Brother International 2011 Annual Report Download - page 29
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 29 of the 2011 Brother International annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
27
Brother Annual Report 2011
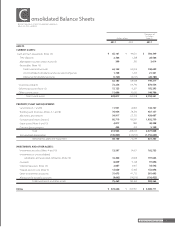
The Company and certain consolidated subsidiaries account for the liability for retirement benefits based on projected benefit obligations
and plan assets at the balance sheet date. Certain small subsidiaries apply the simplified method to state the liability at the amount which
would be paid if employees retired, less plan assets at the balance sheet date.
(ii) Retirement Benefits for Directors and Corporate Auditors
Certain domestic consolidated subsidiaries provide retirement allowances for directors and corporate auditors. Retirement allowances for
directors and corporate auditors are recorded to state the liability which would be paid at the amount if they retired at each balance sheet date.
The retirement benefits for directors and corporate auditors are paid upon the approval of the shareholders.
(15) Asset Retirement Obligations
In March 2008, the ASBJ published the accounting standard for asset retirement obligations, ASBJ Statement No.18, “Accounting Standard for Asset
Retirement Obligations” and ASBJ Guidance No.21, “Guidance on Accounting Standard for Asset Retirement Obligations.” Under this accounting
standard, an asset retirement obligation is defined as a legal obligation imposed either by law or contract that results from the acquisition, con-
struction, development and the normal operation of a tangible fixed asset and is associated with the retirement of such tangible fixed asset. The
asset retirement obligation is recognized as the sum of the discounted cash flows required for the future asset retirement and is recorded in the
period in which the obligation is incurred if a reasonable estimate can be made. If a reasonable estimate of the asset retirement obligation cannot
be made in the period the asset retirement obligation is incurred, the liability should be recognized when a reasonable estimate of asset retirement
obligation can be made. Upon initial recognition of a liability for an asset retirement obligation, an asset retirement cost is capitalized by
increasing the carrying amount of the related fixed asset by the amount of the liability. The asset retirement cost is subsequently allocated to
expense through depreciation over the remaining useful life of the asset. Over time, the liability is accreted to its present value each period. Any
subsequent revisions to the timing or the amount of the original estimate of undiscounted cash flows are reflected as an increase or a decrease in
the carrying amount of the liability and the capitalized amount of the related asset retirement cost. This standard was effective for fiscal years
beginning on or after April 1, 2010.
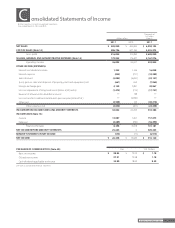
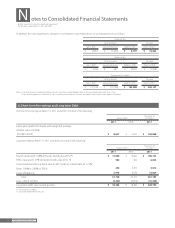
The Group applied this accounting standard effective April 1, 2010. The effect of this change was to decrease operating income by ¥94 million
($1,133 thousand) and income before income taxes and minority interests by ¥627 million ($7,554 thousand).
(16) Stock Options
The ASBJ Statement No.8, “Accounting Standard for Stock Options” and related guidance are applicable to stock options granted on and after May
1, 2006. This standard requires companies to recognize compensation expense for employee stock options based on the fair value at the date of
grant and over the vesting period as consideration for receiving goods or services. The standard also requires companies to account for stock
options granted to non-employees based on the fair value of either the stock option or the goods or services received. In the consolidated bal-
ance sheet, stock options are presented as stock acquisition rights as a separate component of equity until exercised. The standard covers equity-
settled, share-based payment transactions, but does not cover cash-settled, share-based payment transactions. In addition, the standard allows
unlisted companies to measure options at their intrinsic value if they cannot reliably estimate fair value.
The Company applied this accounting standard for stock options to those granted on and after May 1, 2006.
(17) Research and Development Costs
Research and development costs are charged to income as incurred.
(18) Leases
In March 2007, the ASBJ issued ASBJ Statement No.13, “Accounting Standard for Lease Transactions,” which revised the previous accounting stan-
dard for lease transactions issued in June 1993. The revised accounting standard for lease transactions is effective for fiscal years beginning on or
after April 1, 2008.
(Lessee)
Under the previous accounting standard, finance leases that deem to transfer ownership of the leased property to the lessee were to be capital-
ized. However, other finance leases were permitted to be accounted for as operating lease transactions if certain “as if capitalized” information is
disclosed in the note to the lessee’s financial statements. The revised accounting standard requires that all finance lease transactions should be
capitalized to recognize lease assets and lease obligations in the balance sheet. In addition, the accounting standard permits leases which existed
at the transition date and do not transfer ownership of the leased property to the lessee to be accounted for as operating lease transactions.
(Lessor)
Under the previous accounting standard, finance leases that deem to transfer ownership of the leased property to the lessee were to be treated
as sales. However, other finance leases were permitted to be accounted for as operating lease transactions if certain “as if sold” information is
disclosed in the note to the lessor’s financial statements. The revised accounting standard requires that all finance leases that deem to transfer