Dell 2003 Annual Report Download - page 28
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 28 of the 2003 Dell annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Table of Contents
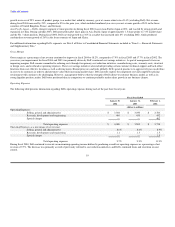
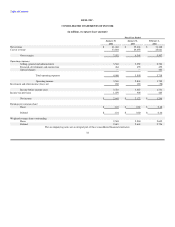
Market Risk
Dell is exposed to a variety of risks, including foreign currency exchange rate fluctuations and changes in the market value of its investments. In the normal
course of business, Dell employs established policies and procedures to manage these risks.
Foreign Currency Hedging Activities
Dell's objective in managing its exposure to foreign currency exchange rate fluctuations is to reduce the impact of adverse fluctuations on earnings and cash
flows associated with foreign currency exchange rate changes. Accordingly, Dell utilizes foreign currency option contracts and forward contracts to hedge its
exposure on forecasted transactions and firm commitments in most of the foreign countries in which it operates. The principal currencies hedged during fiscal
2004 were the Euro, British Pound, Japanese Yen, and Canadian Dollar. Dell monitors its foreign currency exchange exposures to ensure the overall
effectiveness of its foreign currency hedge positions. However, there can be no assurance Dell's foreign currency hedging activities will substantially offset
the impact of fluctuations in currency exchange rates on its results of operations and financial position.
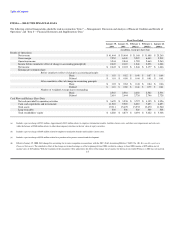
Based on Dell's foreign currency cash flow hedge instruments outstanding at January 30, 2004 and January 31, 2003, Dell estimates a maximum potential
one-day loss in fair value of approximately $53 million and $30 million, respectively, using a Value-at-Risk ("VAR") model. The VAR model estimates were
made assuming normal market conditions and a 95% confidence level. Dell used a Monte Carlo simulation type model that valued its foreign currency
instruments against a thousand randomly generated market price paths. Forecasted transactions, firm commitments, fair value hedge instruments, and accounts
receivable and payable denominated in foreign currencies were excluded from the model. The VAR model is a risk estimation tool, and as such, is not
intended to represent actual losses in fair value that will be incurred by Dell. Additionally, as Dell utilizes foreign currency instruments for hedging forecasted
and firmly committed transactions, a loss in fair value for those instruments is generally offset by increases in the value of the underlying exposure. As a
result of Dell's hedging activities, foreign currency fluctuations did not have a material impact on Dell's results of operations and financial position during
fiscal 2004, 2003, and 2002.
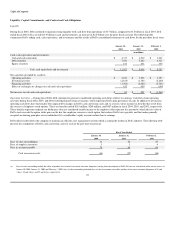
Cash and Investments
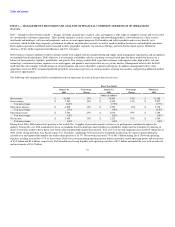
At January 30, 2004, Dell had $11.9 billion of total cash and investments (including investments in equity securities discussed below), all of which are stated
at fair value. Dell's investment policy is to manage its total cash and investments balances to preserve principal and liquidity while maximizing the return on
the investment portfolio through the full investment of available funds. Dell diversifies its investment portfolio by investing in multiple types of investment-
grade securities and through the use of third-party investment managers. Based on Dell's investment portfolio and interest rates at January 30, 2004 and
January 31, 2003, a 100 basis point increase or decrease in interest rates would result in a decrease or increase of approximately $140 million and
$100 million, respectively, in the fair value of the investment portfolio. Changes in interest rates may affect the fair value of the investment portfolio;
however, Dell will not recognize such gains or losses unless the investments are sold.
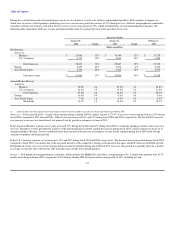
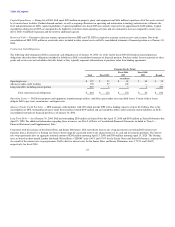
At January 30, 2004, the fair value of investments in equity securities of privately and publicly held technology companies was $110 million. These
investments were made in order to enhance and extend Dell's direct business model and core business initiatives. Because these companies are typically early-
stage companies with products or services that are not yet fully developed or that have not yet achieved market acceptance, these investments are inherently
risky. Dell currently anticipates that it will continue to make minimal additional investments in fiscal 2005 and will focus on managing its current
investments.
25