative arrangements with manufac-
turers and suppliers of components used to build and maintain
certain engines, aeroderivatives, and turbines, under which GE
and these participants share in risks and rewards of these product
programs. Adoption of the standard had no effect as our historical
presentation had been consistent with the new requirements.
We adopted amendments to ASC 320, Investments — Debt and
Equity Securities, and recorded a cumulative effect adjustment to
increase retained earnings as of April 1, 2009, of $62 million.